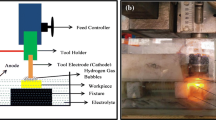
Abstract
The conventional kerosene and powder-added kerosene dielectric performances have been found to degrade in electrical discharge drilling (EDD) efficiency owing to dielectric properties variation, more debris formation, high recast layer thickness (RLT) formation, low residual stress (RS) induced and magnesium and silicon dioxide formation on the machined surface. The cryogenically treated SiC and CFRP powder-added dielectric in EDD on AA8011/h-BN/B4C composites have been carried to evaluate the RLT, RS and surface roughness (SR). Hence, the circular holes have been performed. An analysis found that cryogenically treated SiC powder-added dielectric has a higher improvement percentage than that of conventional kerosene and CFRP powder-added kerosene. Cryogenically treated SiC powder-added kerosene shows an improved performance measure of 62.2% in RLT, 22% in RS and 48.8% in SR of composite. Analysis of variance (ANOVA) found that the pulse duration and current are the most significant factors. Second-order and adaptive neuro-fuzzy inference system predictive models have developed. The statistical indices such as mean absolute percentage error (MAPE), root mean square error (RMSE) and coefficient of determination (R) are calculated to evaluate the modelling and found that low MAPE, RMSE and high R were obtained in both modelling. The complex proportional assessment (COPRAS) method exhibits an improved performance measure of 46.15% in RLT, 5.71% in RS and 21.42% in SR of composite.












Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
The available data and material had been used and discussed in the manuscript.
Code availability
No code has been used in this work.
References
Ilani, M.A.; Khoshnevisan, M.: Study of surfactant effects on intermolecular forces (IMF) in powder-mixed electrical discharge machining (EDM) of Ti-6Al-4V. J. Adv. Manuf. Technol. 5, 1763–1782 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00170-021-07569-3
Yip, W.S.; To, S.; Sun, Z.: Hybrid ultrasonic vibration and magnetic field assisted diamond cutting of titanium alloys. J. Manuf. Process. 62, 743–752 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jmapro.2020.12.037
Phan, N.H.; Muthuramalingam, T.: Multi criteria decision making of vibration assisted EDM process parameters on machining silicon steel using Taguchi-DEAR methodology. SILICON 13(6), 1879–1885 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12633-020-00573-4
Raza, M.H.; Ali, M.A.; Tahir, W.; Zhong, R.Y.; Mufti, N.A.; Ahmad, N.: Cryogenic treatment analysis of electrodes in wire electric discharge machining of squeeze casted Al2024/Al2O3/W composite. J. Adv. Manuf. Technol. (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00170-021-07521-5
Patel, G.; Chandrashekarappa, M.; Kumar, S.; Pimenov, D.Y.; Giasin, K.: Experimental analysis and optimization of EDM parameters on HcHcr steel in context with different electrodes and dielectric fluids using hybrid Taguchi-based PCA-utility and CRITIC-utility approaches. Metals 11(3), 419 (2021). https://doi.org/10.3390/met11030419
Chaudhury, P.; Samantaray, S.A.: comparative study of different dielectric medium for sustainable EDM of Non-Conductive material by Electro-Thermal modelling. Mater. Today: Proc. 41, 437–444 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.matpr.2020.10.162
Jilani, S.T.; Pandey, P.C.: Experimental investigations into the performance of water as dielectric in EDM. Int. J. Mach. Tools Manuf. 24(1), 31–43 (1984). https://doi.org/10.1016/0020-7357(84)90044-1
Muthuramalingam, T.: Effect of diluted dielectric medium on spark energy in green EDM process using TGRA approach. J. Clean. Prod. 238, 117894 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclepro.2019.117894
