Abstract
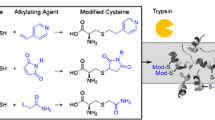
Protein S-glutathionylation is a reversible post-translational modification widely implicated in redox regulated biological functions. Conventional biochemical methods, however, often do not allow such a mixed disulfide modification to be reliably identified on specific cysteine residues or be distinguished from other related oxidized forms. To develop more efficient mass spectrometry (MS)-based analytical strategies for this purpose, we first investigated the MS/MS fragmentation pattern of S-glutathionylated peptides under various dissociation modes, including collision-induced dissociation (CID), higher-energy C-trap dissociation (HCD), and electron transfer dissociation (ETD), using synthetic peptides derived from protein tyrosine phosphatase as models. Our results indicate that a MALDI-based high energy CID MS/MS on a TOF/TOF affords the most distinctive spectral features that would facilitate rapid and unambiguous identification of site-specific S-glutathionylation. For more complex proteomic samples best tackled by LC-MS/MS approach, we demonstrate that HCD performed on an LTQ-Orbitrap hybrid instrument fairs better than trap-based CID and ETD in allowing more protein site-specific S-glutathionylation to be confidently identified by direct database searching of the generated MS/MS dataset using Mascot. Overall, HCD afforded more peptide sequence-informative fragment ions retaining the glutathionyl modification with less neutral losses of side chains to compromise scoring. In conjunction with our recently developed chemo-enzymatic tagging strategy, our nanoLC-HCD-MS/MS approach is sufficiently sensitive to identify endogenous S-glutathionylated peptides prepared from non-stressed cells. It is anticipated that future applications to global scale analysis of protein S-glutathionylation will benefit further from current advances in both speed and mass accuracy afforded by HCD MS/MS mode on the Orbitrap series.

ᅟ




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Dalle-Donne, I., Rossi, R., Giustarini, D., Colombo, R., Milzani, A.: S-glutathionylation in protein redox regulation. Free Radic. Biol. Med. 43, 883–898 (2007)
Forman, H.J., Fukuto, J.M., Torres, M.: Redox signaling: thiol chemistry defines which reactive oxygen and nitrogen species can act as second messengers. Am. J. Physiol. Cell Physiol. 287, C246–C256 (2004)
Giustarini, D., Rossi, R., Milzani, A., Colombo, R., Dalle-Donne, I.: S-glutathionylation: from redox regulation of protein functions to human diseases. J. Cell. Mol. Med. 8, 201–212 (2004)
Biswas, S., Chida, A.S., Rahman, I.: Redox modifications of protein-thiols: emerging roles in cell signaling. Biochem. Pharmacol. 71, 551–564 (2006)
Klatt, P., Lamas, S.: Regulation of protein function by S-glutathiolation in response to oxidative and nitrosative stress. Eur. J. Biochem. 267, 4928–4944 (2000)
Melissa, D., Shelton, P., Chock, B., Mieyal, J.J.: Glutaredoxin: role in reversible protein S-glutathionylation and regulation of redox signal transduction and protein translocation. Antioxid. Redox Signal. 7, 348–366 (2005)
Fratelli, M., Demol, H., Puype, M., Casagrande, S., Eberini, I., Salmona, M., Bonetto, V., Mengozzi, M., Duffieux, F., Miclet, E., Bachi, A., Vandekerckhove, J., Gianazza, E., Ghezzi, P.: Identification by redox proteomics of glutathionylated proteins in oxidatively stressed human T lymphocytes. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U. S. A. 99, 3505–3510 (2002)
Söderdahl, T., Enoksson, M., Lundberg, M., Holmgren, A., Ottersen, O.P., Orrenius, S., Bolcsfoldi, G., Cotgreave, I.A.: Visualization of the compartmentalization of glutathione and protein-glutathione mixed disulfides in cultured cells. FASEB J. 17, 124–126 (2003)
