Abstract
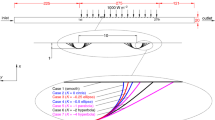
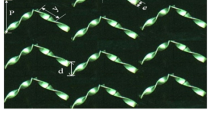
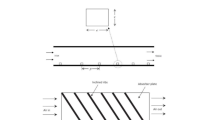
First and second laws of thermodynamics are well-established benchmarks to assess a thermal system. The literature revealed that efficiencies of a solar air heater are still low because the transport properties and heat transfer coefficient of the air are not superior. In the previous study, the heat and fluid flow characteristics and thermohydraulic performance of the solar air heater roughened conic-curve profile ribs were numerically examined. In the present extended work, the thermal efficiency, effective efficiency, and exergy efficiency were analytically evaluated. The entropy generation in the vicinity of the rib and the Bejan number along the length of the absorber plate were numerically analysed. These considerations aimed to provide a comprehensive evaluation and subsequent minimization of entropy generation. The impacts of the conic constant and Reynolds number on the above parameters were considered. The results indicated that decreasing the conic constant induced an increase in all efficiencies and a decrease in the entropy generation number. The maximum effective efficiency of 0.6719 occurred at a Reynolds number of 20,122, whereas the exergy efficiency of 0.01527 was obtained at a Reynolds number of 2786. The highest entropy generation due to heat transfer was found at the upstream and downstream corners of a rib and at the position just behind the detachment point. The largest entropy generation due to viscous dissipation was identified at the position in front of the rib tip. The entropy generation due to heat transfer was much higher than the entropy generation due to viscous dissipation.












Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- A c :
-
Area of the absorber plate (m2)
- Be:
-
Bejan number
- C j :
-
Thermal energy conversion factor
- c p :
-
Air specific heat at a constant pressure (J kg−1 K−1)
- D h :
-
Hydraulic diameter (m)
- f :
-
Friction factor
- F p :
-
Collector efficiency factor
- F R :
-
Heat removal factor
- h :
-
Convective heat transfer coefficient (W m−2 K−1)
- h w :
-
Convective heat transfer coefficient due to wind (W m−2 K−1)
- I :
-
Solar radiation (W m−2)
- K :
-
Conic constant
- k :
-
Thermal conductivity of the air (W m−1 K−1)
- k eff :
-
Effective thermal conductivity of the air (W m−1 K−1)
- k i :
-
Thermal conductivity of the insulation (W m−1 K−1)
- L :
-
Length of the collector (m)
- L i :
-
Thickness of the insulation (m)
- M :
-
Mass flow rate number
- \( \dot{m} \) :
-
Air mass flow rate (kg s−1)
- N :
-
Number of glass covers (–)
- N s :
-
Entropy generation number
- Nu:
-
Nusselt number
- p :
-
Pressure (Pa)
- P m :
-
Pumping power (W)
- \( \dot{Q}_{\text{u}} \) :
-
Useful heat gain (W)
- Re:
-
Reynolds number
- \( \dot{S}_{\text{t}}^{{{\prime \prime \prime }}} \) :
-
Entropy generation due to heat transfer (W m−3 K−1)
- \( \dot{S}_{\text{v}}^{{{\prime \prime \prime }}} \) :
-
Entropy generation due to viscous dissipation (W m−3 K−1)
- T a :
-
Ambient temperature (K)
- T ap :
-
Temperature of the absorber plate (K)
- T f :
-
Average air temperature (K)
- T i :
-
Air inlet temperature (K)
- T o :
-
Air outlet temperature (K)
- T sun :
-
Sun temperature (K)
- u :
-
Horizontal velocity component (m s−1)
- U b :
-
Bottom loss coefficient (W m−2 K−1)
- U e :
-
Edge loss coefficient (W m−2 K−1)
- U L :
-
Total loss coefficient (W m−2 K−1)
- U t :
-
Top loss coefficient (W m−2 K−1)
- V :
-
Air velocity (m s−1)
- v :
-
Vertical velocity component (m s−1)
- V w :
-
Wind velocity (m s−1)
- W :
-
Width of the collector (m)
- Z :
-
Depth of the collector (m)
- \( \beta_{\text{t}} \) :
-
Tilt angle of the collector (°)
- \( \varepsilon_{\text{ap}} \) :
-
Emissivity of the absorber plate
- \( \varepsilon_{\text{g}} \) :
-
Emissivity of the glass cover
- \( \eta_{\text{I}} \) :
-
Thermal efficiency
- \( \eta_{\text{II}} \) :
-
Exergetic efficiency
- \( \eta_{\text{Eff}} \) :
-
Thermo-hydraulic efficiency
- \( \mu \) :
-
Air dynamic viscosity (kg m−1 s−1)
- \( \mu_{\text{eff}} \) :
-
Air effective dynamic viscosity (kg m−1 s−1)
- \( \rho \) :
-
Air density (kg m−3)
- \( \sigma \) :
-
Stefan’s constant
- \( \tau \alpha \) :
-
Effective transmittance–absorptance product
- \( \Delta \) :
-
Difference
References
Joudi, K.A.; Farhan, A.A.: Greenhouse heating by solar air heaters on the roof. Renew. Energy 72, 406–414 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.renene.2014.07.025
