Abstract
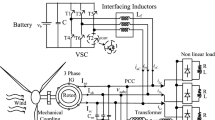
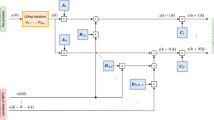
As a kind of fuel cells, solid oxide fuel cell (SOFC) has been an important research area for researchers. However, SOFC gives a challenging control problem because of their operating constraints, complex nonlinearity, slow dynamics, and load disturbance. In this article, a new enhanced model-free discrete-time adaptive terminal sliding-mode control (EMF-ATSMC) is proposed for the SOFC system with input constraints, aiming to regulate the output voltage under the load disturbance. The referred EMF-ATSMC controller is composed of three components: the pseudo-partial-derivative (PPD) estimator, the discrete-time adaptive terminal sliding-mode control, and the anti-windup compensator. First, an enhanced compact form of dynamic linearization data-driven modelling method is used to simplify the SOFC plant considering the load perturbation, and then, the PPD estimator is designed. The discrete-time adaptive terminal sliding-mode control via anti-windup compensator is developed to improve the control performance and guarantee the controlled system stability, wherein the designed anti-windup compensator is employed to eliminate the magnitude and rate saturations of control input. Moreover, the closed-loop system’s stability with the proposed EMF-ATSMC controller is theoretically proved by using the Lyapunov method. Finally, simulation results are given to demonstrate that the proposed EMF-ATSMC controller has excellent dynamic performance and stronger robustness compared with other methods such as improved model-free adaptive constrained control (IMFACC), model-free adaptive control (MFAC), and PID controller.














Similar content being viewed by others
References
Wu, Y.; Huangfu, Y.; Ma, R.; Ravey, A.; Chrenko, D.: A strong robust DC-DC converter of all-digital high-order sliding mode control for fuel cell power applications. J. Power Sour. 413, 222–232 (2019)
Zhang, T.; Feng, G.: Rapid load following of an SOFC power system via stable fuzzy predictive tracking controller. IEEE Trans. Fuzzy Syst. 17(2), 357–371 (2008)
Suther, T.; Fung, A.; Koksal, M.; Zabihian, F.: Macro level modeling of a tubular solid oxide fuel cell. Sustainability 2(11), 3549–3560 (2010)
Sangtongkitcharoen, W.; Vivanpatarakij, S.; Laosiripojana, N.; Arpornwichanop, A.; Assabumrungrat, S.: Performance analysis of methanol-fueled solid oxide fuel cell system incorporated with palladium membrane reactor. Chem. Eng. J. 138(1–3), 436–441 (2008)
Xu, D.; Jiang, B.; Liu, F.: Improved data driven model free adaptive constrained control for a solid oxide fuel cell. IET Control Theory Appl. 10(12), 1412–1419 (2016)
Nayeripour, M.; Hoseintabar, M.: A new control strategy of solid oxide fuel cell based on coordination between hydrogen fuel flow rate and utilization factor. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 27, 505–514 (2013)
Vrečko, D.; Dolanc, G.; Dolenc, B.; Vrančić, D.; Pregelj, B.; Marra, D.; Marra, D.; SorrentIino, M.; Pianese, C.; Pohjoranta, A.: Juričić: feedforward-feedback control of a SOFC power system: a simulation study. ECS Trans. 68(1), 3151 (2015)
Abbaker, A.O.; Wang, H.P.; Tian, Y.: Voltage control of solid oxide fuel cell power plant based on intelligent proportional integral-adaptive sliding mode control with anti-windup compensator. Trans. Inst. Measur. Control 42(1), 116–130 (2020)
Li, Y.; Shen, J.; Lu, J.: Constrained model predictive control of a solid oxide fuel cell based on genetic optimization. J. Power Sour. 196(14), 5873–5880 (2011)
Wu, X.J.; Zhu, X.J.; Cao, G.Y.; Tu, H.Y.: Predictive control of SOFC based on a GA-RBF neural network model. J. Power Sour. 179(1), 232–239 (2008)
Jurado, F.: Predictive control of solid oxide fuel cells using fuzzy Hammerstein models. J. Power Sour. 158(1), 245–253 (2006)
Sun, L.; Hua, Q.; Shen, J.; Xue, Y.; Li, D.; Lee, K.Y.: A combined voltage control strategy for fuel cell. Sustainability 9(9), 1517 (2017)
Qin, Y.; Sun, L.; Hua, Q.; Liu, P.: A fuzzy adaptive PID controller design for fuel cell power plant. Sustainability 10(7), 2438 (2018)
