Abstract
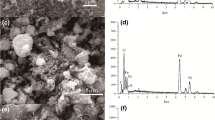
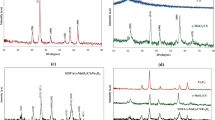
To enhance the ability and practicality of chitosan used for wastewater treatment, this study aimed to modify chitosan through cross-linking and addition of magnetic properties. Cross-linked magnetic chitosan microspheres were prepared using the inverse phase dispersion method and then applied for Cd2+ removal from water. Fe3O4 nanoparticles prepared from local iron sand were embedded with chitosan cross-linked by polyethylene glycol diglycidyl ether (PEDGE) to produce PEDGE cross-linked magnetic chitosan (PEDGE-MCh) microspheres. PEDGE-MCh microspheres were characterized by Fourier transform infrared, scanning electron microscopy energy-dispersive X-ray spectroscopy, and X-ray diffraction analyses. Altogether, the characterization confirmed the formation of cross-linking and the interaction among components in the adsorbent. Additionally, the characterization also revealed the additional features of functional groups, rougher surface, and more amorphous properties beneficial in pollutant removal. Further, the batch adsorption experiments suggest that the cross-linking and addition of Fe3O4 improved the adsorption capacity. The highest adsorption capacity was obtained at pH 5 with a contact time of 40 min. Adsorption isotherm studies indicated that the Cd2+ adsorption onto PEDGE-MCh microsphere was Redlich-Peterson dependent (R2 = 0.9996 and root-mean-square errors = 0.064). The regeneration remained the primary challenge of PEDGE-MCh application in the wastewater treatment.








Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
None.
Code availability
None.
References
Pires, C.T.G.V.M.T.; Vilela, J.A.P.; Airoldi, C.: The effect of chitin alkaline deacetylation at different condition on particle properties. Procedia Chem. 9, 220–225 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.proche.2014.05.026
Younes, I.; Rinaudo, M.: Chitin and chitosan preparation from marine sources. Structure properties and applications. Mar. Drugs 13, 1133–1174 (2015). https://doi.org/10.3390/md13031133
Safitri, E.; Humaira, H.; Murniana, M.; Nazaruddin, N.; Iqhrammullah, M.; Md Sani, N.D.; Esmaeili, C.; Susilawati, S.; Mahathir, M.; Latansa Nazaruddin, S.: Optical pH sensor based on immobilization anthocyanin from Dioscorea alata L. onto polyelectrolyte complex pectin-chitosan membrane for a determination method of salivary pH. Polymers (Basel) 13, 1276 (2021). https://doi.org/10.3390/polym13081276
Kyzas, G.; Bikiaris, D.: Recent modifications of chitosan for adsorption applications: a critical and systematic review. Mar. Drugs 13, 312–337 (2015). https://doi.org/10.3390/md13010312
Jayanudin, J.; Rochmadi, R.; Fahrurrozi, M.; Wirawan, S.: Microencapsulation technology of ginger oleoresin with chitosan as wall material: a review. J. Appl. Pharm. Sci. 6(12), 209–223 (2016). https://doi.org/10.7324/JAPS.2016.601232
Song, Z.; Li, G.; Guan, F.; Liu, W.: Application of chitin/chitosan and their derivatives in the papermaking industry. Polymers (Basel) 10, 389 (2018). https://doi.org/10.3390/polym10040389
Vakili, M.; Rafatullah, M.; Salamatinia, B.; Abdullah, A.Z.; Ibrahim, M.H.; Tan, K.B.; Gholami, Z.; Amouzgar, P.: Application of chitosan and its derivatives as adsorbents for dye removal from water and wastewater: a review. Carbohydr. Polym. 113, 115–130 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.carbpol.2014.07.007
Fan, C.; Li, K.; He, Y.; Wang, Y.; Qian, X.; Jia, J.: Evaluation of magnetic chitosan beads for adsorption of heavy metal ions. Sci. Total Environ. 627, 1396–1403 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2018.02.033
Iqhrammullah, M.; Mustafa, I.: The application of Chitosan modified polyurethane foam adsorbent. RASĀYAN J. Chem. 12, 494–501 (2019). https://doi.org/10.31788/RJC.2019.1225080
Sobahi, T.R.A.; Abdelaal, M.Y.; Makki, M.S.I.: Chemical modification of Chitosan for metal ion removal. Arab. J. Chem. 7, 741–746 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.arabjc.2010.12.011
Islam, S.; Bhuiyan, M.A.R.; Islam, M.N.: Chitin and Chitosan: structure, properties and applications in biomedical engineering. J. Polym. Environ. 25, 854–866 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10924-016-0865-5
