Abstract
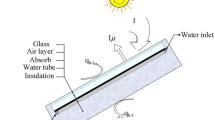
The solar collector’s efficiency is directly depended upon the solar radiation intensity falling on its surface. In order to increase the solar concentration over the collector, side reflectors are introduced which will concentrate both diffuse and direct radiations from the sun toward the collector surface. Therefore, in this study the influence of side (left and right) reflectors on efficiency improvement of the flat plate solar collector (FPSC) was analyzed. For determining the optimum tilt angles of side reflector and collector, a simulation model was developed by using TRNSYS software. The results obtained from simulation were validated with the experimental results for whole year during the daytime of semiarid Asir region of Saudi Arabia. Both simulation and experimental results indicate that optimal left side reflector angle is lowest in winter with the value of 38° and highest in summer with the value of 68°, while the optimal angle of right side reflector is lowest in summer with the value of 43° and highest in winter with the value of 74.5°. The thermal efficiency of FPSC has been improved significantly by adding side reflectors. The average thermal efficiency of FPSC without reflector was 46% which was increased to 58% by adding side reflectors. The addition of side reflectors increases the concentration of solar radiation falling on the collector surface and thus increases the output temperature of water by 12 °C as compared to input water temperature. Thus, the effective size of the system was reduced by adding side reflectors as thermal efficiency was enhanced which implies less space requirement for heating an appropriate quantity of water.

















Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- α :
-
Angle of solar altitude (°)
- β :
-
Tilt angle of collector (°)
- γ 1 :
-
Angle between the horizontal plane and left side reflector (°)
- γ 2 :
-
Angle between the horizontal plane and right side reflector (°)
- δ :
-
Angle of sun declination (°)
- η coll :
-
Solar collector thermal efficiency
- ω :
-
Sun hour angle (°)
- ϕ :
-
The solar collector latitude (°)
- \( \varepsilon_{\text{g}} ,\varepsilon_{\text{p}} \) :
-
Emissivity of plate glass and absorber plate
- ρ Αlum :
-
Aluminum sheet reflectance
- ρ g :
-
Ground reflectance
- σ 1 :
-
Angle of incident from the left side reflector (°)
- σ 2 :
-
Angle of incident from the right side reflector (°)
- θ :
-
South facing solar zenith angle (°)
- AM:
-
Optical air mass
- D :
-
Daylight saving time (h)
- d :
-
Performance coefficient of collector
- e :
-
Root mean square deviation (°)
- EOT:
-
Equation of time
- G dif :
-
Diffuse solar radiation on horizontal surface (W/m2)
- G 0 :
-
Solar constant (1366 W/m2)
- G dif_col :
-
Total diffuse solar radiation (W/m2)
- G dif_sky :
-
Sky-diffuse solar radiation (W/m2)
- G dir_col :
-
Direct solar radiation on collector surface (W/m2)
- G h :
-
Global solar radiation on horizontal surface (W/m2)
- G in :
-
Global solar incident radiation (W/m2)
- G sr1_incident :
-
Solar radiation incident on the left side reflector (W/m2)
- G sr2_incident :
-
Solar radiation incident on the right side reflector (W/m2)
- G gr_reflected :
-
Ground-reflected solar radiation (W/m2)
- G sr1_reflected :
-
Solar radiation reflected from the left side reflector reaches the collector surface (W/m2)
- G sr2_reflected :
-
