Abstract
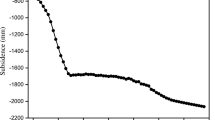
More than 60 countries are suffering from the costly land subsidence. The economic loss induced by land subsidence in the coastal city Shanghai has reached over 46 billion dollars. This paper studied the deformation of each soil layer considering dual effects of building load and groundwater withdrawal. The physical model test based on the geological background in Shanghai was conducted, and the particle image velocimetry was adopted to measure the displacement of each point in soil layers. The later constructed building accelerates the subsidence rate of the earlier one, while the earlier one reduces the subsidence of later one to some extent. Dewatering changes the subsidence distribution which develops at the building load period. Compared with the subsidence caused by the building load, the subsidence caused by the dewatering develops slowly and lasts a longer period of time. Groundwater recharge can mitigate land subsidence effectively, yet the rebound is little. The results can offer a reference to control the land subsidence in soft soil area induced by the high-rise building group and the pumping and recharging of groundwater.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Shi, X.Q.; Fang, R.; Wu, J.C.; Xu, H.X.; Sun, Y.Y.; Yu, J.: Sustainable development and utilization of groundwater resources considering land subsidence in Suzhou, China. Eng. Geol. 124, 77–89 (2012)
Zhang, A.G.: Sustainable development and land subsidence controlling management in Shanghai. Chin. J. Geol. Hazard Control 16(1), 1–4 (2005). (in Chinese)
Zhang, W.R.; Duan, Z.L.; Zeng, Z.Q.; Shi, H.P.: Evaluation on economic losses resulted from land subsidence in Shanghai: 1921–2000. J. Tongji Univ. 31(6), 743–748 (2003). (in Chinese)
Zhang, A.G.; Wei, Z.X.: Past, present and future research on land subsidence in Shanghai City. Hydrogeol. Eng. Geol. 5, 72–75 (2002). (in Chinese)
Shen, S.L.; Xu, Y.S.: Numerical evaluation of land subsidence induced by groundwater pumping in Shanghai. Can. Geotech. J. 48(9), 1378–1392 (2011)
Chai, J.C.; Shen, S.L.; Zhu, H.H.: land subsidence due to ground water drawdown in Shanghai. Geotechnique 54(2), 143–147 (2004)
Xue, Y.Q.; Zhang, Y.; Ye, S.J.: Land subsidence in China. Environ. Geol. 48(6), 713–720 (2005)
Wu, J.C.; Shi, X.Q.; Ye, S.J.; Xue, Y.Q.; Zhang, Y.; Wei, Z.X.; Fang, Z.: Numerical simulation of viscoelastoplastic land subsidence due to groundwater overdrafting in shanghai. China. Journal of Hydrologic Engineering 15(3), 223–236 (2010)
Shi, X.Q.; Wu, J.C.; Ye, S.J.; Zhang, Y.; XueYQ, Wei Z.X.; Li, Q.F.; Yu, J.: Regional land subsidence simulation in Su-Xi-Chang area and Shanghai City, China. Eng. Geol. 100, 27–42 (2008)
Xu, Y.S.; Ma, L.; Shen, S.L.: Influential factors on development of land subsidence with process of urbanization in Shanghai. Rock Soil Mech. 32(S1), 578–582 (2011). (in Chinese)
Yan, X.X.; Gong, S.L.; Zeng, Z.Q.; Yu, J.Y.; Shen, G.P.; Wang, T.J.: Relationship between building density and land subsidence in Shanghai urban zone. Hydrogeol. Eng. Geol. 6, 21–25 (2002). (in Chinese)
Cheng, S.; Zhang, G.; Zheng, R.H.; Sun, Z.Y.: Centrifuge modeling of response of bridge due to exploiting groundwater. Rock and Soil Mechanics 32(6), 1781–1786 (2011). (in Chinese)
Sun, Z.Y.; Zhang, G.; Zhang, J.M.; Li, G.H.; Zheng, R.H.: Centrifuge modeling of ground subsidence due to groundwater pumping. China Civil Eng. J. 41(4), 67–72 (2008). (in Chinese)
Tang, Y.Q.; Cui, Z.D.; Wang, J.X.: Model test study of land subsidence caused by high-rise building group in Shanghai. Bull. Eng. Geol. Environ. 67, 173–179 (2008a)
Tang, Y.Q.; Cui, Z.D.; Wang, J.X.: Application of grey theory-based model to prediction of land subsidence due to engineering environment in Shanghai. Environ Geol. 55, 583–593 (2008b)
Cui, Z.D.; Tang, Y.Q.; Yan, X.X.: Centrifuge modeling of land subsidence caused by the high-rise building group in the soft soil area. Environ. Earth Sci. 59, 1819–1826 (2010)
Liu, H.P.: The study on the land subsidence with the affect of high-rise buildings in Tianjin Binhai new area. PhD Thesis, Changan University, (2010) (in Chinese)
White, D.J.; Take, W.A.; Bolton, M.D.: Soil deformation measurement using particle image velocimetry (PIV) and photogrammetry. Geotechnique 53(7), 619–631 (2003)
White, D.J.; Take, W.A.: Discussion on “application of particle image velocimetry (PIV) in centrifuge testing of uniform clay”. Int. J. Phys. Model. Geotech. 5(4), 27–31 (2005)
Baba, H.O.; Peth, S.: Large scale soil box test to investigate soil deformation and creep movement on slopes by particle image velocimetry (PIV). Soil Tillage Res. 125, 38–43 (2012)
Saiyar, M.; Take, W.A.; IMoore, I.D.: Validation of boundary PIV measurements of soil-pipe interaction. Int. J. Phys. Model. Geotech. 11(1), 23–32 (2011)
Zhang, Y.D.; Tan, T.S.; Leung, C.F.: Application of particle image velocimetry (PIV) in centrifuge testing of uniform clay. Int. J. Phys. Model. Geotech. 5(1), 15–16 (2005)
Zhang, Y.D.; Tan, T.S.; Leung, C.F.: Reply to application of particle image velocimetry (PIV) in centrifuge testing of uniform clay. Int. J. Phys. Model. Geotech. 5(4), 33–36 (2005)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Cui, ZD., Jia, YJ. Physical Model Test of Layered Soil Subsidence Considering Dual Effects of Building Load and Groundwater Withdrawal. Arab J Sci Eng 43, 1721–1734 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13369-017-2716-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13369-017-2716-7