Abstract
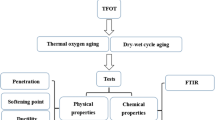
In this study, asphalt binders were modified with polymeric triethylene glycol-based polyboron (PTEGB) and organic-based magnesium oxide (OBMO) at different concentrations. The materials used as additives were synthesized under our laboratory conditions. All modified and unmodified binders were aged by Thin Film Oven Test. (TFOT). The modified and unmodified asphalt binders firstly were evaluated by viscosity aging index obtained from a rotational viscometer. Then, all aged binders were subjected to Fourier transform infrared spectroscopy for obtaining the degree of oxidation. Also, the physical properties of the PTEGB and the OBMO-modified asphalt binders were detected through traditional tests. Marshall stability test was also applied to all aged and non-aged asphalt mixtures to understand mechanical performance and aging effects of the additives on asphalt mixtures. As a result, the optimum PTEGB percentage has been obtained as 2% (w/w), and the optimum OBMO percentage has been obtained as 1% (w/w) according to the aging indexes. The PTEGB and the OBMO additives decreased the TFOT aging of asphalts by 56.7% and 50.6%, respectively. It was also found out that the Marshall stability value of the hot mix asphalt decreased by 23% with the TFOT aging of the original asphalt binder. However, the same value was found as 7% at the OBMO-modified asphalt binder and 8.8% at the PTEGB-modified asphalt binder.








Similar content being viewed by others
References
Lamontagne, J.; Dumas, P.; Mouillet, V.; Kister, J.: Comparison by Fourier transform infrared (FTIR) spectroscopy of different ageing techniques: application to road bitumens. Fuel 80, 483–488 (2001). https://doi.org/10.1016/S0016-2361(00)00121-6
Ouyang, C.; Wang, S.; Zhang, Y.; Zhang, Y.: Low-density polyethylene/silica compound modified asphalts with high-temperature storage stability. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 101, 472–479 (2006). https://doi.org/10.1002/app.23029
Calisici, M.: Improvement of the aging resistance of bitumen by addition of synthetic metal and polymer additives, Gazi University, 2009
Çalışıcı, M.; Gürü, M.; Çubuk, M.K.; Cansız, Ö.F.: Improving the aging resistance of bitumen by addition of polymer based diethylene glycol. Constr. Build. Mater. 169, 283–288 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.conbuildmat.2018.03.018
Wu, S.; Zhao, Z.; Xiao, Y.; Yi, M.; Chen, Z.; Li, M.: Evaluation of mechanical properties and aging index of 10-year field aged asphalt materials. Constr. Build. Mater. 155, 1158–1167 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.conbuildmat.2017.08.102
Zhang, H.; Chen, Z.; Xu, G.; Shi, C.: Evaluation of aging behaviors of asphalt binders through different rheological indices. Fuel 221, 78–88 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.fuel.2018.02.087
De Filippis, P.; Giavarini, C.; Scarsella, M.: Improving the ageing resistance of straight-run bitumens by addition of phosphorus compounds. Fuel (1995). https://doi.org/10.1016/0016-2361(95)00015-W
Ouyang, C.; Wang, S.; Zhang, Y.; Zhang, Y.: Improving the aging resistance of asphalt by addition of Zinc dialkyldithiophosphate. Fuel 85, 1060–1066 (2006). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.fuel.2005.08.023
Ouyang, C.; Wang, S.; Zhang, Y.; Zhang, Y.: Improving the aging resistance of styrene-butadiene-styrene tri-block copolymer modified asphalt by addition of antioxidants. Polym. Degrad. Stab. 91, 795–804 (2006). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.polymdegradstab.2005.06.009
Tur Rasool, R.; Wang, S.; Zhang, Y.; Li, Y.; Zhang, G.: Improving the aging resistance of SBS modified asphalt with the addition of highly reclaimed rubber. Constr. Build. Mater. 145, 126–134 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.conbuildmat.2017.03.242
Banerjee, A.; De Fortier Smit, A.; Prozzi, J.A.: The effect of long-term aging on the rheology of warm mix asphalt binders. Fuel. 97, 603–611 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.fuel.2012.01.072
Petersen, J.C.: Chemical composition of asphalt as related to asphalt durability. State of the Art. Transp. Res. Rec. (1984) 13–30