Solar radiation reflected from the right side reflector reaches the collector surface (W/m2)
- G net_col :
-
Net incoming solar radiation on the collector surface without the additional solar input from reflected solar radiation from reflectors (W/m2)
- G tot_col :
-
Total solar radiation on the collector surface (W/m2)
- H :
-
Altitude above the sea level (m)
- I :
-
Intensity of solar radiation (W/m2)
- L long :
-
Longitude of the solar collector (°)
- L STM :
-
Local standard time meridian (°)
- L ST :
-
Local solar time (h)
- LT:
-
Local time (h)
- N :
-
Day number of the year
- r :
-
Correlation coefficient
- T in :
-
Temperature distribution inside the tank (°C)
- T a :
-
Ambient temperature (°C)
- T out :
-
Outlet fluid temperature (°C)
- T c :
-
Temperature of glass cover (°C)
- T sky :
-
Sky temperature (°C)
- T p :
-
Temperature of absorber plate (°C)
- \( \dot{m} \) :
-
Mass flow rate
- C p :
-
Specific heat capacity
- \( \dot{Q}_{\text{useful}} \) :
-
Heat gain useful
- F R :
-
Heat removal factor
- A p :
-
Absorber plate area
- F′:
-
Collector efficiency factor
- Φ :
-
Plate effectiveness
- U l :
-
Overall loss coefficient
- S :
-
Absorber plate radiation absorption per unit area
References
Wenceslas, K.Y.; Ghislain, T.: Experimental validation of exergy optimization of a flat-plate solar collector in a thermosyphon solar water heater. Arab. J. Sci. Eng. 44, 2535–2549 (2019)
ur Rehman, N.; Uzair, M.; Siddiqui, M.A.; Khamooshi, M.: Regression models and sensitivity analysis for the thermal performance of solar flat-plate collectors. Arab. J. Sci. Eng. 44, 1119–1127 (2019)
Zhou, L.; Li, Y.; Hu, E.; Qin, J.; Yang, Y.: Comparison in net solar efficiency between the use of concentrating and non-concentrating solar collectors in solar aided power generation systems. Appl. Therm. Eng. 75, 685–691 (2015)
Cau, G.; Cocco, D.; Tola, V.: Performance assessment of USC power plants integrated with CCS and concentrating solar collectors. Energy Convers. Manag. 88, 973–984 (2014)
Ahmad, G.E.; Hussein, H.M.S.: Comparative study of PV modules with and without a tilted plane reflector. Energy Convers. Manag. 42, 1327–1333 (2001)
Abd-ur-Rehman, H.M.; Al-Sulaiman, F.A.; Mehmood, A.; Shakir, S.; Umer, M.: The potential of energy savings and the prospects of cleaner energy production by solar energy integration in the residential buildings of Saudi Arabia. J. Clean. Prod. 183, 1122–1130 (2018)
Rehman, S.; Mohandes, M.: Estimation of diffuse fraction of global solar radiation using artificial neural networks. Energy Sources A Recover. Util. Environ. Eff. 31, 974–984 (2009)
Alwetaishi, M.; Balabel, A.: Numerical study of micro-climatically responsive school building design in Saudi Arabia. J. King Saud Univ. Eng. Sci. 31, 224–233 (2018)
Pucar, M.D.J.; Despic, A.R.: The enhancement of energy gain of solar collectors and photovoltaic panels by the reflection of solar beams. Energy 27, 205–223 (2002)
Hellstrom, B.; Adsten, M.; Nostell, P.; Karlsson, B.; Wackelgard, E.: The impact of optical and thermal properties on the performance of flat plate solar collectors. Renew. Energy 28, 331–344 (2003)
Kostić, L.T.; Pavlović, T.M.; Pavlović, Z.T.: Optimal design of orientation of PV/T collector with reflectors. Appl. Energy 87, 3023–3029 (2010)
Kostic, L.T.; Pavlovic, T.M.; Pavlovic, Z.T.: Influence of reflectance from flat aluminum concentrators on energy efficiency of PV/Thermal collector. Appl. Energy 87, 410–416 (2010)