Gutha, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Zhang, W.; Jiao, X.: Magnetic-epichlorohydrin crosslinked chitosan schiff’s base (m-ECCSB) as a novel adsorbent for the removal of Cu(II) ions from aqueous environment. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 97, 85–98 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2017.01.004
Kildeeva, N.R.; Perminov, P.A.; Vladimirov, L.V.; Novikov, V.V.; Mikhailov, S.N.: About mechanism of chitosan cross-linking with glutaraldehyde. Russ. J. Bioorgan. Chem. 35, 360–369 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1134/S106816200903011X
Mirzaei, B.E.; Ramazani, S.A.A.; Shafiee, M.; Danaei, M.: Studies on glutaraldehyde crosslinked chitosan hydrogel properties for drug delivery systems. Int. J. Polym. Mater. 62, 605–611 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1080/00914037.2013.769165
Zhang, X.; Jin, X.; Xu, C.; Shen, X.: Preparation and characterization of glutaraldehyde crosslinked chitosan nanofiltration membrane. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 128, 3665–3671 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1002/app.38580
Jozwiak, T.; Filipkowska, U.; Rodziewicz, J.; Nowosad, E.: Effect of cross-linking with glutaraldehyde on adsorption capacity of chitosan beads. Prog. Chem. Appl. Chitin Deriv. 28, 35–48 (2013)
Kyzas, G.Z.; Deliyanni, E.A.: Mercury removal with modified magnetic Chitosan adsorbents. Molecules 18, 6193–6214 (2013)
Zhao, W.; Huang, X.; Wang, Y.; Sun, S.; Zhao, C.: A recyclable and regenerable magnetic chitosan absorbent for dye uptake. Carbohydr. Polym. 150, 201–208 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.carbpol.2016.05.037
Liu, Z.; Wang, H.; Liu, C.; Jiang, Y.; Yu, G.; Mu, X.; Wang, X.: Magnetic cellulose–chitosan hydrogels prepared from ionic liquids as reusable adsorbent for removal of heavy metal ions. Chem. Commun. 48, 7350 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1039/c2cc17795a
Zhang, X.; Sun, C.; Zhang, L.; Liu, H.; Cao, B.; Liu, L.; Gong, W.: Adsorption studies of cadmium onto magnetic Fe3O4@FePO4 and its preconcentration with detection by electrothermal atomic absorption spectrometry. Talanta 181, 352–358 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.talanta.2018.01.023
Alizadeh, B.; Delnavaz, M.; Shakeri, A.: Removal of Cd(ӀӀ) and phenol using novel cross-linked magnetic EDTA/chitosan/TiO2 nanocomposite. Carbohydr. Polym. 181, 675–683 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.carbpol.2017.11.095
Iqhrammullah, M.; Audina, U.; Husin, H.; Fathana, H.: Adsorptive removal of Cd (II) using oil palm empty fruit bunch-based charcoal/chitosan-EDTA film composite. Sustain. Chem. Pharm. 21, 100449 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scp.2021.100449
Rahmi, R.; Lubis, S.; Az-Zahra, N.; Puspita, K.; Iqhrammullah, M.: Synergetic photocatalytic and adsorptive removals of metanil yellow using TiO2/grass-derived cellulose/chitosan (TiO2/GC/CH) film composite. Int. J. Eng. 34, 1827–1836 (2021). https://doi.org/10.5829/ije.2021.34.08b.03
Nina, M.; Fathana, H.; Iqhrammullah, M.: Preparation and characterization of new magnetic chitosan-glycine-PEGDE (Fe3O4/Ch-G-P) beads for aqueous Cd(II) removal. J. Water Process Eng. 45, 102493 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jwpe.2021.102493
Zein, I.; Jalil, Z.: Identification of magnetite material (Fe3O4) based on natural materials as catalyst for industrial raw material application. J. Phys. Conf. Ser. 1232, 012054 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1088/1742-6596/1232/1/012054
Nurfatimah, R.: Preparation of polyethylene glycol diglycidyl ether (PEDGE) crosslinked chitosan/activated carbon composite film for Cd2+ removal. Carbohydr. Polym. 199, 499–505 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1016/J.CARBPOL.2018.07.051
Hameed, A.M.: Synthesis of Si/Cu amorphous adsorbent for efficient removal of methylene blue dye from aqueous media. J. Inorg. Organomet. Polym. Mater. 30, 2881–2889 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10904-019-01436-1
