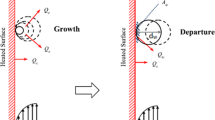
Abstract
Researchers searching for new cooling medium do not limit themselves to liquids alone. Suspension in common fluids with particles in the order of nanometers (typically 10–100 nm) in size is called ‘nano-fluids’. Cooling techniques are one of the vital points in industries and the way to develop the traditional fluids to a high thermal heat transfer fluid is crucial. Development of high thermal fluid as a nanofluid purely depends on the thermal and physical properties of base fluid and the particles dispersed in it and some other factors such as particle shape, particle size and the particle concentration. This paper explains the thermal properties of nanofluid, viz., thermal conductivity, specific heat and other thermal properties. An empirical correlation has been developed to predict the heat flux for nucleate pool boiling of nanofluids considering the effects of temperature, volume fraction and shape of the particle while neglecting Brownian motion of the nanoparticle, cluster/particle agglomeration and the development of the liquid layer over the plate surface. The predicted result has been compared with the Rohsenow equation and the experimental data of other investigators show a good agreement with the predicted data. Using this equation, heat transfer coefficient and heat transfer enhancement ratio of the nucleate pool boiling of Al2O3–water and TiO2–water nanofluids have been calculated. This enhanced thermophysical and heat transfer characteristics of the developed fluid dispersed with nanoparticles can be used for high heat transfer medium for future applications.

Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- A :
-
Surface area of the heater, m2
- C :
-
Specific heat, J/Kg K
- C sf :
-
Experimental constant that depends on surface–fluid combination
- D :
-
Diameter
- g :
-
Gravitational acceleration, m/s2
- h :
-
Heat transfer coefficient
- h fg :
-
Enthalpy of vaporization, J/kg
- k :
-
Thermal conductivity, W/mk
- m :
-
Mass, kg
- n :
-
Shape factor
- φ m :
-
Mass fraction
- σ:
-
Surface tension of liquid–vapor interface, N/m
- l :
-
Liquid
- nf:
-
Nanofluid
- v :
-
Vapor
- Pr:
-
Prandtl number
- Q :
-
Heat, J
- q :
-
Heat flux, W/m2
- R :
-
Heater resistance
- T :
-
Temperature, K
- U :
-
Voltage
- V :
-
Volume, m3
- α :
-
Ratio of thermal conductivities
- μ :
-
Viscosity, kg/ms
- ρ :
-
Density, kg/m3
- φ :
-
Volume fraction
- Ψ:
-
Sphericity
- f :
-
Base fluid
- p :
-
Particle
References
Das S.K., Putra N., Roetzel W.: Pool boiling characteristics of nano-fluids. Int. J. Heat Mass Transf. 46, 851–862 (2003)
Das S.K., Putra N., Roetzel W.: Pool boiling nano-fluids on horizontal narrow tubes. Int. J. Multiph. Flow 29, 1237–1247 (2003)
You S.M., Kim J.H., Kim K.M.: Effect of nanoparticles on critical heat flux of water in pool boiling of heat transfer. Appl. Phys. Lett. 83(16), 3374–3376 (2003)
Vassallo P., Kumar R., D’Amico S.: Pool boiling heat transfer experiments in silica–water nano-fluids. Int. J. Heat Mass Transf. 47(2), 407–411 (2004)
Bang I.C., Chang S.H.: Boiling heat transfer performance and phenomena of Al2O3–water nano-fluids from a plain surface in a pool. Int. J. Heat Mass Transf. 48, 2407–2419 (2005)
Wen D., Ding Y.: Experimental investigation into the pool boiling heat transfer of aqueous based alumina nanofluids. J. Nanopart Res. 7, 265–274 (2005)
Zhou D.W.: Heat transfer enhancement of copper nanofluid with acoustic cavitations. Int. J. Heat Mass Transf. 47, 3109–3117 (2004)
Kim H., Kim J., Kim M.: Experimental study on CHF characteristics of water–TiO2 nano-fluids. Nucl. Eng. Technol. 38, 61–68 (2006)
Kim H., Kim J., Kim M.: Effect of nanoparticles on CHF enhancement in pool boiling of nano-fluids. Int. J. Heat Mass Transf. 49, 5070–5074 (2006)
