Abstract
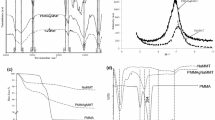
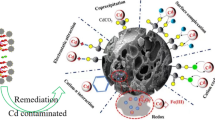
As important parts of microbe–mineral associations, microalgae–montmorillonite composites are common in nature environment, which have been overlooked for a long time. In this study, the binding of Cd(II) in the montmorillonite, microalgae and their 1:5, 1:10 mass ratio composites interface were investigated. The results showed that maximum adsorption capacity of 1:5 and 1:10 mass ratio binary composites were 65.25 mg g−1 and 55.49 mg g−1, respectively, which both higher the theoretically calculated capacity from single montmorillonite and microalgae at pH 5.5. Fourier transform infrared spectrometer (FT-IR) and X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy (XPS) analyses indicated that phosphoryl and carboxyl functional groups on the algal cellular surface played major roles in both microalgae–montmorillonite composite formation and Cd(II) adsorption. Extended X-ray absorption fine structure (EXAFS) further probed that higher sorption on composites were attributed to Cd(II) bridging between microalgae and montmorillonite, in which monodentate phosphoryl-Cd and carboxyl-Cd complexes on microalgae side, leading Cd(II) to a more stabilized state. In addition, the montmorillonite promoted dispersion of microalgae, releasing more carboxyl and phosphoryl functional groups as Cd(II) binding sites on the microalgae surface. These findings highlight the function of microalgae in the microalgae–clay mineral associations for Cd(II) fixation and provide further insight into the sequestration and migration of toxic metals in natural environments.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Sun, Y.; Sun, G.; Xu, Y.; Wang, L.; Liang, X.; Lin, D.: Assessment of sepiolite for immobilization of cadmium-contaminated soils. Geoderma 193–194, 149–155 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.geoderma.2012.07.012
Houessionon, M.G.K.; Ouendo, E.D.; Bouland, C.; Takyi, S.A.; Kedote, N.M.; Fayomi, B.; Fobil, J.N.; Basu, N.: Environmental Heavy Metal Contamination from Electronic Waste (E-Waste) recycling activities worldwide: a systematic review from 2005 to 2017. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 18, 3517 (2021). https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph18073517
Kan, X.; Dong, Y.; Feng, L.; Zhou, M.; Hou, H.: Contamination and health risk assessment of heavy metals in China’s lead-zinc mine tailings: a meta-analysis. Chemosphere 267, 128909 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2020.128909
Ayangbenro, A.S.; Babalola, O.O.: A new strategy for heavy metal polluted environments: a review of microbial biosorbents. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 14, 94 (2017). https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph14010094
Fang, L.; Cai, P.; Li, P.; Wu, H.; Liang, W.; Rong, X.; Chen, W.; Huang, Q.: Microcalorimetric and potentiometric titration studies on the adsorption of copper by P. putida and B. thuringiensis and their composites with minerals. J. Hazard Mater. 181, 1031–1038 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2010.05.118
Li, G.L.; Zhou, C.H.; Fiore, S.; Yu, W.H.: Interactions between microorganisms and clay minerals: new insights and broader applications. Appl. Clay Sci. 177, 91–113 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.clay.2019.04.025
Megharaj, M.; Singleton, I.; McClure, N.C.; Naidu, R.: Influence of petroleum hydrocarbon contamination on microalgae and microbial activities in a long-term contaminated soil. Arch. Environ. Contam. Toxicol. 38, 439–445 (2000). https://doi.org/10.1007/s002449910058
Suresh Kumar, K.; Dahms, H.-U.; Won, E.-J.; Lee, J.-S.; Shin, K.-H.: Microalgae—A promising tool for heavy metal remediation. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 113, 329–352 (2015)
