Abstract
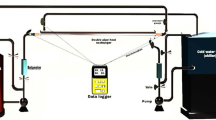
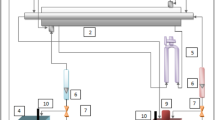
The influence of adding fins of copper foam on the characteristics of heat transfer in a double-pipe heat exchanger is investigated experimentally. The test rig consists of two concentric pipes (copper and Perspex) to form the required double-pipe heat exchanger. The metal foam fins of 40 PPI are made from copper and set at 30° angle with the tube entrance and are distributed in sections inside the annular gap around the inner copper tube to guide the fluid flow and to disturb its structure inside the annular gap. The Reynolds number range for air is from 616 to 2343, with a constant water volume flow rate (2 lpm) in these experiments. The inlet water temperature is controlled at three values (80 °C, 85 °C, and 90 °C). Both parallel and counterflows are examined in this study. The comparison is made between the two cases of with and without insertion of copper foam fins and between parallel and counterflow mode. Results show that the average heat transfer coefficient and the average Nusselt number are increased as the Reynolds number increased, and their largest values are obtained in case of copper foam fins insertion and for counterflow mode. The important finding is no significant pressure drop is found with the enhancement of heat transfer throughout the annular gap of heat exchanger. Results also showed that the effectiveness values are doubled in case of insertion of the copper foam fins. The counterflow pattern is the most efficient flow pattern than the parallel flow.

























Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- A i :
-
Surface area of inner copper pipe, m2
- A o :
-
Surface area of the annular gap, m2
- C p :
-
Specific heat at constant pressure, kJ/kg
- D i :
-
Diameter of inner copper pipe, m
- D h :
-
Hydraulic diameter of annular, m
- \( h_{\text{o}} \) :
-
Convection heat transfer coefficient of cold fluid (air), W/m2 K
- \( h_{\text{i}} \) :
-
Convection heat transfer coefficient of hot fluid (water), W/m2 K
- k :
-
Thermal conductivity of fluid, W/m K
- L :
-
Pipe length, m
- Nu:
-
Nusselt number
- \( {\dot{\text{m}}} \) :
-
Fluid mass flow rate, kg/s
- Q :
-
Thermal power, W
- T :
-
Temperature, °C
- \( \text{Re} \) :
-
Reynolds number
- U i :
-
Overall heat transfer coefficient W/m2 K
- UR:
-
Total error
- \( \varepsilon \) :
-
Effectiveness
- \( {\text{o}} \) :
-
Outlet
- i:
-
Inner
- \( {\text{ave}} \) :
-
Average
- \( {\text{w}} \) :
-
Water
- a:
-
Air
- LPM:
-
Liter per minute
- PPI:
-
Pores per inch
- WOCF:
-
Without copper foam
- WICF:
-
With copper foam
References
Lefebvre, L.P.; Banhart, J.; Dunand, D.C.: Porous metals and metallic foams. Curr Status Recent Dev Adv Eng Mater 10(9), 775–787 (2008)
Alhusseny, A.; Turan, A.; Nasser, A.: Rotating metal foam structure for performance enhancement of double pipe heat exchanger. Int J Heat Mass Transf 105, 124–139 (2017)
Mohammed, A.N.; Ali, M.A.: Effect of metal foam insertion on thermal performance of flat-plate water solar collector under Iraqi climate conditions. Arab J Sci Eng 42(11), 4863–4884 (2017)
Delavar, M.A.; Mohammadvali, F.: Numerical simulation of force convection in a channel with porous part. Int J Therm Environ Eng 6, 7–14 (2013)
Guerroudj, N.; Kahalerras, H.: Mixed convection in an inclined channel with heated porous blocks. Int J Numerical Methods Heat Fluid Flow 22(7), 839–861 (2012)
Hajeej, A. H.: Mixed convection heat transfer enhancement in a channel by using metal foam blocks. M.Sc. Thesis, University of Baghdad (2016).
Hossein A.; Mohammad R.S.; Mohammad R.T.: Optimal distribution of metal foam inserts in a double-pipe heat exchanger. Int. J. Numer. Methods Heat Fluid Flow 0961-5539 (2019).
Ko, K.H.; Anand, N.K.: Use of porous baffles to enhance heat transfer in a rectangular channel. Int. J. Heat Mass Transf. 46, 4191–4199 (2003)
Li, H.Y.; Leong, K.C.; Jin, L.W.; Chai, J.C.: Analysis of fluid flow and heat transfer in a channel with staggered porous blocks. Int. J. Therm. Sci. 49, 950–962 (2010)
Targui, N.; Kahalerras, H.: Analysis of fluid flow and heat transfer in a double pipe heat exchanger with porous structures. Energy Convers. Manag. 49, 3217–3229 (2008)
Pavel, B.I.; Mohamad, A.A.: An experimental and numerical study on heat transfer enhancement for gas heat exchangers fitted with porous media. Int. J. Heat Mass Transf. 47, 4939–4952 (2004)
Xu, H.J.; Qu, Z.G.; Tao, W.Q.: Numerical investigation on self-coupling heat transfer in a counter-flow double-pipe heat exchanger filled with metallic foams. Appl. Therm. Eng. 66, 43–54 (2014)
Yakar, G.; Karabacak, R.: Effects of different fin spacing on the Nusselt number and reynolds number in perforated finned heat exchangers. Heat Transf. Eng. 32, 399–407 (2011)
Zehforoosh, A.; Hossainpour, S.: Numerical investigation of pressure drop reduction without surrendering heat transfer enhancement in partially porous channel. Int. J. Therm. Sci. 49, 1649–1662 (2010)
Salman, A.N.J.; Kamangar, S.; Badruddin, I.A.; Al-Rashed, A.A.A.A.; Quadir, G.A.; Khaleed, H.M.T.; Khan, T.M.Y.: Conjugate heat transfer in porous annulus. J. Porous Media 17, 1109–1119 (2014)
Sheikholeslami, M.; Gorji-Bandpy, M.; Ganji, D.D.: Fluid flow and heat transfer in an air-to-water double-pipe heat exchanger. Eur. Phys. J. Plus 130, 225 (2015)
Jaeger, P.D.; T’Joen, C.; Huisseune, H.; Ameel, B.; Schampheleire, S.D.; Paepe, M.D.: Assessing the influence of four bonding methods on the thermal contact resistance of open-cell aluminum foam. Int. J. Heat Mass Transf. 55, 6200–6210 (2012)
Holman, J.P.: Experimental method for engineers. McGraw-Hill, Tokyo (1979)
Sheikholeslami, M.; Gorji-Bandpy, M.; Ganji, D.D.: Experimental study on turbulent flow and heat transfer in an air to water heat exchanger using perforated circular ring. Exp. Therm. Fluid Sci. 70, 185–195 (2016)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Hamzah, J.A., Nima, M.A. Experimental Study of Heat Transfer Enhancement in Double-Pipe Heat Exchanger Integrated with Metal Foam Fins. Arab J Sci Eng 45, 5153–5167 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13369-020-04371-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13369-020-04371-3