Abstract
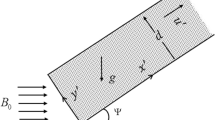
The present article is framed to describe the Jeffery–Hamel flow toward an inclined channel through critical value analysis by using finite difference approach in the occurrence of microrotations and viscous dissipation. Study is carried out by utilizing the fundamental equations of fluid flow, and nonlinear problem is solved by using finite difference method of Keller box. The flow regime is investigated by graphical interpretations of the numerical results corresponding to the variation in physical parameters. Likewise, the stability of the flow in divergent channel is studied by tabulating the critical Reynolds number. The critical Reynolds is computed for variation in opening angle of channel, material parameter and Weissenberg number. It is observed that where increase in Weissenberg number and greater channel opening angles seem to be halting the flow in the diverging, increasing the number of micro-rotating structures is bringing about stability in the flow.










Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- r, \(\theta \), z :
-
Cylindrical coordinate
- u, v, w :
-
Velocity components in r-, \(\theta \)- and z-directions, respectively,
- \(\rho \) :
-
Density
- P :
-
Pressure
- N :
-
Angular momentum
- \(\tau \) :
-
Stress tensor
- \(\mu _{0}\) :
-
Dynamic viscosity
- \(\gamma \) :
-
Spin gradient viscosity
- \(\alpha _{1},\alpha _{2},\alpha _{3}\) :
-
Material parameters
- D :
-
Velocity stress tensor
- \(\nabla V\) :
-
Velocity gradient
- \(\kappa ^{*}\) :
-
Rotational viscosity parameter
- \(\psi _{1,0}\), \(\psi _{2,0}\) :
-
Elasticity parameter
- \(\eta \) :
-
Dimensionless space variable
- F :
-
Linear velocity
- G :
-
Angular velocity
- \(\mathrm {Re}\) :
-
Reynold number
- Wi:
-
Weissenberg number
- K :
-
Material parameter
- \(C_{\mathrm{f}}\) :
-
Skinfriction
References
Eringen, A.C.: Theory of micropolar fluids. J. Math. Mech. 16, 1–18 (1966)
Nadeem, S.: Numerical analysis of water based CNTs flow of micropolar fluid through rotating frame. Comput. Methods Programs Biomed. 186, 105194 (2020)
Khader, M.M.; Sharma, R.P.: Evaluating the unsteady MHD micropolar fluid flow past stretching/shirking sheet with heat source and thermal radiation: implementing fourth order predictor–corrector FDM. Math. Comput. Simul. 181, 333–350 (2021)
Agarwal, R.: Heat and mass transfer in electrically conducting micropolar fluid flow between two stretchable disks. In: Materials Today: Proceedings. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.matpr.2020.11.614
Boukrouche, M.; Laetitia, P.; Ziane, Z.F.: Micropolar fluid flow in a thick domain with multiscale oscillating roughness and friction boundary conditions. J. Math. Anal. Appl. 495(1), 124688 (2021)
Hossam, A.; Mahdy, A.: Transient flow of micropolar dusty hybrid nanofluid loaded with \(Fe_{3}O_{4}\)–\(Ag\) nanoparticles through a porous stretching sheet. Results Phys. 21, 103777 (2021)
El-Sapa, S.: Effect of magnetic field on a microstructure fluid drop embedded in an unbounded another microstructure fluid. Eur. J. Mech. B Fluids 185, 169–180 (2021)
Kato, H.; Shibanuma, H.: Diverging and converging flows of dilute polymer solutions. Bull. JSME 23, 1140–1147 (1980)
Berrehal, H.; Sowmya, G.: Heat transfer analysis of nanofluid flow in a channel with non-parallel walls. J. Mech. Sci. Technol. 35(1), 171–177 (2021)
Hamid, M.; Usman, M.; Haq, R.U.; Tian, Z.: A Galerkin approach to analyze MHD flow of nanofluid along converging/diverging channels. Arch. Appl. Mech. 91, 1907–1924 (2021)
Kumbinarasaiah, S.; Raghunatha, K.R.: The applications of Hermite wavelet method to nonlinear differential equations arising in heat transfer. Int. J. Thermofluids 9, 100066 (2021)
Ayeche, C.M.; Kezzar, M.; Sari, M.R.; Eid, M.R.: Analytical ADM study of time-dependent hydromagnetic flow of biofluid over a wedge. Indian J. Phys. 95(12), 2769–2784 (2021)
Yang, Y.; Rządkowski, G.; Pasban, A.; Tohidi, E.; Shateyi, S.: A high accurate scheme for numerical simulation of two-dimensional mass transfer processes in food engineering. Alex. Eng. J. 60(2), 2629–2639 (2021)
Gahgah, M.; Mohamed, R.S.; Mohamed, K.; Mohamed, R.E.: Duan–Rach modified Adomian decomposition method (DRMA) for viscoelastic fluid flow between nonparallel plane wall. Eur. Phys. J. Plus 135(2), 1–17 (2020)
Nabwey, H.A.; Mahdy, A.: Numerical approach of micropolar dust-particles natural convection fluid flow due to a permeable cone with nonlinear temperature. Alex. Eng. J. 60(1), 1739–1749 (2021)
Akmal, N.; Sagheer, M.; Hussain, S.; Kamran, A.: Study of micropolar nanofluids with power-law spin gradient viscosity model by the Keller box method. Can. J. Phys. 98(1), 16–27 (2020)
Kamran, A.; Hussain, S.; Sagheer, M.; Akmal, N.: A numerical study of magnetohydrodynamics flow in Casson nanofluid combined with Joule heating and slip boundary conditions. Results Phys. 7, 3037–3048 (2017)
Iqbal, Z.; Azhar, E.; Mehmood, Z.; Maraj, E.N.; Kamran, A.: Computational analysis of engine-oil based magnetite nanofludic problem inspired with entropy generation. J. Mol. Liq. 230, 295–304 (2017)
Azhar, E.; Mara, E.N.; Iqbal, Z.: Mechanistic investigation for the axisymmetric transport of nano composite molybdenum disulfide-silicon dioxide in ethylene glycol and sphericity assessment of nanoscale particles. Eur. Phys. J. Plus 132, 143–156 (2018)
Iqbal, Z.; Mehmood, R.; Azhar, E.; Mehmood, Z.: Impact of inclined magnetic field on micropolar Casson fluid using Keller box algorithm. Eur. Phys. J. Plus 132(4), 175 (2017)
Nagler, J.: Jeffery–Hamel flow of non-Newtonian fluid with nonlinear viscosity and wall friction. Appl. Math. Mech. 38(6), 815–830 (2016)
Sadeghy, K.; Khabazi, N.; Taghavi, S.: Magnetohydrodynamic (MHD) flows of viscoelastic fluids in converging/diverging channels. Int. J. Eng. Sci. 45(11), 923–938 (2007)
Turkyilmazoglu, M.: Extending the traditional Jeffery–Hamel flow to stretchable convergent/divergent channels. Comput. Fluids 100, 196–203 (2014)
Keller, H.B.: Accurate difference methods for nonlinear two-point boundary value problems. SIAM J. Numer. Anal. 11(2), 305–320 (1974)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kamran, A., Azhar, E., Akmal, N. et al. Finite Difference Approach for Critical Value Analysis to Describe Jeffery–Hamel Flow Toward an Inclined Channel with Microrotations. Arab J Sci Eng 47, 15261–15268 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13369-021-06532-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13369-021-06532-4