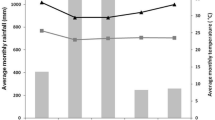
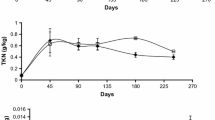
Abstract
The benefits of nitrogen-fixing and potassium-solubilizing microorganisms in plant growth were investigated by using micro-sized ion-selective sensors developed in our laboratory. Azorhizophilus paspali (ATCC 23367) having nitrogen-fixing capability and Paenibacillus mucilaginosus (DSM 24461) having potassium-solubilizing capability were used in media. The microorganisms grown in aseptic conditions were mixed with soil and compost in order to improve plant nutrition, and samples taken from growth medium were examined for 23 days by ammonium- and potassium-selective PVC membrane sensors exhibiting almost Nernstian response. The highest nitrate release were obtained on the 14th day of inoculation in samples using A. paspali. The highest potassium release was obtained on 18th day of inoculation in samples using P. mucilaginosus. The results showed that bacterial inoculation had a more stimulating effect on assimilation of N and K in compost than in soil. In addition, the effect of microbial strains on shoot and root growth and nutrient uptake of tomato was tested in pot experiments using compost. A. paspali and P. mucilaginosus inoculation increased the shoot and root dry weight of tomato seedlings, respectively, 7–14 and 12–19% when compared with the control. The results showed that addition of the microorganisms into compost would be beneficial in plant nutrition. Application of these microorganisms as biofertilizers in barren areas will protect soil from the harmful effects of chemical fertilizers with an environmentally friendly approach.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Fallahzade, J.; Hajabbasi, M.: The effects of irrigation and cultivation on the quality of desert soil in central Iran. Land Degrad. Dev. 23(1), 53–61 (2012)
Tilman, D.; Cassman, K.G.; Matson, P.A.; Naylor, R.; Polasky, S.: Agricultural sustainability and intensive production practices. Nature 418(6898), 671–677 (2002)
Smil, V.: Enriching the Earth: Fritz Haber, Carl Bosch, and the Transformation of World Food Production. MIT Press, Cambridge (2004)
Reed, S.C.; Seastedt, T.R.; Mann, C.M.; Suding, K.N.; Townsend, A.R.; Cherwin, K.L.: Phosphorus fertilization stimulates nitrogen fixation and increases inorganic nitrogen concentrations in a restored prairie. Appl. Soil Ecol. 36(2), 238–242 (2007)
Dos Santos, P.C.; Fang, Z.; Mason, S.W.; Setubal, J.C.; Dixon, R.: Distribution of nitrogen fixation and nitrogenase-like sequences amongst microbial genomes. BMC Genomics 13(1), 162 (2012)
McGlynn, S.E.; Boyd, E.S.; Peters, J.W.; Orphan, V.J.: Classifying the metal dependence of uncharacterized nitrogenases. Front. Microbiol. 3, 419 (2013)
Gruber, N.; Galloway, J.N.: An earth-system perspective of the global nitrogen cycle. Nature 451(7176), 293–296 (2008)
Vitousek, P.M.; Aber, J.D.; Howarth, R.W.; Likens, G.E.; Matson, P.A.; Schindler, D.W.; Schlesinger, W.H.; Tilman, D.G.: Human alteration of the global nitrogen cycle: sources and consequences. Ecol. Appl. 7(3), 737–750 (1997)
Hamdi, Y.: Application of Nitrogen-Fixing Systems in Soil Improvement and Management, vol. 49. Food and Agriculture Org (1982)
Klymenko, O.; Klymenko, M.; Kameneva, I.; Klymenko, N.: Ecologization of fruit crops grafted seedlings growing. In: I International Symposium on Fruit Culture and Its Traditional Knowledge along Silk Road Countries 1032, pp. 125–132 (2013)
Goldstein, A.H.: Involvement of the quinoprotein glucose dehydrogenase in the solubilization of exogenous phosphates by gram-negative bacteria. In: Phosphate in Microorganisms: Cellular and Molecular Biology. ASM Press, Washington, pp. 197–203 (1994)
Hu, X.; Chen, J.; Guo, J.: Two phosphate-and potassium-solubilizing bacteria isolated from Tianmu Mountain, Zhejiang, China. World J. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 22(9), 983–990 (2006)
Diep, C.N.; Hieu, T.N.: Phosphate and potassium solubilizing bacteria from weathered materials of denatured rock mountain, Ha Tien, Kiên Giang province Vietnam. Am. J. Life Sci. 1(3), 88–92 (2013)
Antoun, H., Prévost, D.: Ecology of plant growth promoting rhizobacteria. In: PGPR: Biocontrol and Biofertilization, pp. 1–38. Springer, Berlin (2005)
Bélanger, R., Avis, T.: Ecological processes and interactions occurring in leaf surface fungi. St. Paul, MN: The American Phytopathological Society, pp. 193–208 (2002)
Nishio, M.: Microbial Fertilizers in Japan. ASPAC Food & Fertilizer Technology Center (1996)
Whipps, J.M.: Prospects and limitations for mycorrhizas in biocontrol of root pathogens. Can. J. Bot. 82(8), 1198–1227 (2004)
Vassilev, N.; Vassileva, M.; Nikolaeva, I.: Simultaneous P-solubilizing and biocontrol activity of microorganisms: potentials and future trends. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 71(2), 137–144 (2006)
Zamani, J.; Hajabbasi, M.A.; Alaie, E.; Sepehri, M.; Leuchtmann, A.; Schulin, R.: The effect of Piriformospora indica on the root development of maize (Zea mays L.) and remediation of petroleum contaminated soil. Int. J. Phytoremediat. 18(3), 278–287 (2016)