Nguyen, M.P.; Ngo, T.T.; Le, T.D.: Experimental and numerical investigation of transport phenomena and kinetics for convective shrimp drying. Case Stud. Therm. Eng. 14, 100465 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.csite.2019.100465
Öztürk, H.H.; Demirel, Y.: Exergy-based performance analysis of packed-bed solar air heaters. Int. J. Energy Res. 28(5), 423–432 (2004). https://doi.org/10.1002/er.974
Gupta, D.; Solanki, S.C.; Saini, J.S.: Heat and fluid flow in rectangular solar air heater ducts having transverse rib roughness on absorber plates. Sol. Energy 51(1), 31–37 (1993). https://doi.org/10.1016/0038-092x(93)90039-q
Karwa, R.; Solanki, S.C.; Saini, J.S.: Heat transfer coefficient and friction factor correlations for the transitional flow regime in rib-roughened rectangular ducts. Int. J. Heat Mass Transf. 42(9), 1597–1615 (1999). https://doi.org/10.1016/s0017-9310(98)00252-x
Karwa, R.: Experimental studies of augmented heat transfer and friction in asymmetrically heated rectangular ducts with ribs on the heated wall in transverse, inclined, v-continuous and v-discrete pattern. Int. Commun. Heat Mass Transf. 30(2), 241–250 (2003). https://doi.org/10.1016/s0735-1933(03)00035-6
Ahn, S.W.: The effects of roughness types on friction factors and heat transfer in roughened rectangular duct. Int. Commun. Heat Mass Transf. 28(7), 933–942 (2001). https://doi.org/10.1016/s0735-1933(01)00297-4
Wang, L.; Sundén, B.: Experimental investigation of local heat transfer in a square duct with various-shaped ribs. Heat Mass Transf. 43(8), 759–766 (2006). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00231-006-0190-y
Karmare, S.V.; Tikekar, A.N.: Heat transfer and friction factor correlation for artificially roughened duct with metal grit ribs. Int. J. Heat Mass Transf. 50(21–22), 4342–4351 (2007). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijheatmasstransfer.2007.01.065
Lanjewar, A.; Bhagoria, J.L.; Sarviya, R.M.: Experimental study of augmented heat transfer and friction in solar air heater with different orientations of W-Rib roughness. Exp. Therm. Fluid Sci. 35(6), 986–995 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.expthermflusci.2011.01.019
Kumar, K.; Prajapati, D.R.; Samir, S.: Heat transfer and friction factor correlations development for solar air heater duct artificially roughened with “S” shape ribs. Exp. Therm. Fluid Sci. 82, 249–261 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.expthermflusci.2016.11.012
Hans, V.S.; Saini, R.P.; Saini, J.S.: Heat transfer and friction factor correlations for a solar air heater duct roughened artificially with multiple v-ribs. Sol. Energy 84(6), 898–911 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.solener.2010.02.004
Kabeel, A.E.; Khalil, A.; Shalaby, S.M.; Zayed, M.E.: Investigation of the thermal performances of flat, finned, and v-corrugated plate solar air heaters. J. Sol. Energy Eng. (2016). https://doi.org/10.1115/1.4034027
Phu, N.M.; Tuyen, V.; Ngo, T.T.: Augmented heat transfer and friction investigations in solar air heater artificially roughened with metal shavings. J. Mech. Sci. Technol. 33(7), 3521–3529 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12206-019-0646-x
Hans, V.S.; Gill, R.S.; Singh, S.: Heat transfer and friction factor correlations for a solar air heater duct roughened artificially with broken arc ribs. Exp. Therm. Fluid Sci. 80, 77–89 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.expthermflusci.2016.07.022
Kumar, S.; Saini, R.P.: CFD based performance analysis of a solar air heater duct provided with artificial roughness. Renew. Energy 34(5), 1285–1291 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.renene.2008.09.015
Yadav, A.S.; Bhagoria, J.L.: Heat transfer and fluid flow analysis of solar air heater: a review of CFD approach. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 23, 60–79 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.rser.2013.02.035
Sunil Chamoli, N.S.T.: Numerical based heat transfer and friction factor correlations of rectangular ducts roughened with transverse perforated baffles. Walailak J. Sci. Technol 2, 11 (2014). https://doi.org/10.14456/WJST.2014.33
Zheng, S.; Ji, T.; Xie, G.; Sundén, B.: On the improvement of the poor heat transfer lee-side regions of square cross-section ribbed channels. Numer. Heat Transf. Part A Appl. 66(9), 963–989 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1080/10407782.2014.894396