Muthuramalingam, T.: Measuring the influence of discharge energy on white layer thickness in electrical discharge machining process. Measurement 131, 694–700 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.measurement.2018.09.038
Philip, J.T.; Mathew, J.; Kuriachen, B.: Transition from EDM to PMEDM–Impact of suspended particulates in the dielectric on Ti6Al4V and other distinct material surfaces: a review. J. Manuf. Process. 64, 1105–1142 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jmapro.2021.01.056
Zhang, Y.; Liu, Y.; Ji, R.; Cai, B.: Study of the recast layer of a surface machined by sinking electrical discharge machining using water-in-oil emulsion as dielectric. Appl. Surf. Sci. 257(14), 5989–5997 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apsusc.2011.01.083
Al-Khazraji, A.; Amin, S.A.; Ali, S.M.: The effect of SiC powder mixing electrical discharge machining on white layer thickness, heat flux and fatigue life of AISI D2 die steel. Int. J. Eng. Sci. Technol. 19(3), 1400–1415 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jestch.2016.01.014
Guu, Y.H.; Hocheng, H.; Tai, N.H.; Liu, S.Y.: Effect of electrical discharge machining on the characteristics of carbon fiber reinforced carbon composites. J. Mater. Sci. 36(8), 2037–2043 (2001). https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1017539100832
Arooj, S.; Shah, M.; Sadiq, S.; Jaffery, S.H.I.; Khushnood, S.: Effect of current in the EDM machining of aluminum 6061 T6 and its effect on the surface morphology. Arab. J. Sci. Eng. 39(5), 4187–4199 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13369-014-1020-z
Rouniyar, A.K.; Shandilya, P.: Experimental investigation on recast layer and surface roughness on Aluminum 6061 alloy during magnetic field assisted powder mixed electrical discharge machining. J. Mater. Eng. Perform. 29(12), 7981–7992 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11665-020-05244-4
Ekici, E.; Motorcu, A.R.: Evaluation of drilling Al/SiC composites with cryogenically treated HSS drills. Int. J. Adv. Manuf. Technol. 74(9–12), 1495–1505 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00170-014-6085-z
Sidhu, S.S.; Bains, P.S.: Study of the recast layer of particulate reinforced metal matrix composites machined by EDM. Mater. Today Proc. 4(2), 3243–3251 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.matpr.2017.02.210
Paswan, K.; Pramanik, A.; Chattopadhyaya, S.; Basak, A.K.: A novel approach towards sustainable electrical discharge machining of metal matrix composites (MMCs). Int. J. Adv. Manuf. Technol. 106(3), 1477–1486 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00170-019-04816-6
Gudipudi, S.; Nagamuthu, S.; Subbian, K.S.; Chilakalapalli, S.P.R.: Fabrication and experimental study to optimize the recast layer and the material removal in electric discharge machining (EDM) of AA6061-B4C composite. Mater. Today Proc. 19, 448–454 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.matpr.2019.07.634
Singh Bains, P.; Sidhu, S.S.; Payal, H.S.: Study of magnetic field-assisted ED machining of metal matrix composites. Mater. Manuf. Process. 31(14), 1889–1894 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1080/10426914.2015.1127953
Singh, B.; Kumar, J.; Kumar, S.: Influences of process parameters on MRR improvement in simple and powder-mixed EDM of AA6061/10% SiC composite. Mater. Manuf. Process. 30(3), 303–312 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1080/10426914.2014.930888
Singh, B.; Kumar, J.; Kumar, S.: Experimental investigation on surface characteristics in powder-mixed electrodischarge machining of AA6061/10% SiC composite. Mater. Manuf. Process. 29(3), 287–297 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1080/10426914.2014.880463
Bains, P.S.; Sidhu, S.S.; Payal, H.S.; Kaur, S.: Magnetic field influence on surface modifications in powder mixed EDM. SILICON 11(1), 415–423 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12633-018-9907-z