Arslan, D.; Gürü, M.; Kürşat Çubuk, M.; Çubuk, M.: Improvement of bitumen and bituminous mixtures performances by triethylene glycol based synthetic polyboron. Constr. Build. Mater. 25, 3863–3868 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.conbuildmat.2011.04.007
ÇALIŞICI, M.: NİKEL OKSİT KATKI MADDESİNİN ASFALT BAĞLAYICININ FİZİKSEL ÖZELLİKLERİNE VE KARIŞIMIN STABİLİTESİNE ETKİLERİ. Mühendislik Bilimleri ve Tasarım Dergisi 9(3), 894–899 (2021)
Zhang, F.; Hu, C.: The research for SBS and SBR compound modified asphalts with polyphosphoric acid and sulfur. Constr. Build. Mater. 43, 461–468 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.conbuildmat.2013.03.001
Çalişici, M.; Döndü, E.: Magnezyum Temelli Metalik Katkının Asfalt Bağlayıcının Fiziksel Özelliklerine Etkileri. Osmaniye Korkut Ata Üniversitesi Fen Bilimleri Enstitüsü Dergisi 2, 79–82 (2019)
Arslan, D.; Gürü, M.; Çubuk, M.K.: Improvement of bitumen and bituminious mixtures performance properties with organic based zincphosphate compound. J. Fac. Eng. Archit. Gazi Univ. 27, 459–466 (2012)
Arslan, D.; Gürü, M.; Çubuk, M.K.: Improvement of hot mix asphalt performance in cold regions by organic-based synthetic compounds. Cold Reg. Sci. Technol. 85, 250–255 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.coldregions.2012.09.014
Liu, Y.; Qiu, Z.; Zhao, C.; Nie, Z.; Zhong, H.; Zhao, X.; Liu, S.; Xing, X.: Characterization of bitumen and a novel multiple synergistic method for reducing bitumen viscosity with nanoparticles and surfactants. RSC Adv. 10, 10471–10481 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1039/d0ra00335b
Becker, Y.; Méndez, M.P.; Rodríguez, Y.: Polymer modified asphalt. Vis. Tecnol. 9, 40–50 (2001)
Tayfur, S.; Ozen, H.; Aksoy, A.: Investigation of rutting performance of asphalt mixtures containing polymer modifiers. Constr. Build. Mater. 21, 328–337 (2007). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.conbuildmat.2005.08.014
Al-Hadidy, A.I.; Qiu Tan, Y.: Mechanistic analysis of ST and SBS-modified flexible pavements. Constr. Build. Mater. 23, 2941–2950 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.conbuildmat.2009.02.023
Çubuk, M.; Gürü, M.; Çubuk, M.K.: Improvement of bitumen performance with epoxy resin. Fuel 88, 1324–1328 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.fuel.2008.12.024
Porto, M.; Caputo, P.; Loise, V.; Eskandarsefat, S.; Teltayev, B.; Rossi, C.O.: Bitumen and bitumen modification: a review on latest advances. Appl. Sci. 9, 742 (2019). https://doi.org/10.3390/app9040742
Arslan, D.; Gürü, M.; Kürşat Çubuk, M.: Preventing of rutting and crackings in the bituminous mixtures by monoethylene and diethylene glycol based synthetic polyboron compounds. Constr. Build. Mater. 50, 102–107 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.conbuildmat.2013.09.039
Cortizo, M.S.; Larsen, D.O.; Bianchetto, H.; Alessandrini, J.L.: Effect of the thermal degradation of SBS copolymers during the ageing of modified asphalts. Polym. Degrad. Stab. 86, 275–282 (2004). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.polymdegradstab.2004.05.006
Larsen, D.O.; Alessandrini, J.L.; Bosch, A.; Cortizo, M.S.: Micro-structural and rheological characteristics of SBS-asphalt blends during their manufacturing. Constr. Build. Mater. 23, 2769–2774 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.conbuildmat.2009.03.008
Weigel, S.; Stephan, D.: The prediction of bitumen properties based on FTIR and multivariate analysis methods. Fuel 208, 655–661 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.fuel.2017.07.048
Qin, Q.; Schabron, J.F.; Boysen, R.B.; Farrar, M.J.: Field aging effect on chemistry and rheology of asphalt binders and rheological predictions for field aging. Fuel 121, 86–94 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.fuel.2013.12.040
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that there is no conflict of interest regarding the publication of this paper.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Çalışıcı, M., Gürü, M. & Çubuk, M.K. Improving Asphalt Binder and Hot Mix Asphalt Aging Properties by Adding Synthetic Polyboron and Organic Magnesium Oxide. Arab J Sci Eng 48, 4711–4718 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13369-022-07180-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13369-022-07180-y