Abstract
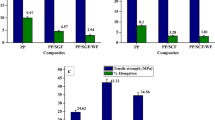
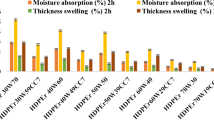
Wood polymer composites (WPCs) are considered as one of the highly competent classes of hybrid composite materials having potential applications in automotive, furniture, and construction industry. In this present study, fabrication of PP-g-MA compatibilized PP-wood flour composites was accomplished utilizing melt blending extrusion. The extruder was operated at a temperature profile of 180–210 °C. Wood flour, prior to its incorporation in polymeric material, was sieved to get fine wood flour particles. Compression-molded specimens of composites were characterized for their morphological attributes and for the determination of their chemical makeup, mechanical features, and thermal stability. FTIR analysis determined the chemical makeup of WPCs. Thermogravimetric analysis revealed the thermal stability of composites at temperature higher than 280 °C. Composites were rated as V2 grade according to their flammability performance. SEM analysis manifested the dispersed state of wood flour in the PP matrix. Mechanical properties manifested the increased stiffness of WPCs owing to increase in loading of wood flour which was associated with the restricted motion of polymer chains imparted by the wood flour particles. Surface topology study of in-hole drilled surface was also carried out by performing machining of WPCs for the analysis of surface roughness as a function of drill speed. Furthermore, the environmental sustainability of WPCs machining was demonstrated, and the reduction in waste generation through drilling of composites was observed.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Li, Y.-F.; Liu, Y.-X.; Wang, X.-M.; Wu, Q.-L.; Yu, H.-P.; Li, J.: Wood-polymer composites prepared by the in situ polymerization of monomers within wood. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 119, 3207–3216 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1002/app.32837
Ge, S. bo, Gu, H.P., Ma, J. jiao, Yang, H.Q., Jiang, S. cheng, Liu, Z., Peng, W. xi: Potential use of different kinds of carbon in production of decayed wood plastic composite. Arab. J. Chem. 11, 838–843 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.arabjc.2017.12.026
Kohl, D.; Link, P.; Böhm, S.: Wood as a technical material for structural vehicle components. Procedia CIRP. 40, 557–561 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.procir.2016.01.133
Abid, U.; Gill, Y.Q.; Irfan, M.S.; Umer, R.; Saeed, F.: Potential applications of polycarbohydrates, lignin, proteins, polyacids, and other renewable materials for the formulation of green elastomers. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 181, 1–29 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2021.03.057
Adhikary, K.B.; Pang, S.; Staiger, M.P.: Dimensional stability and mechanical behaviour of wood-plastic composites based on recycled and virgin high-density polyethylene (HDPE). Compos. Part B Eng. 39, 807–815 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.compositesb.2007.10.005
Nyemba, W.R., Hondo, A., Mbohwa, C., Madiye, L.: Unlocking economic value and sustainable furniture manufacturing through recycling and reuse of sawdust. In: Procedia Manufacturing. pp. 510–517. Elsevier B.V. (2018)
Khan, M.Z.R., Srivastava, S.K., Gupta, M.K.: A state-of-the-art review on particulate wood polymer composites: Processing, properties and applications, (2020)
Ashori, A.; Matini Behzad, H.; Tarmian, A.: Effects of chemical preservative treatments on durability of wood flour/HDPE composites. Compos. Part B Eng. 47, 308–313 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.compositesb.2012.11.022
Kazemi Najafi, S.: Use of recycled plastics in wood plastic composites - a review. Waste Manag. 33, 1898–1905 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.wasman.2013.05.017
Gill, Y.Q.; Song, M.; Abid, U.: Permeation characterization and modelling of polyethylene/clay nanocomposites for packaging. Polym. Bull. 77, 3749–3765 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00289-019-02930-9
Gill, Y.Q.; Abid, U.; Song, M.: High performance Nylon12/clay nanocomposites for potential packaging applications. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 137, 49247 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1002/app.49247
Chan, C.; Vandi, L.-J.; Pratt, S.; Halley, P.; Richardson, D.; Werker, A.; Laycock, B.: Composites of wood and biodegradable thermoplastics: a review. Polym. Rev. (2017). https://doi.org/10.1080/15583724.2017.1380039
Kamdem, D.P., Jiang, H., Cui, W., Freed, J., Matuana, L.M.: Properties of wood plastic composites made of recycled HDPE and wood flour from CCA-treated wood removed from service. In: Composites Part A: Applied Science and Manufacturing. pp. 347–355. Elsevier (2004)
Liu, C., Feng, Y.: Low-carbon economy: Theoretical study and development path choice in China. In: Energy Procedia. pp. 487–493. Elsevier Ltd (2011)