Iqhrammullah, M.; Saleha, S.; Maulina, F.P.; Idroes, R.: Polyurethane film prepared from ball-milled algal polyol particle and activated carbon filler for NH3–N removal. Heliyon 6, e04590 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.heliyon.2020.e04590
Nagarpita, M.V.; Roy, P.; Shruthi, S.B.; Sailaja, R.R.N.: Synthesis and swelling characteristics of chitosan and CMC grafted sodium acrylate-co-acrylamide using modified nanoclay and examining its efficacy for removal of dyes. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 102, 1226–1240 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2017.04.099
Trikkaliotis, D.G.; Christoforidis, A.K.; Mitropoulos, A.C.; Kyzas, G.Z.: Adsorption of copper ions onto chitosan/poly(vinyl alcohol) beads functionalized with poly(ethylene glycol). Carbohydr. Polym. 234, 115890 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.carbpol.2020.115890
Ibrahim, A.G.; Sayed, A.Z.; Abd El-Wahab, H.; Sayah, M.M.: Synthesis of a hydrogel by grafting of acrylamide-co-sodium methacrylate onto chitosan for effective adsorption of Fuchsin basic dye. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 159, 422–432 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2020.05.039
Freundlich, H.M.F.: Over the adsorption in solution. J. Phys. Chem. 57, 385–471 (1906)
Foo, K.Y.; Hameed, B.H.: Insights into the modeling of adsorption isotherm systems. Chem. Eng. J. 156, 2–10 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2009.09.013
Al-Ghouti, M.A.; Da’ana, D.A.: Guidelines for the use and interpretation of adsorption isotherm models: a review. J. Hazard. Mater. 393, 122383 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2020.122383
Iqhrammullah, M.; Suyanto, H.; Pardede, M.; Karnadi, I.; Kurniawan, K.H.; Chiari, W.; Abdulmadjid, S.N.: Cellulose acetate-polyurethane film adsorbent with analyte enrichment for in-situ detection and analysis of aqueous Pb using Laser-Induced Breakdown Spectroscopy (LIBS). Environ. Nanotechnol. Monit. Manag. 16, 100516 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.enmm.2021.100516
Yin, W.; Zhao, C.; Xu, J.; Zhang, J.; Guo, Z.; Shao, Y.: Removal of Cd(II) and Ni(II) from aqueous solutions using activated carbon developed from powder-hydrolyzed-feathers and Trapa natans husks. Colloids Surf. A Physicochem. Eng. Asp. 560, 426–433 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1016/J.COLSURFA.2018.10.031
Fathana, H.; Iqhramullah, M.; Rahmi, R.; Adlim, A.; Lubis, S.: Tofu wastewater-derived amino acids identification using LC-MS/MS and their uses in the modification of chitosan/TiO2 film composite. Chem. Data Collect. 35, 100754 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cdc.2021.100754
Acknowledgements
Authors appreciate the collaboration between Universitas Syiah Kuala, Aceh, Indonesia and The University of Agriculture Peshawar, Pakistan during the research and the making of this article.
Funding
This research is funded by Universitas Syiah Kuala through Penelitian Lektor Kepala scheme.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
RR, LL and FF contributed to conceptualization; RR and JJ contributed to methodology; MI contributed to software; MI, MF and LL contributed to validation; MI and RR contributed to formal analysis; RS and MI contributed to investigation; RR contributed to resources; JJ and MI contributed to data curation; RR contributed to writing—original draft preparation; MI, MF, and MI contributed to writing—review and editing; JJ contributed to visualization; RR, LL, and FF contributed to supervision; RR contributed to project administration; RR contributed to funding acquisition.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors delcare that they have no conflict of interest.
Consent for Publication
All authors have read and agreed to the submitted version of the manuscript.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Rahmi, R., Lelifajri, L., Iqbal, M. et al. Preparation, Characterization and Adsorption Study of PEDGE-Cross-linked Magnetic Chitosan (PEDGE-MCh) Microspheres for Cd2+ Removal. Arab J Sci Eng 48, 159–167 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13369-022-06786-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13369-022-06786-6