Bobacka, J.; Ivaska, A.; Lewenstam, A.: Plasticizer-free all-solid-state potassium-selective electrode based on poly (3-octylthiophene) and valinomycin. Anal. Chim. Acta 385(1), 195–202 (1999)
Gallardo, J.; Alegret, S.; Munoz, R.; De-Roman, M.; Leija, L.; Hernández, P.; Del Valle, M.: An electronic tongue using potentiometric all-solid-state PVC-membrane sensors for the simultaneous quantification of ammonium and potassium ions in water. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 377(2), 248–256 (2003)
Khorramdel, S.; Seyyedi, S.: Effects of compost extract and biofertilizers on quantitative and qualitative yield and different cuttings of sweet majoram (Majorana hortensis L.). J. Sci. Technol. Greenh. Cult. 6(23) (2015)
Molla, A.H.; Haque, M.M.; Haque, M.A.; Ilias, G.: Trichoderma-enriched biofertilizer enhances production and nutritional quality of tomato (Lycopersicon esculentum Mill.) and minimizes NPK fertilizer use. Agric. Res. 1(3), 265–272 (2012)
Meunchang, S.; Panichsakpatana, S.; Weaver, R.: Tomato growth in soil amended with sugar mill by-products compost. Plant Soil 280(1), 171–176 (2006)
Haque, M.M.; Ilias, G.; Molla, A.: Impact of Trichoderma-enriched biofertilizer on the growth and yield of mustard (Brassica rapa L.) and tomato (Solanum lycopersicon Mill.). Agriculturists 10(2), 109–119 (2012)
Meena, R.K.; Sanjay, K.; Sutanu, M.; Devendra, K.; Manoj, K.: Effect of organic manures and biofertilizers on growth, flowering, yield and quality of tomato cv. PUSA SHEETAL. Int. J. Agric. Sci. 10(1), 329–332 (2014)
Lynn, T.M.; Win, H.S.; Kyaw, E.P.; Latt, Z.K.; Yu, S.: Characterization of phosphate solubilizing and potassium decomposing strains and study on their effects on tomato cultivation. Int. J. Innov. Appl. Stud. 3(4), 959–966 (2013)
Chatterjee, R.; Khalko, S.: Influence of organic amendments and inorganic fertilizers on late blight incidence and yield of tomato (Lycopersicon esculentum Mill.). Int. J. Geol. Agric. Environ. Sci. 1(1), 36–38 (2013)
Denarie, J.; Debelle, F.; Prome, J.-C.: Rhizobium lipo-chitooligosaccharide nodulation factors: signaling molecules mediating recognition and morphogenesis. Annu. Rev. Biochem. 65(1), 503–535 (1996)
Dobbelaere, S.; Vanderleyden, J.; Okon, Y.: Plant growth-promoting effects of diazotrophs in the rhizosphere. Crit. Rev. Plant Sci. 22(2), 107–149 (2003)
Meena, V.S.; Maurya, B.; Verma, J.P.: Does a rhizospheric microorganism enhance K+ availability in agricultural soils? Microbiol. Res. 169(5), 337–347 (2014)
Yadav, B.K.; Sidhu, A.S.: Dynamics of potassium and their bioavailability for plant nutrition. In: Potassium solubilizing microorganisms for sustainable agriculture. pp. 187–201. Springer, Berlin (2016)
Wang, P.; Wu, S.-H.; Wen, M.-X.; Wang, Y.; Wu, Q.-S.: Effects of combined inoculation with Rhizophagus intraradices and Paenibacillus mucilaginosus on plant growth, root morphology, and physiological status of trifoliate orange (Poncirus trifoliata L. Raf.) seedlings under different levels of phosphorus. Sci. Hortic. 205, 97–105 (2016)
Datta, J., Banerjee, A., Sikdar, M.S., Gupta, S., Mondal, N.: Impact of combined exposure of chemical, fertilizer, bio-fertilizer and compost on growth, physiology and productivity of Brassica campestries in old alluvial soil (2009)
Shaukat, K.; Affrasayab, S.; Hasnain, S.: Growth responses of Helianthus annus to plant growth promoting rhizobacteria used as a biofertilizers. Int. J. Agric. Res. 1(6), 573–581 (2006)
Baldani, J.I.; Baldani, V.L.: History on the biological nitrogen fixation research in graminaceous plants: special emphasis on the Brazilian experience. Anais da Academia Brasileira de Ciências 77(3), 549–579 (2005)
Döbereiner, J.: Recent advances in associations of diazotrophs with plant roots. Dev. Soil Sci. 18, 229–242 (1989)
Goswami, D.; Parmar, S.; Vaghela, H.; Dhandhukia, P.; Thakker, J.N.: Describing Paenibacillus mucilaginosus strain N3 as an efficient plant growth promoting rhizobacteria (PGPR). Cogent Food Agric. 1(1), 1000714 (2015)
Ma, M.; Wang, Z.; Li, L.; Jiang, X.; Guan, D.; Cao, F.; Chen, H.; Wang, X.; Shen, D.; Du, B.: Complete genome sequence of Paenibacillus mucilaginosus 3016, a bacterium functional as microbial fertilizer. J. Bacteriol. 194(10), 2777–2778 (2012)
Acknowledgements
I am indebted to Prof. Dr. Ibrahim Isildak for helpful comments regarding this research. The author would like to acknowledge the financial support of Yildiz Technical University Scientific Research Projects Coordinatorship (Project Number: 2016-07-04-GEP01).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Attar, A. Effects of Azorhizophilus paspali and Paenibacillus mucilaginosus as Biofertilizer and Determination of Nutritional Efficiency by Sensors. Arab J Sci Eng 43, 3477–3484 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13369-018-3126-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13369-018-3126-1