Abstract
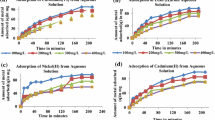
The present work utilized raw red mud and hydrochloric acid-modified red mud (RMA) as adsorbents for Cr(VI), Cu(II) and Pb(II) removal from aqueous solution. pH, X-ray fluorescence, infrared spectrometry and porosity characteristics using gas adsorption were performed for characterization of adsorbents. Batch experiments were conducted to determine the influence of solution pH, temperature, initial metal ion concentration and adsorbent dose on the kinetics (0–120 min) of the metal ions removal. Equilibrium data were analyzed using Langmuir and Freundlich isotherms. Monolayer adsorption capacities of raw and acid-modified adsorbents were found to be 9.615 and 9.542 for chromium, 78.125 and 77.519 for copper and 52.083 and \(79.365\,\upmu \hbox {mol g}^{-1}\) for lead, respectively. Acid activation has only marginal influence on the monolayer capacity of copper and chromium adsorption, but influences lead adsorption. Pseudo-second-order kinetic model suited well than other models like pseudo-first-order and intraparticle diffusion models examined. Equilibrium was attained in 10 min for chromium and 20 and 40 min on average for copper and lead, respectively, at all the conditions used in the study. The order of metal ions interaction with the surface as well as the rate of uptake was chromium > copper > lead. These findings revealed that raw and RMA serve as effective adsorbents for the removal of Cr(VI), Cu(II) and Pb(II) from aqueous solutions.
Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- RM:
-
Red mud
- RMA:
-
Acid-modified red mud
- XRF:
-
X-Ray fluorescence
- IR:
-
Infrared spectroscopy
- \({q}_{{t}}\) :
-
Amount of metal ion adsorbed at time \(t(\upmu \hbox {mol/g}\))
- \(C_0\) :
-
Initial metal ion concentration (\(\upmu \hbox {mol/L}\))
- \(C_\mathrm{e}\) :
-
Metal ion concentration in solution at equilibrium (\(\upmu \hbox {mol/L}\))
- C :
-
Intraparticle diffusion model intercept
- \({k}_{1}\) :
-
Pseudo-first-order constant (min\(^{-1}\))
- \({k}_{2}\) :
-
Pseudo-second-order constant (\(\hbox {g}/\upmu \hbox {mol/min}\))
- \({K}_{\mathrm{F}}\) :
-
Freundlich constant (\(\upmu \hbox {mol/g})/(\upmu \hbox {mol/L})^{1/\mathrm{n}}\)
- \({k}_{\mathrm{id}}\) :
-
Intraparticle diffusion rate constant (\(\upmu \hbox {mol/g}/\hbox {min}^{1/2})\)
- m :
-
Amount of adsorbent (g)
- n :
-
Adsorption intensity
- \({q}_\mathrm{m}\) :
-
Monolayer adsorption capacity (\(\upmu \hbox {mol/g}\))
- qe:
-
Amount of metal ion ions adsorbed per unit mass of adsorbent (\(\upmu \hbox {mol/g}\))
- qe,plot:
-
Calculated equilibrium amount adsorbed per unit mass of adsorbent (\(\upmu \hbox {mol/g}\))
- qe,exp’t:
-
Experimental equilibrium amount adsorbed per unit mass of adsorbent (\(\upmu \hbox {mol/g}\))
- b :
-
Langmuir equilibrium coefficient (\(\hbox {L g}^{-1})\)
- \({R}^{2}\) :
-
Coefficient of determination of regression
- \({R}_{{L}}\) :
-
Separation factor
- T :
-
Temperature (\({^{\circ }}\hbox {C}\))
- V :
-
Volume of the solution (L)
- w/w :
-
Weight percent
References
World Health Organization: Health in water resources development. (2007). Available at: http://www.who.int/docstore/watersanitationhealth/vector/waterresources.htm
United Nations World Water Development Report, UNESCO: Water for people water for life. (2003). Available at: http://www.unesco.org/water/wwap/wwdr1/exsummary/index.shtml
