Abstract
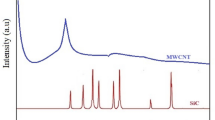
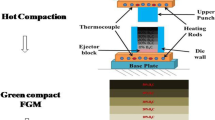
This paper investigates the sliding wear behaviour of nanoparticle-filled aluminium matrix nano-composites (AMNCs). Two different nano-reinforcements undertaken for this study are SiC and Al2O3. The percentage reinforcement is also varied from 0.5 to 1.5 wt%. For investigating the wear behaviour, factors such as applied normal load, sliding speed and sliding distance are considered. Also Taguchi design of experimental technique is employed for the study and analysis of sliding wear. Findings showed that nano-SiC particulate-reinforced AMNCs show better wear resistance than nano-Al2O3-reinforced AMNCs. Also regression and artificial neural network are used to develop a model to predict the wear rate of these composites.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Orbulov I.N., Ginsztler J., Kun P.: Infiltration characteristics and compressive behaviour of metal matrix syntactic foams. Mater. Sci. Forum 729, 68–73 (2013)
Orbulov, I.N.; Májlinger, K.: Description of the compressive response of metal matrix syntactic foams. Mater. Des. 49, 1–9 (2013)
Orbulov I.N., Májlinger K.: Microstructure of metal—matrix composites reinforced by ceramic microballoons. Mater. Technol. 46, 375–82 (2013)
Orbulov I.N.: Compressive properties of aluminium matrix syntactic foams. Mater. Sci. Eng. A-Struct. Mater. Prop. Microstruct. Process. 555, 52–56 (2012)
Wang S., Wang Y., Li C., Chi Q., Fei Z.: The dry sliding wear behavior of interpenetrating titanium trialuminide/aluminium composites. Appl. Compos. Mater. 14, 129–144 (2007)
Messler, Jr.; Robert, W.: Joining composite materials and structures. Mater. Struct. 647–696 (2004)
Kang Y.C., Chan S.L.: Tensile properties of nanometric Al2O3 particulate-reinforced aluminium matrix composites. Mater. Chem. Phys. 85, 438–443 (2004)
Molina-Aldareguia J.M., Reyes E.M.: Metal matrix composites reinforced with nano-size reinforcements. Compos. Sci. Technol. 70, 2227 (2010)
Yingguang L., Jianqiu Z., Tongde S.: Effect of nano-metal particles on the fracture toughness of metal—ceramic composite. Mater. Des. 45, 67–71 (2013)
Sahin Y.: Tribological behaviour of metal matrix and its composite. Mater. Des. 28, 1348–1352 (2007)
Ravindran P., Manisekar K., Narayanasamy P., Selvakumar N., Narayanasamy R.: Application of factorial techniques to study the wear behaviour of Al hybrid composites with graphite addition. Mater. Des. 39, 42–54 (2012)
Yamagushi K., Takakura N., Imatani S.: Compaction and sintering characteristics of composite metal powder. J. Mater. Process. Technol. 63, 346 (1997)
Lee, H.S.; Yeo, J.S.; Hong, S.H.; Yoon, D.J.; Na, K.H.: The fabrication process andmechanical properties of SiCp/Al–Simetalmatrix composites for automobile air-conditioner compressor pistons. J. Mater. Process. Technol. 113, 202–208 (2001)
Manna I., Nandi P., Bandyopadhyay B., Ghoshray K., Ghoshray A.: Microstructural and nuclear magnetic resonance studies of solid-state amorphization in Al–Ti–Si composites prepared by mechanical alloying. Acta. Mater. 52, 4133–4142 (2004)
Hassan S.F., Gupta M.: Development of high-performance magnesium nano-composites using solidification processing route. Mater. Sci. Technol. 20, 1383–1388 (2004)
Sankaranarayanan S., Sabat R.K., Jayalakshmi S., Suwas S., Gupta M.: Effect of nano scaleboron carbide particle addition on the microstructural evolution and mechanical response of pure magnesium. Mater. Des. 56, 428–436 (2014)
Hassan S., Gupta M.: Development of high performance magnesium nanocomposite using nano-Al2O3 as reinforcement. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 392, 163–168 (2005)
Tun K., Jayaramanavar P., Nguyen Q., Chan J., Kwok R., Gupta M.: Investigation into tensile and compressive responses of Mg–ZnO composites. Mater. Sci. Technol. 28, 582–588 (2012)
Zhou D.S., Tang J., Qiu F., Wang J.G., Jiang Q.C.: Effects of nano-TiCp on the microstructures and tensile properties of TiCp/Al–Cu composites. Mater. Charact. 94, 80–85 (2014)
Melendez I.M., Neubauer E., Angerer P., Danninger H., Torralba J.M.: Influence of nano-reinforcements on the mechanical properties and microstructure of titanium matrix composites. Compos. Sci. Technol. 71, 1154–1162 (2011)
Liu Y., Han Z., Cong H.: Effects of sliding velocity and normal load on the tribological behavior of a nanocrystalline Al based composite. Wear 268, 976–983 (2010)
Zhang Y.S., Wang K., Han Z., Liu G.: Dry sliding wear behavior of copper with nano-scaled twins. Wear 262, 1463–1470 (2007)
La P.Q., Ma J.Q., Zhu Y.T., Yang J., Lu W.M., Xue Q.J., Valiev R.Z.: Dry-sliding tribological properties of ultrafine-grained Ti prepared by severe plastic deformation. Acta Mater. 53, 5167–5173 (2005)
Zhang Y.S., Han Z., Wang K., Lu K.: Friction and wear behaviors of nanocrystalline surface layer of pure copper. Wear 260, 942–948 (2006)
Iglesias P., Bermudez M.D., Moscoso W., Rao B.C., Shankar M.R., Chandrasekar S.: Friction and wear of nanostructured metals created by large strain extrusion machining. Wear 263, 636–642 (2007)
Ravindran P., Manisekar K., Vinoth Kumar S., Rathika P.: Investigation of microstructure and mechanical properties of aluminium hybrid nano-composites with the additions of solid lubricant. Mater. Design 51, 448–456 (2013)
Al-Qutub, A.M.: Effect of heat treatment on friction and wear behavior of Al-6061 composite reinforced with 10 % submicron Al2O3 particles. Arabian J. Sci. Eng. 34(1B) (2009)
Al-Dheylan, K.; Hafeez, S.: Tensile failure micromechanisms of 6061 aluminum reinforced with submicron Al2O3 metal—matrix composites. Arabian J. Sci. Eng. 31(2C) (2006)
Aleksendric D.: Neural network prediction of brake friction materials wear. Wear 268, 117–125 (2010)
Tsao, C.C.; Hocheng, H.: Evaluation of thrust force and surface roughness in drilling composite material using Taguchi analysis and neural network. J. Mater. Process. Technol. 203, 342–348 (2008)
Bernardos P.G., Vosniakos G.C.: Prediction of surface roughness in CNC face milling using neural network and Taguchi’s design of experiments. Robot. Comput. Integr. Manuf. 18, 343–354 (2002)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ekka, K.K., Chauhan, S.R. & Varun Dry Sliding Wear Characteristics of SiC and Al2O3 Nanoparticulate Aluminium Matrix Composite Using Taguchi Technique. Arab J Sci Eng 40, 571–581 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13369-014-1528-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13369-014-1528-2