Syed, K.H.; Kuppan, P.: Studies on recast-layer in EDM using aluminium powder mixed distilled water dielectric fluid. Int. J. Eng. Technol. 5(2), 1775–1780 (2013)
Chen, S.L.; Lin, M.H.; Huang, G.X.; Wang, C.C.: Research of the recast layer on implant surface modified by micro-current electrical discharge machining using deionized water mixed with titanium powder as dielectric solvent. Appl. Surf. Sci. 311, 47–53 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apsusc.2014.04.204
Ekmekci, N.; Ekmekci, B.: Electrical discharge machining of Ti6Al4V in hydroxyapatite powder mixed dielectric liquid. Mater. Manuf. Process. 31(13), 1663–1670 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1080/10426914.2015.1090591
Sahu, S.K.; Jadam, T.; Datta, S.; Nandi, G.: Effect of using SiC powder-added dielectric media during electro-discharge machining of Inconel 718 superalloys. J. Braz. Soc. Mech. Sci. 40(7), 1–19 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s40430-018-1257-7
Azhiri, R.B.; Bideskan, A.S.; Javidpour, F.; Tekiyeh, R.M.: Study on material removal rate, surface quality, and residual stress of AISI D2 tool steel in electrical discharge machining in presence of ultrasonic vibration effect. Int. J. Adv. Manuf. Technol. 101(9), 2849–2860 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00170-018-3023-5
Hu, F.Q.; Cao, F.Y.; Song, B.Y.; Hou, P.J.; Zhang, Y.; Chen, K.; Wei, J.Q.: Surface properties of SiCp/Al composite by powder-mixed EDM. Procedia CIRP 6, 101–106 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.procir.2013.03.036
Sidhu, S.S.; Yazdani, M.: Comparative analysis of MCDM techniques for EDM of SiC/A359 composite. Arab. J. Sci. Eng. 43(3), 1093–1102 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13369-017-2726-5
Talla, G.; Gangopadhyay, S.; Biswas, C.K.: Influence of graphite powder mixed EDM on the surface integrity characteristics of Inconel 625. Part. Sci. Technol. 35(2), 219–226 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1080/02726351.2016.1150371
Malhotra, P.; Singh, N.K.; Tyagi, R.K.; Sikarwar, B.S.: Comparative study of rotary-EDM, gas assisted-EDM, and gas assisted powder mixed-EDM of the hybrid metal matrix composite. Adv. Mater. Process. Technol. 7(1), 27–41 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1080/2374068X.2020.1855398
Jadam, T.; Sahu, S.K.; Datta, S.; Masanta, M.: EDM performance of Inconel 718 superalloy: application of multi-walled carbon nanotube (MWCNT) added dielectric media. J. Braz. Soc. Mech. Sci. 41(8), 1–20 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s40430-019-1813-9
Alagarsamy, S.V.; Ravichandran, M.; Sakthivelu, S.; Dinesh Kumar, S.; Chanakyan, C.; Meignanamoorthy, M.: Optimization of electric discharge machining parameters on surface roughness for Al/ZrO2 composite through response surface methodology. Mater. Today: Proc. 27, 1006–1012 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.matpr.2020.01.344
Khan, A.A.: Electrode wear and material removal rate during EDM of aluminum and mild steel using copper and brass electrodes. Int. J. Adv. Manuf. Technol. 39(5), 482–487 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00170-007-1241-3
Kibria, G.; Sarkar, B.R.; Pradhan, B.B.; Bhattacharyya, B.: Comparative study of different dielectrics for micro-EDM performance during microhole machining of Ti-6Al-4V alloy. Int. J. Adv. Manuf. Technol. 48(5–8), 557–570 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00170-009-2298-y
Zhang, W.; Deng, X.; Sui, G.; Yang, X.: Improving interfacial and mechanical properties of carbon nanotube-sized carbon fiber/epoxy composites. Carbon 145, 629–639 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.carbon.2019.01.063