Kumar, R.; Kaushik, S.C.; Garg, H.P.: Analytical study of collector solar-gain enhancement by multiple reflectors. Energy 20, 511–522 (1995)
Kostić, L.T.; Pavlović, Z.T.: Optimal position of flat plate reflectors of solar thermal collector. Energy Build. 45, 161–168 (2012)
Seitel, S.C.: Collector performance enhancement with flat reflectors. Sol. Energy 17, 291–295 (1975)
Chen, H.; Ji, J.; Pei, G.; Yang, J.; Zhang, Y.: Experimental and numerical comparative investigation on a concentrating photovoltaic system. J. Clean. Prod. 174, 1288–1298 (2018)
Tanaka, H.: Solar thermal collector augmented by flat plate booster reflector: optimum inclination of collector and reflector. Appl. Energy 88, 1395–1404 (2011)
Tanaka, H.: Theoretical analysis of solar thermal collector and flat plate bottom reflector with a gap between them. Energy Rep. 1, 80–88 (2015)
Pavlović, Z.T.; Kostić, L.T.: Variation of reflected radiation from all reflectors of a flat plate solar collector during a year. Energy 80, 75–84 (2015)
Bhowmik, H.; Amin, R.: Efficiency improvement of flat plate solar collector using reflector. Energy Rep. 3, 119–123 (2017)
Baccoli, R.; Frattolillo, A.; Mastino, C.; Curreli, S.; Ghiani, E.: A comprehensive optimization model for flat solar collector coupled with a flat booster bottom reflector based on an exact finite length simulation model. Energy Convers. Manag. 164, 482–507 (2018)
Duffie, J.A.; Beckman, W.A.: Solar Engineering of Thermal Processes, 4th edn. Wiley, New York (2013)
Tiwari, G.N.; Tiwari, A.; Shyam, : Handbook of Solar Energy. Springer, New York (2016)
Sivakumar, P.; Christraj, W.; Sridharan, M.; Jayamalathi, N.: Performance improvement study of solar. ARPN J. Eng. Appl. Sci. 7, 45–49 (2012)
Acknowledgements
The authors of the present work feel grateful and would like to thank King Khalid University, Abha, and Center of Research Excellence in Renewable Energy (CoRE-RE), King Fahd University of Petroleum and Minerals, Dhahran, Saudi Arabia, for providing facilities and supports in performing experiments.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Appendices
Appendix A
Time | T in | T out | T 3 | T 4 | T amp | I |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
8:30 | 31.9 | 43.5 | 34.8 | 33.7 | 17 | 230 |
9:00 | 34.5 | 47.3 | 33.1 | 35.1 | 17 | 305 |
9:30 | 36.5 | 50.1 | 32.1 | 36.1 | 18 | 370 |
10:00 | 38.1 | 54.6 | 33.6 | 37.5 | 18 | 397 |
10:30 | 40.5 | 59.4 | 34.8 | 38.4 | 18 | 479 |
11:00 | 42.1 | 65.3 | 35.1 | 39.4 | 19 | 535 |
11:30 | 43.7 | 67 | 36.9 | 40.8 | 19 | 606 |
12:00 | 44.7 | 68 | 37.8 | 42.7 | 19 | 708 |
12:30 | 45.8 | 70 | 38.7 | 43.1 | 20 | 788 |
13:00 | 46.3 | 72 | 39.4 | 44.5 | 20 | 805 |
13:30 | 47.9 | 70 | 40.5 | 41.8 | 21 | 847 |
14:00 | 48 | 68 | 41.5 | 43.8 | 21 | 793 |
14:30 | 44 | 55 | 42.6 | 41.5 | 21 | 787 |
15:00 | 42 | 50.6 | 43.1 | 41.3 | 20 | 732 |
15:30 | 40 | 48.2 | 52.6 | 40.8 | 20 | 645 |
16:30 | 38 | 46.3 | 50.7 | 39.2 | 19 | 585 |
17:00 | 37 | 44.5 | 41.8 | 37.5 | 19 | 483 |
Appendix B
See Table 4.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
El-Assal, B., Irshad, K. & Ali, A. Effect of Side Reflectors on the Performance of Flat Plate Solar Collector: A Case Study for Asir Region, Saudi Arabia. Arab J Sci Eng 45, 1035–1050 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13369-019-04221-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13369-019-04221-x