Kanamadi, R.D.; Ahalya, N.; Ramachandra, T.V.: Biosorption of heavy metals by low cost adsorbents. CESTechnical Report: 112, Energy and Wetlands Research Group, Centre for Ecological Sciences, Indian Institute of Science, Bangalore, 560 012 (2006)
Nas, S.M.; Okbah, M.A.; Kasem, S.M.: Environmental assessment of heavy metal pollution in bottom sediments of Aden Port, Yemen. Int. J. Oceans Oceanogr. 1, 99–109 (2006)
Singh, J.; Kalamdhad, A.S.: Effects of heavy metals on soil, plants, human health and aquatic life. Int. J. Res. Chem. Environ. 1, 15–21 (2011)
Di Benedetto, M.: Les metaux lourds, methodes spectrometriques d’analyse. Génie des Procédés, Ecole Nationale Supérieure des Mines de Saint-Etienne (1997)
Gebrekidan, M.; Samuel, Z.: Concentration of Heavy Metals in Drinking Water from Urban Areas of the Tigray Region, Northern Ethiopia, vol. 3, pp. 105–121. CNCS, Mekelle University ISSN:2220-184X (2011)
UNESCO: United Nations, Economic and Social Commission for Western Asia Waste-Water Treatment Technologies: A General Review (2003) http://www.igemportal.org/Resim/Wastewater%20Treatment%20Technologies_%20A%20general%20rewiev.pdf. Accessed 8 Aug 2017
Ozdesa, D.; Gundogdua, A.; Kemera, B.; Durana, C.; Senturka, H.B.; Soylakb, M.: Removal of Pb(II) ions from aqueous solution by a waste mud from copper mine industry: equilibrium, kinetic and thermodynamic study. J. Hazard. Mater. 166, 1480–1487 (2009)
Katsumataa, H.; Kanecoa, S.; Inomataa, K.; Itoh, K.; Funasaka, K.M.; Suzukid, T.; Kiyohisa, O.: Removal of heavy metals in rinsing wastewater from plating factory by adsorption with economical viable materials. J. Environ. Manage. 69, 187–191 (2003)
Ali, I.: Water treatment by adsorption columns: evaluation at ground level. Sep. Purif. Rev. 43, 175–205 (2014)
Kurniawan, T.A.; Chan, G.Y.S.; Wai-hung, L.; Sandhya, B.: Comparisons of low-cost adsorbents for treating wastewaters laden with heavy metals, review. Sci. Total Environ. 366, 409–426 (2006)
Resolutions Adopted by the Conference: Resolution 1, annexes I and II. Report of the United Nations Conference on Environment and Development, Rio de Janeiro June 3–14, and Corrigenda. United Nations publication, Sales No. E.93.I.8, vol. 1 (1992)
Momo, M.N.; Tematio, P.; Yemefack, M.: Multi-scale organization of the Doumbouo-Fokoué bauxites ore deposits (West Cameroon): implication to the landscape lowering. Open J. Geol. 2, 14–24 (2012)
Sushil, S.; Batra, V.S.: Catalytic applications of red mud, an aluminium industry waste: a review. Appl. Catal. B Environ. 81, 64–77 (2008)
Agatzini-Leonardou, S.; Oustadakis, P.; Tsakiridis, P.E.; Markopoulos, Ch: Titanium leaching from red mud by diluted sulfuric acid at atmospheric pressure. J. Hazard. Mater. 157, 579–586 (2008)
Briger, P.L.: Hydromine’s Project Development Program in Cameroon, U. S.–Africa Infrastructure Conference Washington, D.C. Report (2010)
Brunori, C.; Cremisini, C.; Massanisso, P.; Pinto, V.; Torricelli, L.: Reuse of a treated red mud bauxite waste: studies on environmental compatibility. J. Hazard. Mater. 117, 55–63 (2005)
Wang, S.; Ang, H.M.; Tadé, M.O.: Review: novel applications of red mud as coagulant, adsorbent and catalyst for environmentally benign processes. Chemosphere 72, 1621–1635 (2008)