Kliuev, M.; Maradia, U.; Boccadoro, M.; Perez, R.; Stirnimann, J.; Wegener, K.: Experimental study of EDM-drilling and shaping of SiSiC and SiC. Procedia CIRP 42, 191–196 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.procir.2016.02.269
Raj Kumar, D.; Jeyaprakash, N.; Yang, C.H.; Ramkumar, K.R.: Investigation on drilling behavior of CFRP composites using optimization technique. Arab. J. Sci. Eng. 45, 8999–9014 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13369-020-04649-6
Patel, K.M.; Pandey, P.M.; Rao, P.V.: Determination of an optimum parametric combination using a surface roughness prediction model for EDM of Al2O3/SiCw/TiC ceramic composite. Mater. Manuf. Process. 24(6), 675–682 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1080/10426910902769319
Mata, F.; Beamud, E.; Hanafi, I.; Khamlichi, A.; Jabbouri, A.; Bezzazi, M.: Multiple regression prediction model for cutting forces in turning carbon-reinforced PEEK CF30. Adv. Mater. Sci. Eng. (2010). https://doi.org/10.1155/2010/824098
Kannan, V.S.; Lenin, K.; Srinivasan, D.; Kumar, D.R.: Investigation on laser square hole drilling of AA7475/SiC/ZrSiO4 composites. SILICON (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12633-021-01252-8
Stefano, N.M.; Casarotto Filho, N.; Vergara, L.G.L.; da Rocha, R.U.G.: COPRAS (Complex Proportional Assessment): state of the art research and its applications. IEEE Lat. Am. Trans. 13(12), 3899–3906 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1109/TLA.2015.7404925
Aghdeab, S.H.; Shwaish, R.R.; Salman, T.M.: Determination and analysis of residual stress for AISI L2 tool steel in electric discharge machine (EDM). IOP Conf. Ser. Mater. Sci. Eng. 1094(1), 012074 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1088/1757-899X/1094/1/012074
Rao, P.S.; Ramji, K.; Satyanarayana, B.: Effect of wire EDM conditions on generation of residual stresses in machining of aluminum 2014 T6 alloy. Alex. Eng. J. 55(2), 1077–1084 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.aej.2016.03.014
Singaravel, B.; Shekar, K.C.; Reddy, G.G.; Prasad, S.D.: Experimental investigation of vegetable oil as dielectric fluid in Electric discharge machining of Ti-6Al-4V. Ain Shams Eng. 11(1), 143–147 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.asej.2019.07.010
Kumar, S.S.; Uthayakumar, M.; Kumaran, S.T.; Varol, T.; Canakci, A.: Investigating the surface integrity of aluminium based composites machined by EDM. Def. Technol. 15(3), 338–343 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.dt.2018.08.011
Peças, P.; Henriques, E.: Effect of the powder concentration and dielectric flow in the surface morphology in electrical discharge machining with powder-mixed dielectric (PMD-EDM). Int. J. Adv. Manuf. Technol. 37(11–12), 1120–1132 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00170-007-1061-5
Raj kumar, D.; Jeyaprakash, N.; Yang, C.H.; Sivasankaran, S.: Optimization of drilling process on carbon-fiber reinforced plastics using genetic algorithm. Surf. Rev. Lett. 28(03), 1–13 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1142/S0218625X20500560
Raj kumar, D.; Ranjithkumar, P.; Jenarthanan, M.P.: Experimental investigation and analysis of factors influencing delamination and thrust force during drilling of carbon-fibre reinforced polymer composites. Pigment Resin Technol. (2017). https://doi.org/10.1108/PRT-10-2016-0097
Mehrabi, M.; Pesteei, S.M.: Modeling of heat transfer and fluid flow characteristics of helicoidal double-pipe heat exchangers using adaptive neuro-fuzzy inference system (ANFIS). Int. Commun. Heat Mass Transf 38(4), 525–532 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.icheatmasstransfer.2010.12.025
Zavadskas, E.K.; Turskis, Z.: A new additive ratio assessment (ARAS) method in multicriteria decision-making. Technol. Econ. Dev. Econ. 16(2), 159–172 (2010). https://doi.org/10.3846/tede.2010.10