Dalle-Donne, I., Rossi, R., Giustarini, D., Colombo, R., Milzani, A.: Actin S-glutathionylation: evidence against a thiol-disulphide exchange mechanism. Free Radic. Biol. Med. 35, 1185–1193 (2003)
Mawatari, S., Murakami, K.: Different types of glutathionylation of hemoglobin can exist in intact erythrocytes. Arch. Biochem. Biophys. 421, 108–114 (2004)
Landino, L.M., Moynihan, K.L., Todd, J.V., Kennett, K.L.: Modulation of the redox state of tubulin by the glutathione/glutaredoxin reductase system. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 314, 555–560 (2004)
Craghill, J., Cronshaw, A.D., Harding, J.J.: The identification of a reaction site of glutathione mixed-disulphide formation on S-crystallin in human lens. Biochem. J. 379, 595–600 (2004)
Aracena-Parks, P., Goonasekera, S.A., Gilman, C.P., Dirksen, R.T., Hidalgo, C., Hamilton, S.L.: Identification of cysteines involved in S-nitrosylation, S-glutathionylation, and oxidation to disulfides in ryanodine receptor type 1. J. Biol. Chem. 281(52), 40354–40368 (2006)
Barbirz, S., Happersberger, H.P., Przybylski, M., Glocker, M.O.: Selective cyanylation of cysteinyl residues as an approach for the mass spectrometric determination of protein structures. Eur. Mass Spectrom. 5, 123–131 (1999)
Sullivan, D.M., Levine, R.L., Finkel, T.: Detection and affinity purification of oxidant-sensitive proteins using biotinylated glutathione ethyl ester. Methods Enzymol. 353, 101–113 (2002)
Brennan, J.P., Miller, J.I.A., Fuller, W., Wait, R., Begum, S., Dunn, M.J., Eaton, P.: The utility of N,N-biotinyl glutathione disulfide in the study of protein S-glutathiolation. Mol. Cell. Proteomics 5(2), 215–225 (2006)
Hamnell-Pamment, Y., Lind, C., Palmberg, C., Bergman, T., Cotgreave, I.A.: Determination of site-specificity of S-glutathionylated cellular proteins. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 332, 362–369 (2005)
Su, D., Gaffrey, M.J., Guo, J., Hatchell, K.E., Chu, R.K., Clauss, T.R.W., Aldrich, J.T., Wu, S., Purvine, S., Camp, D.G., Smith, R.D., Thrall, B.D., Qian, W.J.: Proteomic identification and quantification of S-glutathionylation in mouse macrophages using resin-assisted enrichment and isobaric labeling. Free Radic. Biol. Med. 67, 460–470 (2014)
Chiang, B.Y., Chou, C.C., Hsieh, F.T., Gao, S., Lin, J.C.Y., Lin, S.H., Chen, T.C., Khoo, K.H., Lin, C.H.: In vivo tagging and characterization of S-glutathionylated proteins by a chemoenzymatic method. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 51, 5871–5875 (2012)
Samarasinghe, K.T.G., Godage, D.N.P.M., VanHecke, G.C., Ahn, Y.-H.: Metabolic synthesis of clickable glutathione for chemoselective detection of glutathionylation. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 136, 11566–11569 (2014)
Srikanth, R., Wilson, J., Bridgewater, J.D., Numbers, J.R., Lim, J., Olbris, M.R., Kettani, A., Vachet, R.W.: Improved sequencing of oxidized cysteine and methionine containing peptides using electron transfer dissociation. J. Am. Soc. Mass Spectrom. 18, 1499–1506 (2007)
Olsen, J.V., Macek, B., Lange, O., Makarov, A., Horning, S., Mann, M.: Higher-energy C-trap dissociation for peptide modification analysis. Nat. Methods 4(9), 709–712 (2007)
Syka, J.E., Coon, J.J., Schroeder, M.J., Shabanowitz, J., Hunt, D.F.: Peptide and protein sequence analysis by electron transfer dissociation mass spectrometry. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U. S. A. 101, 9528–9533 (2004)
Chi, A., Huttenhower, C., Geer, L.Y., Coon, J.J., Syka, J.E.P., Bai, D.L., Shabanowitz, J., Burke, D.J., Troyanskaya, O.G., Hunt, D.F.: Analysis of phosphorylation sites on proteins from Saccharomyces cerevisiae by electron transfer dissociation (ETD) mass spectrometry. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U. S. A. 104(7), 2193–2198 (2007)
Good, D.M., Wirtala, M., McAlister, G.C., Coon, J.J.: Performance characteristics of electron transfer dissociation mass spectrometry. Mol. Cell. Proteomics 6(11), 1942–1951 (2007)