Vilar, A.B.V.J.P.; Botelho, C.M.S.; Boaventura, R.A.R.: A review of the use of red mud as adsorbent for the removal of toxic pollutants from water and wastewater. Environ. Technol. 32, 231–249 (2011)
Sutar, H.; Mishra, S.C.; Sahoo, S.K.; chakraverty, A.P.; Maharana, H.S.: Progress of red mud utilization: an overview. Am. Chem. Sci. J. 4, 255–279 (2014)
Sieliechi, J.M.; Noumi, G.B.; Fadimatou, M.; Ali, A.; Kapseu, C.: Speciation of heavy metals in sediments sampled from different pollution sources of Lake Dang, Ngaoundere-Cameroon. Int. J. Environm. Prot. 2, 10–19 (2013)
Ekenguele, N.L.; Baussand, P.; Ekodeck, G.E.: Heavy metals accumulation in sediment cores of the municipal Lake of Yaounde, Cameroon. Glob. J. Environ. Res. 6, 100–110 (2012)
Kayalto, B.; Mbofung, C.M.F.; Tchatchueng, J.B.; Ahmed, A.: Contribution à l’évaluation de la contamination par les métaux lourds de trois espèces de poissons, des sédiments et des eaux du Lac Tchad. Int. J. Biol Chem. Sci. 8, 468–480 (2014)
Fonge, B.A.; Tening, A.S.; Egbe, A.E.; Awo, E.M.; Focho, D.A.; Oben, P.M.; Asongwe, G.A.; Zoneziwoh, R.M.: Fish (Arius heudelotii Valenciennes, 1840) as bioindicator of heavy metals in Douala Estuary of Cameroon. Afr. J. Biotechnol. 10, 16581–16588 (2011)
Komlóssy, G.; Morrison, W.B.: Comparison of bauxite resources—geo-economical considerations. J. Earth Sci. 2, 10–19 (2010)
Tsamo, C.; Kofa, G.P.; Kamga, R.: Decreasing yield and alumina content of red mud by optimization of the bauxite processing process. Int. J. Metall. Eng. 6, 1–9 (2017). doi:10.5923/j.ijmee.20170601.01
Saranya, N.; Nakkeeran, E.; Shrihari, S.; Selvaraju, N.: Equilibrium and kinetic studies of hexavalent chromium removal using a novel biosorbent: Ruellia patula Jacq. Arab. J. Sci. Eng. 42, 1545–1557 (2017). doi:10.1007/s13369-017-2416-3
Gräfe, M.; Power, G.; Klauber, C.: Bauxite residue issues: III. Alkalinity and associated chemistry. Hydrometallurgy 108, 60–79 (2011)
Snars, K.; Gilkes, R.J.: Evaluation of bauxite residues (red muds) of different origins for environmental applications. Appl. Clay Sci. 46, 13–20 (2009)
Sahu, R.C.; Patel, R.; Ray, B.C.: Utilization of \(\text{ CO }_{2}\)-neutralized red mud for removal of arsenate from aqueous solutions. J. Hazard. Mater. 179, 1007–1013 (2010)
Castaldi, P.; Silvetti, M.; Santona, L.; Enzo, S.; Melis, P.: XRD, FTIR and thermal analysis of bauxite ore-processing waste (red mud) exchanged with heavy metals. Clays Clay Miner. 56, 461–469 (2008)
Mistry, B.D.: A Handbook of Spectroscopic Data Chemistry (UV, JR, PMR, JJCNMR and Mass Spectroscopy). Oxford Book Company, Jaipur (2009)
Vo-Dinh, T.; Spellicy, R.L.: Pollutant emission monitoring using QC laser-based mid-IR sensors. In: Proceedings of SPIE on Water, Ground and Air Pollution Monitoring and Remediation, vol. 4199 (2001)
Lefevre, G.: In situ Fourier-transform infrared spectroscopy studies of inorganic ions adsorption on metal oxides and hydroxides. Adv. Colloid Interface Sci. 107, 109–123 (2004)
Emdadi, L.: Characterizing Porous Materials and Powders. University of Maryland, College Park, MD (2013)
Quantachrome Instruments: Physisorption Methods and Techniques, ppt (1992) http://slideplayer.com/slide/1710170/. Accessed 8 Aug 2017
Imamoglu, M.; Tekir, O.: Removal of copper(II) and lead(II) ions from aqueous solutions by adsorption on activated carbon from a new precursor hazelnut husks. Desalination 228, 108–113 (2008)