Ding, Y.; Chen, H.; Wang, L.; Yang, C.Y.; Yurong, H.; Yang, W.; Lee, W.P.; Zhang, L.; Huo, R.: Heat transfer intensification using nanofluids. KONA 25 (2007)
Prakash N.G.; Anoop, K.B.; Das, S.K.: Effect of surface particle interaction on boiling heat transfer of nanoparticle suspensions. J. Appl. Phys. 102 (2007)
Prakash N.G.; Anoop, K.B.; Sateesh, G.; Das, S.K.: Effect of surface orientation on pool boiling heat transfer of nanoparticle suspensions. Int. J. Multiph. Flow (2007)
Golubovic M.N., Hettiarachchi M.H.D., Worek W.M., Minkowycz W.J.: Nanofluids and critical heat flux, experimental and analytical study. Appl. Therm. Eng. 29, 1281–1288 (2009)
Liu, Z.; Liao, L.: Sorption and agglutination phenomenon of Nanofluids on a plain heating surface during pool boiling. Int. J. Heat Mass Transf. 51 2593–2602 (2008)
Trisaksri V., Wongwises S.: Nucleate pool boiling heat transfer of TiO2–R141b nanofluids. Int. J. Heat Mass Transf. 52, 1582–15888 (2009)
Roy G., Nguyen C.T., Lajoie P.R.: Numerical investigation of laminar flow and heat transfer in a radial flow cooling system with the use of nanofluids. Superlattices Microstruct. 35, 497–511 (2004)
Trisaksri V., Wongwises S.: Critical review of heat transfer characteristics of nanofluids. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 11, 512–523 (2007)
Riehl, R.R.: Analysis of mini-loop heat pipe behavior nsing nanofluid
Mirmasoumi S., Behzadmehr A.: Numerical study of laminar mixed convection of a nanofluid in a horizontal tube using two-phase mixture model. Appl. Therm. Eng. 28, 717–727 (2008)
Zhu, D.; Li, X.; Wang, N.; Wang, X.; Gao, J.; Li, H.: Dispersion behavior and thermal conductivity characteristics of Al2O3–H2O nanofluids. Curr. Appl. Phys. (2008)
Chein R., Chuang J.: Experimental microchannel heat sink performance studies using nanofluids. Int. J. Therm. Sci. 46, 57–66 (2007)
Namburu, P.K.; Das, D.K.; Tanguturi, K.M.; Vajjha, R.S.: Numerical study of turbulent flow and heat transfer characteristics of nanofluids considering variable properties. Int. J. Therm. Sci. (2008)
Banerjee, D.; Ponnappan, R.: Flow loop experiments using nanofluid coolants. In: Proceedings of the Fourth U.S. Air Force-Taiwan Nanoscience Initiative Workshop (2007)
Akbarinia A.: Impacts of nanofluid flow on skin friction factor and Nusselt number in curved tubes with constant mass flow. Int. J. Heat Fluid Flow 29, 229–241 (2008)
Longo, G.: Nano-Fluids (2007)
Kulkarni, D.P.; Vajjha, R.S.; Das, D.K.; Oliva, D.: Application of aluminum oxide nanofluids in diesel electric generator as jacket water coolant. Appl. Therm. Eng. (2007)
Xuan, Y.; Roetzel, W.: Conceptions for heat transfer correlation of nanofluids. Int. J. Heat Mass Transf. 43, 3701–3707 (2000)
Brinkman, H.C.: The viscosity of concentrated suspensions and solutions. J. Chem. Phys. 20(4), 571 (1952)
Pak, B.C.; Cho, Y.I.: Hydrodynamic and heat transfer study of dispersed fluid with submicron metallic oxide particles. Exp. Heat Transf. 11, 15 (1998)
Wang, X.; Xu, X.; Choi, S.U.S.: Thermal conductivity of nanoparticle–fluid mixture. J. Therm. Phys. Heat Transf. 13, 474–80 (1999)
Maxwell, J.C.: A Treatise on Electricity and Magnetism, vol. 1. Clarendon, Oxford (1904)
Hamilton R.L., Crosser O.K.: Thermal conductivity of heterogeneous two-component systems. Ind. Eng. Chem. Fundam. 1(3), 187 (1962)
Jang S.P., Choi S.U.S.: Role of Brownian motion in the enhanced thermal conductivity of nanofluids. Appl. Phys. Lett. 84, 4316–4318 (2004)
Rohsenow W.M.: A method of correlating heat transfer data for surface boiling liquids. Trans. ASME 74, 969–976 (1952)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Das, S., Bhaumik, S. A Correlation for the Prediction of Heat Flux for Nucleate Pool Boiling Heat Transfer of Nanofluid. Arab J Sci Eng 39, 4997–5006 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13369-014-1081-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13369-014-1081-z