Xia, L.; Xia, L.; Li, H.; Li, H.; Song, S.; Song, S.: Cell surface characterization of some oleaginous green algae. J. Appl. Phycol. 28, 2323–2332 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10811-015-0768-1
Gupta, S.S.; Bhattacharyya, K.G.: Adsorption of heavy metals on kaolinite and montmorillonite: a review. Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 14, 6698 (2012)
Hong, Z.; Rong, X.; Cai, P.; Dai, K.; Liang, W.; Chen, W.; Huang, Q.: Initial adhesion of Bacillus subtilis on soil minerals as related to their surface properties. Eur. J. Soil Sci. 63, 457–466 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1365-2389.2012.01460.x
Wang, H.; Wu, P.; Liu, J.; Yang, S.; Ruan, B.; Rehman, S.; Liu, L.; Zhu, N.: The regulatory mechanism of Chryseobacterium sp. resistance mediated by montmorillonite upon cadmium stress. Chemosphere 240, 124851 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2019.124851
Qu, C.; Ma, M.; Chen, W.; Cai, P.; Huang, Q.: Surface complexation modeling of Cu(II) sorption to montmorillonite–bacteria composites. Sci. Total Environ. 607–608, 1408–1418 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2017.07.068
Du, H.; Huang, Q.; Peacock, C.L.; Tie, B.; Lei, M.; Liu, X.; Wei, X.: Competitive binding of Cd, Ni and Cu on goethite organo–mineral composites made with soil bacteria. Environ. Pollut. 243, 444–452 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envpol.2018.08.087
Sawalha, M.F.; Peralta-Videa, J.R.; Romero-González, J.; Gardea-Torresdey, J.L.: Biosorption of Cd(II), Cr(III), and Cr(VI) by saltbush (Atriplex canescens) biomass: thermodynamic and isotherm studies. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 300, 100–104 (2006). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jcis.2006.03.029
Shanmugam, S.; Karthik, K.; Veerabagu, U.; Hari, A.; Swaminathan, K.; Al-Kheraif, A.A.; Whangchai, K.: Bi-model cationic dye adsorption by native and surface-modified Trichoderma asperellum BPL MBT1 biomass: from fermentation waste to value-added biosorbent. Chemosphere 277, 130311 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2021.130311
Shanmughaprabha, P.; Sasireka, S.; Sabarathinam, S.; Selvakumari, G.: Equilibrium and kinetic studies of uptake of nickel in aqueous solution. Desalin. Water Treat. 59, 160–167 (2017). https://doi.org/10.5004/dwt.2017.0051
Chen, H.; Tan, W.; Lv, W.; Xiong, J.; Wang, X.; Yin, H.; Fang, L.: Molecular mechanisms of lead binding to ferrihydrite-bacteria composites: ITC, XAFS, and μ-XRF investigations. Environ. Sci. Technol. (2020). https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.est.9b06288
Du, H.; Qu, C.; Liu, J.; Chen, W.; Cai, P.; Shi, Z.; Yu, X.-Y.; Huang, Q.: Molecular investigation on the binding of Cd(II) by the binary mixtures of montmorillonite with two bacterial species. Environ. Pollut. 229, 871–878 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envpol.2017.07.052
Moon, E.M.; Peacock, C.L.: Adsorption of Cu(II) to ferrihydrite and ferrihydrite–bacteria composites: importance of the carboxyl group for Cu mobility in natural environments. Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta 92, 203–219 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.gca.2012.06.012
Qu, C.; Du, H.; Ma, M.; Chen, W.; Cai, P.; Huang, Q.: Pb sorption on montmorillonite-bacteria composites: a combination study by XAFS, ITC and SCM. Chemosphere 200, 427–436 (2018)
Koningsberger, D.C.; Mojet, B.L.; Dorssen, G.E.V.; Ramaker, D.E.: XAFS Spectroscopy: fundamental principles and data analysis. Top. Catal. 10, 143–155 (2000). https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1019105310221
Newville, M.: IFEFFIT: interactive XAFS analysis and FEFF fitting. J. Synchrotron Radiat. 8, 322–324 (2001)
