Abstract
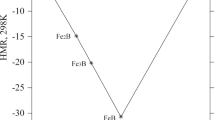
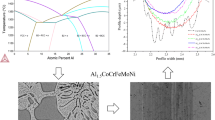
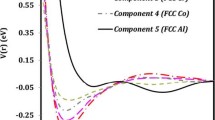
Microstructural formation mechanism of NiCoFeCuMn equiatomic high-entropy alloys has been discussed from a viewpoint of interaction energy. It is indicated that when the interaction energy (Iij) is higher than a threshold value (It), spinodal decomposition may occur, leading to segregation of similar atoms and formation of a phase independently. Segregation of similar atoms is prone to appear in the alloys containing Fe–Cu or Cu–Cr components. However, when it is Iij < It, heterogeneous atoms segregation may appear. Components like Mn–Ni, Mn–Cu and Mn–Co et al. in the NiCoFeCuMn alloy prone to segregate. For the equiatomic HEAs, interaction energy Iij can effectively reflect the formation mechanism of single-FCC crystal structure and is a principle criterion for material design.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Yeh, J.W.; Chen, S.K.; Lin, S.J.; Gan, J.Y.; Chin, T.S.; Shun, T.T.; Tsau, C.H.; Chang, S.Y.: Nanostructured high-entropy alloys with multiple principal elements: novel alloy design concepts and outcomes. Adv. Eng. Mater. 6, 299–303 (2004)
Li, W.; Liu, P.; Liaw, P.K.: Microstructures and properties of high-entropy alloy films and coatings: a review. Mater. Res. Lett. 6, 199–229 (2018)
Yeh, J.-W.; Lin, S.-J.: Breakthrough applications of high-entropy materials. J. Mater. Res. 33, 3129–3137 (2018)
Koch, C.C.: Nanocrystalline high-entropy alloys. J. Mater. Res. 32, 3435–3444 (2017)
Chou, H.P.; Chang, Y.S.; Chen, S.K.; Yeh, J.W.: Microstructure, thermophysical and electrical properties in AlxCoCrFeNi (0 ≤ x≤2) high-entropy alloys. Mater. Sci. Eng. B 163, 184–189 (2009)
Wang, X.; Zhang, Y.; Qiao, Y.; Chen, G.: Novel microstructure and properties of multicomponent CoCrCuFeNiTix alloys. Intermetallics 15, 357–362 (2007)
Hsu, C.Y.; Wang, W.R.; Tang, W.Y.; Chen, S.K.; Yeh, J.W.: Microstructure and mechanical properties of new AlCoxCrFeMo0.5Ni high-entropy alloys. Adv. Eng. Mater. 12, 44–49 (2010)
Sheng, G.; Liu, C.T.: Phase stability in high entropy alloys: formation of solid-solution phase or amorphous phase. Prog. Nat. Sci. Mater. Int. 21, 433–446 (2011)
Dong, Y.; Lu, Y.; Jiang, L.; Wang, T.; Li, T.: Effects of electro-negativity on the stability of topologically close-packed phase in high entropy alloys. Intermetallics 52, 105–109 (2014)
Poletti, M.; Battezzati, L.: Electronic and thermodynamic criteria for the occurrence of high entropy alloys in metallic systems. Acta Mater. 75, 297–306 (2014)
Zhang, Y.; Zhou, Y.J.: Solid solution formation criteria for high entropy alloys. Mater. Sci. Forum. Trans. Tech. Publ. 561, 1337–1339 (2007)
Zhang, Y.; Zhou, Y.J.; Lin, J.P.; Chen, G.L.; Liaw, P.K.: Solid-solution phase formation rules for multi-component alloys. Adv. Eng. Mater. 10, 534–538 (2008)
Ren, M.X.; Li, B.S.; Fu, H.Z.: Formation condition of solid solution type high-entropy alloy. T. Nonferr. Metal. Soc. 23, 991–995 (2013)
Otto, F.; Yang, Y.; Bei, H.; George, E.P.: Relative effects of enthalpy and entropy on the phase stability of equiatomic high-entropy alloys. Acta Mater. 61, 2628–2638 (2013)
Zhang, F.; Zhang, C.; Chen, S.; Zhu, J.; Cao, W.; Kattner, U.: An understanding of high entropy alloys from phase diagram calculations. Calphad 45, 1–10 (2014)
Senkov, O.; Miller, J.; Miracle, D.; Woodward, C.: Accelerated exploration of multi-principal element alloys with solid solution phases. Nat. Commun. 6, 6529 (2015)
