Abstract
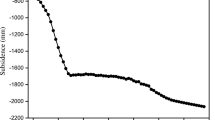
The paper discusses the influence of a group of high-rise buildings on land subsidence, based on a modeling exercise. The model consisted of five layers of soils typical of the Shanghai area, with the buildings placed on piles set in the upper silty sand horizon. It was loaded to represent the construction sequence of the four buildings. The main settlement was observed to be in the underlying clayey layer. The model demonstrated the increase in pore water pressure with staged loading, its effect on deformation and the increase in effective stress over time. It indicated the largest amount of settlement over time occurs between the buildings.
Résumé
L’article discute de l’influence d’un groupe de quatre bâtiments de grande hauteur sur le tassement des sols, sur la base d’une modélisation. Le modèle comportait cinq couches de sols typiques de la région de Shanghai, les bâtiments étant fondés sur pieux sur la couche silto-sableuse supérieure. Un chargement mécanique a représenté la séquence de construction des bâtiments. Le tassement principal s’est réalisé dans la couche argileuse sous-jacente. Le modèle a montré l’augmentation de la pression interstitielle, fonction du niveau de chargement mécanique, l’augmentation des contraintes effectives avec le temps et la déformation des terrains. Le modèle a montré que, dans le cas étudié, l’amplitude maximum de tassement se réalisait entre les bâtiments.












Similar content being viewed by others
References
Dong JG, Zhao XH (1996) The new computing method of the foundation settlement for the piles (in Chinese). Chinese J Geotech Eng 18(1):80–84
Lu C (2005) Study on land subsidence caused by the high-rise building group in shanghai and the Model Test in the lab (in Chinese). Tongji University, Shanghai, China
Monjoie A, Paepe R, Su HY (1992) Land subsidence in Shanghai (P.R. of China). Bull. Eng Geol Environ 46(1):5–7
Tang YQ et al (2007) Application of grey theory-based model to prediction of ground settlement caused by engineering environment in Shanghai. Environ Geol. doi:10.1007/s00254-007-1009-y
Xie T, Yuan WZ, Yao Y (2003) Model test study on effect of vertical bearing capacity for large-scale pile group (in Chinese). J Highway and Transportation Res Devel 20(5):61–64
Xue Y et al (2005) Land subsidence in China. Environ Geol 48:713–720
Yan XX, Gong SL (2002) Relationship between building density and land subsidence in Shanghai urban zone (in Chinese). Hydrogeol Eng Geol 29(6):21–25
Zhang AG (2002) Continuable development of Shanghai and the prevention and control of land subsidence (in Chinese). In: Wei ZX, Li QF (eds) Proceedings of the national symposium on land subsidence, Shanghai Institute of Geology Survey, Shanghai, pp 17–22
Zhang ZY, Lv XL (2003) Experiment study on excess pore water pressure soils covered by clay layer (in Chinese). Chinese J Rock Mech Eng 22(1):131–136
Acknowledgments
This work is supported by the research grant (40372124) from National Natural Science Foundation of China and Shanghai Key Subject (Geotechnical Engineering) Foundation.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Tang, YQ., Cui, ZD., Wang, JX. et al. Model test study of land subsidence caused by high-rise building group in Shanghai. Bull Eng Geol Environ 67, 173–179 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10064-008-0121-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10064-008-0121-x