Ravel, B.; Newville, M.: ATHENA, ARTEMIS, HEPHAESTUS: data analysis for X-ray absorption spectroscopy using IFEFFIT. J. Synchrotron Radiat. 12, 537–541 (2005). https://doi.org/10.1107/s0909049505012719
Rong, X.; Huang, Q.; He, X.; Chen, H.; Cai, P.; Liang, W.: Interaction of Pseudomonas putida with kaolinite and montmorillonite: a combination study by equilibrium adsorption, ITC, SEM and FTIR. Colloids Surf. B 64, 49–55 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.colsurfb.2008.01.008
Shanmughaprabha, P.; Sasireka, S.; Sabarathinam, S.; Selvakumari, G.: Efficiency of may flower seed carbon to uptake Fe (II) from aqueous solution: kinetic and isotherm studies. Environ. Prog. Sustain. Energy (2018). https://doi.org/10.1002/ep.12996
Vollrath, S.; Behrends, T.; Koch, C.B.; Cappellen, P.V.: Effects of temperature on rates and mineral products of microbial Fe(II) oxidation by leptothrix cholodnii at microaerobic conditions. Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta 108, 107–124 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.gca.2013.01.019
Zhang, L.; Luo, H.; Liu, P.; Fang, W.; Geng, J.: A novel modified graphene oxide/chitosan composite used as an adsorbent for Cr(VI) in aqueous solutions. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 87, 586–596 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2016.03.027
Li, Y.; Song, S.; Xia, L.; Yin, H.; García Meza, J.V.; Ju, W.: Enhanced Pb(II) removal by algal-based biosorbent cultivated in high-phosphorus cultures. Chem. Eng. J. 361, 167–179 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2018.12.070
Liu, Y.; Alessi, D.S.; Owttrim, G.W.; Kenney, J.P.L.; Zhou, Q.; Lalonde, S.V.; Konhauser, K.O.: Cell surface acid-base properties of the cyanobacterium Synechococcus: influences of nitrogen source, growth phase and N: P ratios. Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta 187, 179–194 (2016)
Chubar, N.; Visser, T.; Avramut, C.; de Waard, H.: Sorption and precipitation of Mn2+ by viable and autoclaved Shewanella putrefaciens: effect of contact time. Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta 100, 232–250 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.gca.2012.09.051
Huang, R.; Huo, G.; Song, S.; Li, Y.; Xia, L.; Gaillard, J.-F.: Immobilization of mercury using high-phosphate culture-modified microalgae. Environ. Pollut. 254, 112966 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envpol.2019.112966
Fang, L.; Huang, Q.; Wei, X.; Liang, W.; Rong, X.; Chen, W.; Cai, P.: Microcalorimetric and potentiometric titration studies on the adsorption of copper by extracellular polymeric substances (EPS), minerals and their composites. Biores. Technol. 101, 5774–5779 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biortech.2010.02.075
Chen, X.; Chen, L.; Shi, J.; Wu, W.; Chen, Y.: Immobilization of heavy metals by Pseudomonas putida CZ1/goethite composites from solution. Colloids Surf., B 61, 170–175 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.colsurfb.2007.08.002
Yan, S.; Cai, Y.; Li, H.; Song, S.; Xia, L.: Enhancement of cadmium adsorption by EPS-montmorillonite composites. Environ. Pollut. 252, 1509–1518 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envpol.2019.06.071
Xia, L.; Li, H.; Song, S.: Cell surface characterization of some oleaginous green algae. J. Appl. Phycol. 28, 2323–2332 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10811-015-0768-1
Cui, J.; Zhang, Z.; Han, F.: Effects of pH on the gel properties of montmorillonite, palygorskite and montmorillonite-palygorskite composite clay. Appl. Clay Sci. 190, 105543 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.clay.2020.105543
Manirethan, V.; Raval, K.; Balakrishnan, R.M.: Adsorptive removal of trivalent and pentavalent arsenic from aqueous solutions using iron and copper impregnated melanin extracted from the marine bacterium Pseudomonas stutzeri. Environ. Pollut. 257, 113576 (2019)