Lai, T.; Peng, X.; Tie, G.; Liu, J.; Guo, M.: High accurate squareness measurement squareness method for ultra-precision machine based on error separation. Precis. Eng. 49, 15–23 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.precisioneng.2017.01.005
Al-Mukhtar, M.; Al-Yaseen, F.: Modeling water quality parameters using data-driven models, a case study Abu-Ziriq marsh in south of Iraq. Hydrology 6(1), 24 (2019). https://doi.org/10.3390/hydrology6010024
Zavadskas, E.K.; Kaklauskas, A.; Sarka, V.: The new method of multicriteria complex proportional assessment of projects. Technol. Econ. Dev. Econ. 1, 131–139 (1994)
Yeo, S.H.; Tan, H.C.; New, A.K.: Assessment of waste streams in electric-discharge machining for environmental impact analysis. Proc. Inst. Mech. Eng. B J. Eng. Manuf. 212(5), 393–401 (1998). https://doi.org/10.1243/0954405981515996
Zavadskas, E.K.; Kaklauskas, A.; Vilutiene, T.: Multicriteria evaluation of apartment blocks maintenance contractors: lithuanian case study. Int. J. Strat. Property Manag. 13, 319–338 (2009). https://doi.org/10.3846/1648-715X.2009.13.319-338
Goswami, S.S.S.; Behera, D.K.K.; Afzal, A.; Razak Kaladgi, A.; Khan, S.A.A.; Rajendran, P.; Subbiah, R.; Asif, M.: Analysis of a robot selection problem using two newly developed hybrid MCDM models of TOPSIS-ARAS and COPRAS-ARAS. Symmetry 13(8), 1331 (2021). https://doi.org/10.3390/sym13081331
Razmjooy, N.; Ashourian, M.; Foroozandeh, Z.: Metaheuristics and Optimization in Computer and Electrical Engineering. Springer International Publishing AG, Berlin (2020)
Razmjooy, N.; Estrela, V.V.; Loschi, H.J.; Fanfan, W.: A comprehensive survey of new meta-heuristic algorithms. Recent Advances in Hybrid Metaheuristics for Data Clustering. Wiley Publishing, New York (2019)
Ramezani, M.; Bahmanyar, D.; Razmjooy, N.: A new improved model of marine predator algorithm for optimization problems. Arab. J. Sci. Eng. (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13369-021-05688-3
Razmjooy, N.; Khalilpour, M.; Ramezani, M.: A new meta-heuristic optimization algorithm inspired by FIFA world cup competitions: theory and its application in PID designing for AVR system. J. Control. Autom. Electr. 27(4), 419–440 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s40313-016-0242-6
Zhang, G.; Xiao, C.; Razmjooy, N.: Optimal parameter extraction of PEM fuel cells by meta-heuristics. Int. J. Ambient Energy (2020). https://doi.org/10.1080/01430750.2020.1745276
Funding
The authors did not receive support from any organization for the submitted work.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
JV was involved in conceptualization, methodology, writing, reviewing the discussion and editing. TM had contributed to computation, methodology, software and writing the discussion; KASL participated in conceptualization, analysis, writing and reviewing, writing the manuscript, methodology, software and writing the discussion; RP and KC took part in reviewing the manuscript language.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Ethics declarations
The manuscript has not been published elsewhere and it has not been submitted simultaneously for publication elsewhere.
Consent to participate
All persons named as authors in this manuscript have participated in the planning, design and performance of the research, and in the interpretation of the results.
Consent for publication
All authors have endorsed the publication of this research.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Vivek, J., Maridurai, T., Lewise, K.A.S. et al. Recast Layer Thickness and Residual Stress Analysis for EDD AA8011/h-BN/B4C Composites Using Cryogenically Treated SiC and CFRP Powder-Added Kerosene. Arab J Sci Eng 47, 15613–15632 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13369-022-06636-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13369-022-06636-5