Dursun, S.; Guclu, D.; Berktay, A.; Guner, T.: Removal of chromate from aqueous system by activated red-mud. Asian J. Chem. 20, 6473–6478 (2008)
Rajkumar, M.; Nagendran, N.; Sasikumar, S.S.: Removal of trivalent chromium from wastewater using red mud. Ind. J. Environ. Prot. 21, 97–100 (2001)
Nadaroglu, H.; Kalkan, E.; Demir, N.: Removal of copper from aqueous solution using red mud. Desalination 251, 90–95 (2010)
Vaclavikova, M.; Misaelides, P.; Gallios, G.; Jakabsky, S.; Hredzak, S.: Removal of cadmium, zinc, copper and lead by red mud, an iron oxides containing hydrometallurgical waste. Stud. Surf. Sci. Catal. 155, 517–525 (2005)
Gupta, S.S.; Bhattacharyya, K.G.: Immobilization of Pb(II), Cd(II) and Ni(II) ions on kaolinite and montmorillonite surfaces from aqueous medium. J. Environ. Manage. 87, 46–58 (2008)
Gupta, S.S.; Bhattacharyya, K.G.: Interaction of metal ions with clays: I. A case study with Pb(II). Appl. Clay Sci. 30, 199–208 (2005)
Echeverria, J.; Indurain, J.; Churio, E.; Garrido, J.: Simultaneous effect of pH, temperature, ionic strength, and initial concentration on the retention of Ni on illite. Colloids Surf. A Physicochem. Eng. Asp. 218, 175–187 (2003)
Zhao, L.; Qin, H.; Wu, R.; Zou, H.: Review: recent advances of mesoporous materials in sample preparation. J. Chromatogr. A 1228, 193–204 (2012)
Wells, A.F.: Structural Inorganic Chemistry, 5th edn, p. 1288. Clarendon Press, Oxford (1984) (metallic radii for 12-coordination); Huheey, pp. 292 (covalent radii for nonmetals); R.D. Shannon, Acta Crystallogr., Sect. A: Found. Crystallogr., vol. 32, p. 751 (1976) (ionic radii for 6-coordination)
Ionic radius. https://www.saylor.org/site/wp-content/uploads/.../Ionic-Radius.pdf. Accessed 30 June 2017
Gupta, V.K.; Gupta, M.; Sharma, S.: Process development for the removal of lead and chromium from aqueous solutions using red mud—an aluminium industry waste. Water Res. 35, 1125–1134 (2000)
Horsfall Jr., M.; Abia, A.A.; Spiff, A.I.: Kinetic studies on the adsorption of \(\text{ Cd }^{2+}\), \(\text{ Cu }^{2+}\), \(\text{ Zn }^{2+}\) ions from aqueous solutions by cassava (Manihot esculenta Cranz) tuber bark waste. Bioresour. Technol. 97, 283–291 (2006)
Bhattacharyya, K.G.; Gupta, S.S.: Pb(II) uptake by kaolinite and montmorillonite in aqueous medium: influence of acid activation of the clays. Colloids Surf. A Physicochem. Eng. Asp. 277, 191–200 (2006)
Shukla, A.; Zhang, Y.H.; Dubey, P.; Margrave, J.L.; Shukla, S.S.: The role of sawdust in the removal of unwanted materials from water. J. Hazard. Mater. B95, 137–152 (2002)
Tor, A.; Cengeloglu, Y.: Removal of congo red from aqueous solution by adsorption onto acid activated red mud. J. Hazard. Mater. B138, 409–415 (2006)
Sujana, M.G.; Thakur, R.S.; Rao, S.B.: Removal of fluoride from aqueous solution by using alum sludge. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 206, 94–101 (1998)
Bishnoi, N.R.; Bajaj, M.; Sharma, N.; Gupta, A.: Adsorption of Cr(VI) on activated rice husk carbon and activated alumina. Bioresour. Technol. 91, 305–307 (2004)
Mehrotra, A.; Gopal, K.; Seth, P.K.: Annual Report VIO Hyderabad State. Indian Council of Agriculture Research, ICAR, New Delhi (1999)
Saravanan, D.; Sudha, P.N.: Batch adsorption studies for the removal of copper from wastewater using natural biopolymer. Int. J. ChemTech Res. 6, 3496–3508 (2014)