Troparevsky, M.C.; Morris, J.R.; Kent, P.R.; Lupini, A.R.; Stocks, G.M.: Criteria for predicting the formation of single-phase high-entropy alloys. Phys. Rev. X 5, 011041 (2015)
Hao, S.M.: Material Thermodynamics. Chemical Industry Press, Bei Jing (2004)
Hillert, M.: Phase Equilibria, Phase Diagrams and Phase Transformations Their Thermodynamic Basics. Cambridge University Press, New York (2008)
Chen, M.R.; Lin, S.J.; Yeh, J.W.; Chuang, M.H.; Chen, S.K.; Huang, Y.S.: Effect of vanadium addition on the microstructure, hardness, and wear resistance of Al0.5CoCrCuFeNi high-entropy alloy. Metall. Mater. Trans. A 37, 1363–1369 (2006)
Huang, Y.S.; Chen, L.; Lui, H.W.; Cai, M.H.; Yeh, J.W.: Microstructure, hardness, resistivity and thermal stability of sputtered oxide films of AlCoCrCu05NiFe high-entropy alloy. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 457, 77–83 (2007)
Hsu, C.Y.; Juan, C.C.; Wang, W.R.; Sheu, T.S.; Yeh, J.W.; Chen, S.K.: On the superior hot hardness and softening resistance of AlCoCrxFeMo0.5Ni high-entropy alloys. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 528, 3581–3588 (2011)
Lin, C.M.; Tsai, H.L.: Evolution of microstructure, hardness, and corrosion properties of high-entropy Al0.5CoCrFeNi alloy. Intermetallics 19, 288–294 (2011)
Qiu, X.W.; Liu, C.G.: Microstructure and properties of Al2CrFeCoCuTiNix high-entropy alloys prepared by laser cladding. J. Alloy. Compd. 553, 216–220 (2013)
Qiu, X.W.; Zhang, Y.P.; He, L.; Liu, C.G.: Microstructure and corrosion resistance of AlCrFeCuCo high entropy alloy. J. Alloy. Compd. 549, 195–199 (2013)
Senkov, O.N.; Senkova, S.V.; Woodward, C.: Effect of aluminum on the microstructure and properties of two refractory high-entropy alloys. Acta Mater. 68, 214–228 (2014)
Senkov, O.; Wilks, G.; Miracle, D.; Chuang, C.; Liaw, P.: Refractory high-entropy alloys. Intermetallics 18, 1758–1765 (2010)
Juan, C.C.; Tsai, M.H.; Tsai, C.W.; Lin, C.M.; Wang, W.R.; Yang, C.C.; Chen, S.K.; Lin, S.J.; Yeh, J.W.: Enhanced mechanical properties of HfMoTaTiZr and HfMoNbTaTiZr refractory high-entropy alloys. Intermetallics 62, 76–83 (2015)
Murty, B.; Yeh, J.W.; Ranganathan, S.: High-entropy alloys. Butterworth-Heinemann, Oxford (2014)
Wang, Z.; Guo, S.; Liu, C.T.: Phase selection in high-entropy alloys: from nonequilibrium to equilibrium. JOM 66, 1966–1972 (2014)
Praveen, S.; Murty, B.S.; Kottada, R.S.: Phase evolution and densification behavior of nanocrystalline multicomponent high entropy alloys during spark plasma sintering. JOM 65, 1797–1804 (2013)
Zhou, Y.: Material analysis methods. Mechanical Industry Press, Beijing (2004)
Wu, Z.; Bei, H.; Otto, F.; Pharr, G.M.; George, E.P.: Recovery, recrystallization, grain growth and phase stability of a family of FCC-structured multi-component equiatomic solid solution alloys. Intermetallics 46, 131–140 (2014)
Acknowledgements
This research work is supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (51761002), the National Key R&D Program of China (2016YFB0301400), the Guangxi Natural Science Foundation (2018GXNSFDA050008), the Training Plan of High-Level Talents of Guangxi University (XMPZ160714) and the research project of Guangxi Key Laboratory of Processing for Non-ferrous Metallic and Featured Materials (GXYSSF1807).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Tang, C., Ye, H. & Zhan, Y. Mechanism of FCC structure formation in NiCoFeCuMn equiatomic high-entropy alloys. Arab J Sci Eng 44, 6637–6644 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13369-019-03875-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13369-019-03875-x