Triwiyatno, A.; Kurniahadi, A.: Designing hydrogen and oxygen flow rate control on a solid oxide fuel cell simulator using the Fuzzy logic control method. Processes 8(2), 154 (2020)
Yan, J.J.; Liao, T.L.: Discrete sliding mode control for hybrid synchronization of continuous Lorenz systems with matched/unmatched disturbances. Tran. Inst. Measur. Control 40(5), 1417–1424 (2018)
Ji, N.; Xu, D.; Liu, F.: A novel adaptive neural network constrained control for solid oxide fuel cells via dynamic anti-windup. Neurocomputing 214, 134–142 (2016)
Liu, D.; Yang, G.H.: Performance-based data-driven model-free adaptive sliding mode control for a class of discrete-time nonlinear processes. J. Process Control 68, 186–194 (2018)
Feng, J.; Cao, L.; Ma, L.; Zhao, D.; Spurgeon, S.K.: Model-free adaptive sliding mode control for continuous stirred tank reactor, In 37th Chinese Control Conference (CCC). Wuhan, China, IEEE 2018, 3035–3040 (2018)
Abbaker, A.M.O.; Wang, H.P.; Tian, Y.: Adaptive integral type-terminal sliding mode control for PEMFC air supply system using time delay estimation algorithm. Asian J. control (2020). https://doi.org/10.1002/asjc.2451
Paul, S.; Yu, W.; Li, X.: Discrete-time sliding mode for building structure bidirectional active vibration control. Trans. Inst. Measur. Control 41(2), 433–446 (2019)
Martinez, D.I.; De-Rubio, J.J.; Vargas, T.M.; Garcia, V.; Ochoa, G.; Balcazar, R.; Cruz, D.R.; Aguilar, A.; Novoa, J.F.; Aguilar-Ibanez, C.: Stabilization of robots with a regulator containing the sigmoid mapping. IEEE Access. 8, 89479–89488 (2020)
Rubio, J.D.J.; Ochoa, G.; Mujica-Vargas, D.; Garcia, E.; Balcazar, R.; Elias, I.; Cruz, D.R.; Juarez, C.F.; Aguilar, A.; Novoa, J.F.: Structure regulator for the perturbations attenuation in a quadrotor. IEEE Access. 7, 138244–138252 (2019)
Escobedo-Alva, J.O.; Garcia-Estrada, E.C.; Paramo-Carranza, L.A.; Meda-Campana, J.A.; Tapia-Herrera, R.: Theoretical application of a hybrid observer on altitude tracking of quadrotor losing GPS signal. IEEE Access. 6, 76900–76908 (2018)
Martinez, D.I.; Rubio, J.D.J.; Aguilar, A.; Pacheco, J.; Gutierrez, G.J.; Garcia, V.; Vargas, T.M.; Ochoa, G.; Cruz, D.R.; Juarez, C.F.: Stabilization of two electricity generators. Complexity 2020, 1–13 (2020)
Aguilar-Ibanez, C.; Suarez-Castanon, M.S.: A trajectory planning based controller to regulate an uncertain 3D overhead crane system. Int. J. Appl. Math. Comput. Sci. 29(4), 693–702 (2019)
García-Sánchez, J.R.; Tavera-Mosqueda, S.; Silva-Ortigoza, R.; Hernández-Guzmán, V.M.; Sandoval-Gutiérrez, J.; Marcelino-Aranda, M.; Taud, H.; Marciano-Melchor, M.: Robust switched tracking control for wheeled mobile robots considering the actuators and drivers. Sensors 18(12), 4316 (2018)
Zhang, B.; Cao, R.; Hou, Z.: The model-free adaptive cross-coupled control for two-dimensional linear motor. Trans. Inst. Measur. Control 42(5), 1059–1069 (2020)
Bu, X.; Hou, Z.; Zhang, H.: Data-driven multiagent systems consensus tracking using model free adaptive control. IEEE Trans. Neural Netw. Learn. Syst. 29(5), 1514–1524 (2017)
Xu, D.; Jiang, B.; Shi, P.: Adaptive observer based data-driven control for nonlinear discrete-time processes. IEEE Trans. Autom.n Sci. Eng. 11(4), 1549–1558 (2014)
Ma, H.; Wu, J.; Xiong, Z.: Discrete-time sliding-mode control with improved quasi-sliding-mode domain. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 63(10), 6292–6304 (2016)
Hou, Z.; Jin, S.: A novel data-driven control approach for a class of discrete-time nonlinear systems. IEEE Trans. Control Syst. Technol. 19(6), 1549–1558 (2011)
Hou, Z.; Bu, X.: Model free adaptive control with data dropouts. Exp. Syst. Appl. 38(8), 10709–10717 (2011)
Bu, X.; Hou, Z.; Yu, F.; Wang, F.: Robust model free adaptive control with measurement disturbance. IET Control Theory Appl. 6(9), 1288–1296 (2012)
Mustafa, G.I.; Wang, H.P.; Tian, Y.: Model-free adaptive fuzzy logic control for a half-car active suspension system. Stud. Inform. Control. 28(1), 13–24 (2019)
Hou, Z., Jin, S.: Data-driven model-free adaptive control for a class of MIMO nonlinear discrete-time systems, IEEE Transactions on Neural Networks 22(12), pp. 2173–2188 (011).