Han, S.W.; Kim, D.K.; Hwang, I.G.; Bae, J.H.: Development of pellet-type adsorbents for removal of heavy metal ions from aqueous solutions using red mud. J. Ind. Eng. Chem. 8, 120–125 (2002)
Pradhan, J.; Das, S.N.; Thakur, R.S.: Adsorption of hexavalent chromium from aqueous solution by using activated red mud. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 217, 137–141 (1999)
Apak, R.; Tütem, E.; Hügül, M.; Hizal, J.: Heavy metal cation retention by unconventional sorbents (red muds and fly ashes). Water Res. 32, 430–440 (1998)
Zhu, C.; Luan, Z.; Wang, Y.; Shan, X.: Removal of cadmium from aqueous solutions by adsorption on granular red mud (GRM). Sep. Purif. Technol. 57, 161–169 (2007)
Weber, W. J.; Morris, J. C.: Kinetics of adsorption on carbon from solution. J. Sanitary Eng. Div. 89, 31–60 (1963)
Guo, X.; Zhang, S.; Shan, X.-Q.: Adsorption of metal ions on lignin. J. Hazard. Mater. 151, 134 (2008)
Khan, S.A.; Rehman, R.; Khan, M.A.: Adsorption of chromium(III), chromium(VI) and silver(I) on bentonite. Waste Manage. 15, 271 (1995)
Malliou, E.; Loizidou, M.; Spyrellis, N.: Uptake of lead and cadmium by clinoptilolite. Sci. Total Environ. 149, 139–144 (1994)
Srivastava, S.K.; Tyagi, R.; Pant, N.; Pal, N.: Studies on the removal of some toxic metal ions. Part II: removal of lead and cadmium by montmorillonite and kaolinite. Environ. Technol. Lett. 10, 275–282 (1989)
Chantawong, V.; Harvey, N.W.; Bashkin, V.N.: Adsorption of lead nitrate on Thai Kaolin and ball clay. Asian J Energy Environ. 2, 33–48 (2001)
Yadava, K.P.; Tyagi, B.S.; Singh, V.N.: Effect of temperature on the removal of lead(II) by adsorption on China clay and wollastonite. J. Chem. Technol. Biotechnol. 51, 47–60 (1991)
Gupta, V.K.; Carrott, P.J.M.; Carrott, Ribeiro; Suhas, M.M.L.: Low-cost adsorbents: growing approach to wastewater treatment—a review. Crit. Rev. Environ. Sci. Technol. 39, 783–842 (2009). doi:10.1080/10643380801977610
Kavitha, G.; Sridevi, V.; Chitti Babu, N.: Biosorption of lead from aqueous solution by Gracilaria corticata (red algae) and its statistical analysis using response surface methodology. Int. J. Ind. Chem. Biotechnol. 2, 11–34 (2016). doi:10.21276/ijicab.2016.2.4.2
Vaishya, R.C.; Prasad, S.C.: Adsorption of copper(II) on sawdust. Indian J. Environ. Prot. 11, 284 (1991)
Acemioglu, B.; Samil, A.; Alma, M.H.; Gundogan, R.: Copper(II) removal from aqueous solution by organosolv lignin and its recovery. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 89, 1537 (2003)
Merdy, P.; Guillon, E.; Aplincourt, M.; Dumonceau, J.; Vezin, H.: Copper sorption on a straw lignin: experiments and EPR characterization. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 245, 24 (2002)
Pandy, K.K.; Prasad, G.; Singh, V.N.: Copper removal from aqueous solution by fly ash. Water Res. 19, 869–873 (1985)
Pandy, K.K.; Prasad, G.; Singh, V.N.: Mixed adsorbents for Cu(II) removal from aqueous solutions. Environ. Technol. Lett. 7, 547–554 (1986)
Schmuhl, R.; Krieg, H.M.; Keizer, K.: Adsorption of Cu(II) and Cr(VI) ions by chitosan: kinetics and equilibrium studies. Water SA 27, 1–7 (2001)
Khan, S.A.; Rehman, R.; Khan, M.A.: Adsorption of chromium(III), chromium(VI), and silver(I) on bentonite. Waste Manage. 15, 271–282 (1995)
Pandy, K.K.; Prasad, G.; Singh, V.N.: Removal of Cr(VI) from aqueous solutions by adsorption on fly ash-wollastonite. J. Chem. Technol. Biotechnol. 34A, 367–374 (1984)