Teuber, L.; Osburg, V.S.; Toporowski, W.; Militz, H.; Krause, A.: Wood polymer composites and their contribution to cascading utilisation. J. Clean. Prod. 110, 9–15 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclepro.2015.04.009
Turku, I.; Kärki, T.; Puurtinen, A.: Durability of wood plastic composites manufactured from recycled plastic. Heliyon. (2018). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.heliyon.2018.e00559
Hutyrova, Z., Zajac, J., Mital, D., Botko, F., Harnicarova, M., Valícek, J.: Wood filled plastics – machining and surface quality. In: 2nd International Electronic Conference on Materials. pp. 1–9. MDPI (2016)
Hutyrová, Z., Zajac, J., Michalik, P., Mita̘, D., Duplák, J., Gajdoš, S.: Study of surface roughness of machined polymer composite material. Int. J. Polym. Sci. 2015, (2015). https://doi.org/10.1155/2015/303517
Gill, Y.Q.; Ehsan, H.; Irfan, M.S.; Saeed, F.; Shakoor, A.: Synergistic augmentation of polypropylene composites by hybrid morphology polyaniline particles for antistatic packaging applications. Mater. Res. Express. 7, 15331 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1088/2053-1591/ab61b5
Mamoor, G.M., Irfan, M.S., Gill, Y.Q., Qaiser, A.A., Saeed, F.: Effect of recycled polypropylene on the mechanical and rheological properties of polypropylene-nbr thermoplastic vulcanisates. Prog. Rubber, Plast. Recycl. Technol. 28, 189–200 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1177/147776061202800404
Rane, A.V., Kanny, K., Abitha, V.K., Thomas, S.: Chapter 5 - Methods for synthesis of nanoparticles and fabrication of nanocomposites. In: Mohan Bhagyaraj, S., Oluwafemi, O.S., Kalarikkal, N., and Thomas, S.B.T.-S. of I.N. (eds.) Micro and Nano Technologies. pp. 121–139. Woodhead Publishing (2018)
Guo, Y., Zhu, S., Chen, Y., Li, D.: Thermal properties of wood-plastic composites with different compositions. Materials (Basel). 16, (2019). https://doi.org/10.3390/ma12060881
Kaymakci, A.; Gulec, T.; Hosseinihashemi, S.K.; Ayrilmis, N.: Physical, mechanical and thermal properties of wood/ zeolite/plastic hybrid composites. Maderas Cienc. y Tecnol. 19, 339–348 (2017). https://doi.org/10.4067/S0718-221X2017005000029
Chun, S.J.; Lee, S.Y.: Thermal stability of polypropylene-based wood plastic composites by the addition of ammonium polyphosphate. J. Korean Wood Sci. Technol. 42, 682–690 (2014). https://doi.org/10.5658/WOOD.2014.42.6.682
Adebayo, G.O.; Hassan, A.; Yahya, R.; Sarih, N.M.; Bello, K.A.; Ekebafe, L.: Impact and thermal analysis of heat-treated and untreated mangrove wood/high-density polyethylene composites. Polym. Bull. 77, 3813–3829 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00289-019-02943-4
Kaboorani, A.: Thermal properties of composites made of heat-treated wood and polypropylene. J. Compos. Mater. 43, 2599–2607 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1177/0021998309345291
Gomes, V.N.C.; Carvalho, A.G.; Furukava, M.; Medeiros, E.S.; Colombo, C.R.; Melo, T.J.A.; Araújo, E.M.; Morais, D.D.S.; Ueki, M.M.; Paskocimas, C.A.; Santos, A.S.F.: Characterization of wood plastic composite based on HDPE and cashew nutshells processed in a thermokinetic mixer. Polym. Compos. 39, 2662–2673 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1002/pc.24257
Wang, Y.; Jow, J.; Su, K.; Zhang, J.: Dripping behavior of burning polymers under UL94 vertical test conditions. J. Fire Sci. 30, 477–501 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1177/0734904112446125
Umemura, T., Arao, Y., Nakamura, S., Tomita, Y., Tanaka, T.: Synergy effects of wood flour and fire retardants in flammability of wood-plastic composites. In: Energy Procedia. pp. 48–56. Elsevier Ltd (2014)
Yaşar, N.; Boy, M.; Günay, M.: The effect of drilling parameters for surface roughness in drilling of AA7075 alloy. MATEC Web Conf. 112, 01018 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1051/matecconf/201711201018
Wang, C.-Y.; Chen, Y.-H.; An, Q.-L.; Cai, X.-J.; Ming, W.-W.; Chen, M.: Drilling temperature and hole quality in drilling of CFRP/aluminum stacks using diamond coated drill. Int. J. Precis. Eng. Manuf. 16, 1689–1697 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12541-015-0222-y
Shetty, D., Shetty, N., Rajat, A., Shetty, G., Patil, P.: Characterization of machining parameters on thrust force and surface roughness in drilling of 40–60 Wt. % BD CFRP composite. Int. J. Appl. Eng. Res. 12, 5570–5577 (2017)
Acknowledgements
The authors gratefully acknowledge the support provided by Department of Polymer and Process Engineering (PPE), University of Engineering and Technology Lahore. Dr. Yasir Qayyum Gill also wants to thank Mr. Umer Butt and Mr. Nizam Abbas for their help with the experimentation.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Gill, Y.Q., Abid, U., Irfan, M.S. et al. Fabrication, Characterization, and Machining of Polypropylene/Wood Flour Composites. Arab J Sci Eng 47, 5973–5983 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13369-021-05768-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13369-021-05768-4