Abbaker, A.M.O.; Wang, H.P.; Tian, Y.: Robust model-free adaptive interval type-2 fuzzy sliding mode control for PEMFC system using disturbance observer. Int. J. Fuzzy Syst. 22, 2188–2203 (2020)
Hou, Z.S.: The Parameter Identification, Adaptive Control and Model Free Learning Adaptive Control for Nonlinear Systems, (Ph.D. dissertation), Northeastern University, Shengyang, China, (1994).
Hou, Z.; Zhu, Y.: Controller-dynamic-linearization-based model free adaptive control for discrete-time nonlinear systems. IEEE Trans. Ind. Inform. 9(4), 2301–2309 (2013)
Cao, R.M.; Hou, Z.S.: Model-free learning adaptive control of a PH neutralization process. Comput. Eng. Appl. 42(28), 191–194 (2006)
Chi, R.H.; Hou, Z.S.: A model-free periodic adaptive control for freeway traffic density via ramp metering. Acta Automatica Sinica. 36(7), 1029–1032 (2010)
Luo, Y.; Hu, Y.; Jiang, F.; Chen, R.; Wang, Y.: Active fault-tolerant control based on multiple input multiple output-model free adaptive control for four wheel independently driven electric vehicle drive system. Appl. Sci. 9(2), 276 (2019)
Bai, L.; Feng, Y.W.; Li, N.; Xue, X.F.: Robust model-free adaptive iterative learning control for vibration suppression based on evidential reasoning. Micromachines 10(3), 196 (2019)
Lv, F.L.; Chen, H.B.; Fan, C.J.; Chen, S.B.: Application of model-free adaptive control to impulse TIG welding. J. Shanghai Jiaotong Univ. 43(1), 62–70 (2009)
Hou, Z.; Xiong, S.: On model-free adaptive control and its stability analysis. IEEE Trans. Autom. Control 64(11), 4555–4569 (2019)
Wang, W.; Hou, Z.: New adaptive quasi-sliding mode control for nonlinear discrete time systems. J. Syst. Eng. Electron. 19(1), 154–160 (2008)
Xu, D.; Shi, Y.; Ji, Z.: Model-free adaptive discrete-time integral sliding-mode-constrained-control for autonomous 4WMV parking systems. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 65(1), 834–843 (2017)
Weng, Y.; Gao, X.: Adaptive sliding mode decoupling control with data-driven sliding surface for unknown MIMO nonlinear discrete systems. Circuits Syst. Signal Process. 36(3), 969–997 (2017)
Hou, Z.; Wang, W.; Jin, S.: Adaptive quasi-sliding-mode control for a class of nonlinear discrete-time systems. Control Theor. Appl. 26(5), 505–509 (2009)
Gao, W.; Homaifa, Y.; Wang, A.: discrete-time variable structure control systems. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 42(2), 117–122 (1995)
Wang, X.; Li, X.; Wang, J.; Fang, X.; Zhu, X.: Data-driven model-free adaptive sliding mode control for the multi degree-of-freedom robotic exoskeleton. Inform. Sci. 327, 246–257 (2016)
Spurgeon, S.K.: Hyperplane design techniques for discrete-time variable structure control systems. Int. J. Control 55(2), 445–456 (1992)
Mahato, N.; Banerjee, A.; Gupta, A.; Omar, S.; Balani, K.: Progress in material selection for solid oxide fuel cell technology: a review. Prog. Mater. Sci. 72, 141–337 (2015)
Benko, D.; Biles, D.C.; Robinson, M.P.; Spraker, J.S.: Numerical approximation for singular second order differential equations. Math. Comput. Modell. 49(5–6), 1109–1114 (2009)
Khalil, H.K.; Grizzle, J.W.: Nonlinear systems. Upper Saddle River. Prentice hall, NJ (2002)
Acknowledgements
This work was partially supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (61773212) and by International Science and Technology Cooperation Program of China (2015DFA01710)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
AM, O.A., Wang, H. & Tian, Y. Enhanced Model-Free Discrete-Time Adaptive Terminal Sliding-Mode Control for SOFC Power Plant with Input Constraints. Arab J Sci Eng 47, 2851–2864 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13369-021-05835-w
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13369-021-05835-w