Singh, S.; Singh, B.; Hans, V.S.; Gill, R.S.: CFD (computational fluid dynamics) investigation on Nusselt number and friction factor of solar air heater duct roughened with non-uniform cross-section transverse rib. Energy 84, 509–517 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.energy.2015.03.015
Chaube, A.; Sahoo, P.K.; Solanki, S.C.: Analysis of heat transfer augmentation and flow characteristics due to rib roughness over absorber plate of a solar air heater. Renew. Energy 31(3), 317–331 (2006). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.renene.2005.01.012
Singh, I.; Singh, S.: CFD analysis of solar air heater duct having square wave profiled transverse ribs as roughness elements. Sol. Energy 162, 442–453 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.solener.2018.01.019
Bezbaruah, P.J.; Das, R.S.; Sarkar, B.K.: Thermo-hydraulic performance augmentation of solar air duct using modified forms of conical vortex generators. Heat Mass Transf. 55(5), 1387–1403 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00231-018-2521-1
Alam, T.; Kim, M.-H.: Heat transfer enhancement in solar air heater duct with conical protrusion roughness ribs. Appl. Therm. Eng. 126, 458–469 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.applthermaleng.2017.07.181
Singh, S.: Performance evaluation of a novel solar air heater with arched absorber plate. Renew. Energy 114, 879–886 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.renene.2017.07.109
Kumar, R.; Goel, V.; Kumar, A.; Khurana, S.; Singh, P.; Bopche, S.B.: Numerical investigation of heat transfer and friction factor in ribbed triangular duct solar air heater using Computational fluid dynamics (CFD). J. Mech. Sci. Technol. 32(1), 399–404 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12206-017-1240-8
Yadav, A.S.; Bhagoria, J.L.: A numerical investigation of turbulent flows through an artificially roughened solar air heater. Numer. Heat Transf. Part A Appl. 65(7), 679–698 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1080/10407782.2013.846187
Kumar, R.; Geol, V.; Kumar, A.: A parametric study of the 2D model of solar air heater with elliptical rib roughness using CFD. J. Mech. Sci. Technol. 31(2), 959–964 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12206-017-0148-7
Thakur, D.S.; Khan, M.K.; Pathak, M.: Performance evaluation of solar air heater with novel hyperbolic rib geometry. Renew. Energy 105, 786–797 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.renene.2016.12.092
Rashidi, S.; Javadi, P.; Esfahani, J.A.: Second law of thermodynamics analysis for nanofluid turbulent flow inside a solar heater with the ribbed absorber plate. J. Therm. Anal. Calorim. 135(1), 551–563 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10973-018-7164-4
Sahu, M.K.; Prasad, R.K.: Exergy based performance evaluation of solar air heater with arc-shaped wire roughened absorber plate. Renew. Energy 96, 233–243 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.renene.2016.04.083
Matheswaran, M.M.; Arjunan, T.V.; Somasundaram, D.: Analytical investigation of solar air heater with jet impingement using energy and exergy analysis. Sol. Energy 161, 25–37 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.solener.2017.12.036
Kumar, A.; Layek, A.: Energetic and exergetic performance evaluation of solar air heater with twisted rib roughness on absorber plate. J. Clean. Prod. 232, 617–628 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclepro.2019.05.363
Matheswaran, M.M.; Arjunan, T.V.; Somasundaram, D.: Analytical investigation of exergetic performance on jet impingement solar air heater with multiple arc protrusion obstacles. J. Therm. Anal. Calorim. 137(1), 253–266 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10973-018-7926-z
Matheswaran, M.M.; Arjunan, T.V.; Somasundaram, D.: Energetic, exergetic and enviro-economic analysis of parallel pass jet plate solar air heater with artificial roughness. J. Therm. Anal. Calorim. 136(1), 5–19 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10973-018-7727-4
Velmurugan, P.; Kalaivanan, R.: Energy and exergy analysis of solar air heaters with varied geometries. Arab. J. Sci. Eng. 40(4), 1173–1186 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13369-015-1612-2
Yadav, S.; Kaushal, M.: Exergetic performance evaluation of solar air heater having arc shape oriented protrusions as roughness element. Sol. Energy 105, 181–189 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.solener.2014.04.001
Chamoli, S.; Thakur, N.S.: Exergetic performance evaluation of solar air heater having V-down perforated baffles on the absorber plate. J. Therm. Anal. Calorim. 117(2), 909–923 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10973-014-3765-8