Du, H.; Lin, Y.; Chen, W.; Cai, P.; Rong, X.; Shi, Z.-H.; Huang, Q.: Copper adsorption on composites of goethite, cells of Pseudomonas putida and humic acid. Eur. J. Soil Sci. 68, 514–523 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1111/ejss.12430
Lei, M.; Tao, J.; Yang, R.; Tie, B.; Liu, X.; Wei, X.; Du, H.: Binding of Sb(III) by Sb-tolerant Bacillus cereus cell and cell-goethite composite: implications for Sb mobility and fate in soils and sediments. J. Soils Sediments 19, 2850–2858 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11368-019-02272-z
Zhu, C.; Liu, F.; Zhang, Y.; Wei, M.; Zhang, X.; Ling, C.; Li, A.: Nitrogen-doped chitosan-Fe(III) composite as a dual-functional material for synergistically enhanced co-removal of Cu(II) and Cr(VI) based on adsorption and redox. Chem. Eng. J. 306, 579–587 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2016.07.096
Zeng, L.; Chen, Y.; Zhang, Q.; Guo, X.; Peng, Y.; Xiao, H.; Chen, X.; Luo, J.: Adsorption of Cd(II), Cu(II) and Ni(II) ions by cross-linking chitosan/rectorite nano-hybrid composite microspheres. Carbohyd. Polym. 130, 333–343 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.carbpol.2015.05.015
Chen, L.; Wu, P.; Chen, M.; Lai, X.; Ahmed, Z.; Zhu, N.; Dang, Z.; Bi, Y.; Liu, T.: Preparation and characterization of the eco-friendly chitosan/vermiculite biocomposite with excellent removal capacity for cadmium and lead. Appl. Clay Sci. 159, 74–82 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.clay.2017.12.050
Mikutta, R.; Zang, U.; Chorover, J.; Haumaier, L.; Kalbitz, K.: Stabilization of extracellular polymeric substances (Bacillus subtilis) by adsorption to and coprecipitation with Al forms. Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta 75, 3135–3154 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.gca.2011.03.006
Li, Y.; Xia, L.; Huang, R.; Xia, C.; Song, S.: Algal biomass from the stable growth phase as a potential biosorbent for Pb(II) removal from water. RSC Adv. 7, 34600–34608 (2017)
Ding, L.; Tan, W.-F.; Xie, S.-B.; Mumford, K.; Lv, J.-W.; Wang, H.-Q.; Fang, Q.; Zhang, X.-W.; Wu, X.-Y.; Li, M.: Uranium adsorption and subsequent re-oxidation under aerobic conditions by Leifsonia sp. - Coated biochar as green trapping agent. Environ. Pollut. 242, 778–787 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envpol.2018.07.050
Li, M.; Zhang, Z.; Li, R.; Wang, J.J.; Ali, A.: Removal of Pb(II) and Cd(II) ions from aqueous solution by thiosemicarbazide modified chitosan. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 86, 876 (2016)
Bigi, A.; Foresti, E.B.; Gazzano, M.; Ripamonti, A.; Roveri, N.: Cadmium substituted tricalcium phosphate and crystal structure refinement of beta-tricadmium phosphate. Chem. Informationsdienst 17, 170–171 (1986)
Post, M.L.; Trotter, J.: Crystal and molecular structure of cadmium(II) cyanoacetate. J. Chem. Soc., Dalton Trans. 5, 285–288 (1974)
Post, M.L.; Trotter, J.: Crystal and molecular structure of cadmium(II) maleate dihydrate. J. Chem. Soc. Dalton Trans. 7, 674 (1974)
Karlsson, T.; Persson, P.; Skyllberg, U.: Extended X-ray absorption fine structure spectroscopy evidence for the complexation of cadmium by reduced sulfur groups in natural organic matter. Environ. Sci. Technol. 39, 3048–3055 (2005). https://doi.org/10.1021/es048585a
Acknowledgements
This work was financially supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Grant Nos. 32061123009, 52074203), Qingchuang Talent Incubation Program from Colleges and universities in Shandong Province (Grant No. 2019.133).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Tan, J., Li, Y., Xia, L. et al. Enhancement of Cd(II) Adsorption on Microalgae–Montmorillonite Composite. Arab J Sci Eng 47, 6715–6727 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13369-021-06063-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13369-021-06063-y