Gupta, G.S.; Prasad, G.; Singh, V.N.: Removal of chrome dye from aqueous solutions by mixed adsorbents: fly ash and coal. Water Res. 24, 45–50 (1990)
Han, I.; Schlautman, M.A.; Batchelor, B.: Removal of hexavalent chromium from groundwater by granular activated carbon. Water Environ. Res. 72, 29–39 (2000)
Namasivayam, C.; Ranganathan, K.: Waste Fe(III)/Cr(III) hydroxide as adsorbent for the removal of Cr(VI) from aqueous solution and chromium plating industry wastewater. Environ. Pollut. 82, 255–261 (1993)
Zhou, Y.; Haynes, R.J.: A comparison of water treatment sludge and red mud as adsorbents of As and Se in aqueous solution and their capacity for desorption and regeneration. Water Air Soil Pollut. 223, 5563–5573 (2012)
Zhang, S.; Liu, C.; Luan, Z.; Peng, X.; Ren, H.; Wang, J.: Arsenate removal from aqueous solutions using modified red mud. J. Hazard. Mater. 152, 486–492 (2008)
Gupta, V.K.; Gupta, M.; Sharma, S.: Process development for the removal of lead and chromium from aqueous solutions using red mud—an aluminium industry waste. Water Res. 35, 1125–1134 (2001)
Gupta, V.K.; Sharma, S.: Removal of cadmium and zinc from aqueous solutions using red mud. Environ. Sci. Technol. 36, 3612–3617 (2002)
Gupta, V.K.; Suhas,; Ali, I.; Saini, V.K.: Removal of rhodamine B, fast green, and methylene blue from wastewater using red mud, an aluminum industry waste. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 43, 1740–1747 (2004)
Namasivayam, C.; Arasi, D.J.S.E.: Removal of congo red from wastewater by adsorption onto waste red mud. Chemosphere 34, 401–417 (1997)
Namasivayam, C.; Yamuna, R.T.; Arasi, D.J.S.E.: Removal of procion orange from wastewater by adsorption on waste red mud. Sep. Sci. Technol. 37, 2421–2431 (2002)
Namasivayam, C.; Yamuna, R.T.; Arasi, D.J.S.E.: Removal of acid violet from wastewater by adsorption on waste red mud. Environ. Geol. 41, 269–273 (2001)
Zhao, Y.; Yue, Q.; Li, Q.; Baoyu Gao, B.; Han, S.; Yu, H.: The regeneration characteristics of various red mud granular adsorbents (RMGA) for phosphate removal using different desorption reagents. J. Hazard. Mater. 182, 309–316 (2010)
Tor, A.; Danaoglu, N.; Arslan, G.; Cengeloglu, Y.: Removal of fluoride from water by using granular red mud: batch and column studies. J. Hazard. Mater. 164, 271–278 (2009)
Evans, K.: The history, challenges, and new developments in the management and use of bauxite residue. J. Sustain. Metall. (2016). doi:10.1007/s40831-016-0060-x
Mayes, W.M.; Burke, I.T.; Gomes, H.I.; Anton, A.D.; Molna, M.; Feigl, V.; Ujaczki, E.: Advances in understanding environmental risks of red mud after the Ajka spill Hungary. J. Sustain Metall. (2016). doi:10.1007/s40831-016-0050-z
Al-Khatib, I.A.; Monou, M.; Zahra, A.S.F.A.; Shaheen, H.Q.; Kassinos, D.: Solid waste characterization, quantification and management practices in developing countries. A case study: Nablus district–Palestine. J. Environ. Manage. 91, 1131–1138 (2010)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Tsamo, C., Djomou Djonga, P.N., Dangwang Dikdim, J.M. et al. Kinetic and Equilibrium Studies of Cr(VI), Cu(II) and Pb(II) Removal from Aqueous Solution Using Red Mud, a Low-Cost Adsorbent. Arab J Sci Eng 43, 2353–2368 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13369-017-2787-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13369-017-2787-5