Singh, S.; Chander, S.; Saini, J.S.: Exergy based analysis of solar air heater having discrete V-down rib roughness on absorber plate. Energy 37(1), 749–758 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.energy.2011.09.040
Hedayatizadeh, M.; Ajabshirchi, Y.; Sarhaddi, F.; Farahat, S.; Safavinejad, A.; Chaji, H.: Analysis of exergy and parametric study of a v-corrugated solar air heater. Heat Mass Transf. 48(7), 1089–1101 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00231-011-0957-7
Gholami, A.; Ajabshirchi, Y.; Ranjbar, S.F.: Thermo-economic optimization of solar air heaters with arcuate-shaped obstacles. J. Therm. Anal. Calorim. 138(2), 1395–1403 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10973-019-08273-x
Phu, N.M.; Bao, T.T.; Hung, H.N.; Tu, N.T.; Van Hap, N.: Analytical predictions of exergoeconomic performance of a solar air heater with surface roughness of metal waste. J. Therm. Anal. Calorim. (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10973-020-09787-5
Demirel, Y.; Kahraman, R.: Thermodynamic analysis of convective heat transfer in an annular packed bed. Int. J. Heat Fluid Flow 21(4), 442–448 (2000). https://doi.org/10.1016/s0142-727x(00)00032-1
Ngo, T.T.; Phu, N.M.: Computational fluid dynamics analysis of the heat transfer and pressure drop of solar air heater with conic-curve profile ribs. J. Therm. Anal. Calorim. 139(5), 3235–3246 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10973-019-08709-4
Kumar, A.; Layek, A.: Nusselt number and friction factor correlation of solar air heater having twisted-rib roughness on absorber plate. Renew. Energy 130, 687–699 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.renene.2018.06.076
Nadda, R.; Kumar, A.; Maithani, R.: Developing heat transfer and friction loss in an impingement jets solar air heater with multiple arc protrusion obstacles. Sol. Energy 158, 117–131 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.solener.2017.09.042
Yadav, S.; Kaushal, M.: Nusselt number and friction factor correlations for solar air heater duct having protrusions as roughness elements on absorber plate. Exp. Therm. Fluid Sci. 44, 34–41 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.expthermflusci.2012.05.011
Singh, S.; Chander, S.; Saini, J.S.: Heat transfer and friction factor correlations of solar air heater ducts artificially roughened with discrete V-down ribs. Energy 36(8), 5053–5064 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.energy.2011.05.052
McAdams, W.H.: Heat transmission, 3rd edn. McGraw-Hill, New York (1954)
Duffie, John A.; Beckman, William A.: Solar engineering of thermal processes, 4th edn. Wiley, New York (2013)
Klein, S.A.: Engineering equation solver (EES), Professional V9.457-3D, F-Chart Software (2013)
Singh Bisht, V.; Kumar Patil, A.; Gupta, A.: Review and performance evaluation of roughened solar air heaters. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 81, 954–977 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.rser.2017.08.036
Animasaun, I.L.; Ibraheem, R.O.; Mahanthesh, B.; Babatunde, H.A.: A meta-analysis on the effects of haphazard motion of tiny/nano-sized particles on the dynamics and other physical properties of some fluids. Chin. J. Phys. 60, 676–687 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cjph.2019.06.007
Koriko, O.K.; Adegbie, K.S.; Animasaun, I.L.; Ijirimoye, A.F.: Comparative analysis between three-dimensional flow of water conveying alumina nanoparticles and water conveying alumina–iron(iii) oxide nanoparticles in the presence of lorentz force. Arab. J. Sci. Eng. 45(1), 455–464 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13369-019-04223-9
Chu, S.X.; Liu, L.H.: Entropy generation analysis of two-dimensional high-temperature confined jet. Int. J. Therm. Sci. 48(5), 998–1006 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijthermalsci.2008.07.001
Meibodi, S.S.; Kianifar, A.; Mahian, O.; Wongwises, S.: Second law analysis of a nanofluid-based solar collector using experimental data. J. Therm. Anal. Calorim. 126(2), 617–625 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10973-016-5522-7
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Phu, N.M., Van Hap, N. Performance Evaluation of a Solar Air Heater Roughened with Conic-Curve Profile Ribs Based on Efficiencies and Entropy Generation. Arab J Sci Eng 45, 9023–9035 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13369-020-04676-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13369-020-04676-3