Bean, M.F., Carr, S.A.: Characterization of disulfide bond position in proteins and sequence analysis of cysteine-bridged peptides by tandem mass spectrometry. Anal. Biochem. 201, 216–226 (1992)
Rinna, A., Torres, M., Forman, H.J.: Stimulation of the alveolar macrophage respiratory burst by ADP causes selective glutathionylation of protein tyrosine phosphatase 1B. Free Radic. Biol. Med. 41, 86–91 (2006)
Cross, J.V., Templeton, D.J.: Oxidative stress inhibits MEKK1 by site-specific glutathionylation in the ATP-binding domain. Biochem. J. 381, 675–683 (2004)
Shelton, M.D., Kern, T.S., Mieyal, J.J.: Glutaredoxin regulates nuclear factor κ-B and intercellular adhesion molecule in Muller cells: model of diabetic retinopathy. J. Biol. Chem. 282, 12467–12474 (2007)
Clavreul, N., Adachi, T., Pimental, D.R., Ido, Y., Schöneich, C., Cohen, R.A.: S-glutathiolation by peroxynitrite of p21ras at cysteine-118 mediates its direct activation and downstream signaling in endothelial cells. FASEB J. 20, 518–520 (2006)
Lander, H.M.: An essential role for free radicals and derived species in signal transduction. FASEB J. 11, 118–124 (1997)
Meissner, F., Molawi, K., Zychlinsky, A.: Superoxide dismutase 1 regulates caspase-1 and endotoxic shock. Nat. Immunol. 9, 866–872 (2008)
Huang, Z., Pinto, J.T., Deng, H., Richie, J.P.J.: Inhibition of caspase-3 activity and activation by protein glutathionylation. Biochem. Pharmacol. 75, 2234–2244 (2008)
Zheng, M., Åslund, F., Storz, G.: Activation of the OxyR transcription factor by reversible disulfide bond formation. Science 279, 1718–1721 (1998)
Kim, S.O., Merchant, K., Nudelman, R., Beyer, W.F.J., Keng, T., DeAngelo, J., Hausladen, A., Stamler, J.S.: OxyR: a molecular code for redox-related signaling. Cell 109, 383–396 (2002)
Prinarakis, E., Chantzoura, E., Thanos, D., Spyrou, G.: S-glutathionylation of IRF3 regulates IRF3-CBP interaction and activation of the IFN beta pathway. EMBO J. 27, 865–875 (2008)
Dalle-Donne, I., Rossi, R., Colombo, G., Giustarini, D., Milzani, A.: Protein S-glutathionylation: a regulatory device from bacteria to humans. Trends Biochem. Sci. 34(2), 85–96 (2009)
Barrett, W.C., DeGnore, J.P., Konig, S., Fales, H.M., Keng, Y.F., Zhang, Z.Y., Yim, M.B., Chock, P.B.: Regulation of PTP1B via glutathionylation of the active site cysteine 215. Biochemistry 38, 6699–6705 (1999)
Wang, Z., Park, K., Comer, F., Hsieh-Wilson, L.C., Saudek, C.D., Hart, G.W.: Site-specific GlcNAcylation of human erythrocyte proteins. Diabetes 58, 309–317 (2009)
Chong, C.M., Gao, S.J., Chiang, B.Y., Hsu, W.H., Lin, T.C., Chen, T.C., Lin, C.H.: An acyloxymethyl ketone-based probe to monitor the activity of glutathionylspermidine amidase in Escherichia coli. Chem. BioChem. 12(15), 2306–2309 (2011)
Olsen, J.V., de Godoy, L.M., Li, G., Macek, B., Mortensen, P., Pesch, R., Makarov, A., Lange, O., Horning, S., Mann, M.: Parts per million mass accuracy on an Orbitrap mass spectrometer via lock mass injection into a C-trap. Mol. Cell. Proteomics 4(12), 2010–2021 (2005)
Chiang, B.Y., Chen, T.C., Pai, C.H., Chou, C.C., Chen, H.H., Ko, T.P., Hsu, W.H., Chang, C.Y., Wu, W.F., Wang, A.H.J., Lin, C.H.: Protein S-thiolation by glutathionylspermidine (Gsp): the role of Escherichia coli Gsp synthetase/amidase in redox regulation. J. Biol. Chem. 285(33), 25345–25353 (2010)
Choi, S., Jeong, J., Na, S., Lee, H.S., Kim, H.Y., Lee, K.J., Paek, E.: New algorithm for the identification of intact disulfide linkages based on fragmentation characteristics in tandem mass spectra. J. Proteome Res. 9(1), 626–635 (2010)
Wells, J.M., McLuckey, S.A.: Collision‐induced dissociation (CID) of peptides and proteins. Methods Enzymol. 402, 148–185 (2005)
Chen, Y.Y., Chu, H.M., Pan, K.T., Teng, C.H., Wang, D.L., Wang, A.H., Khoo, K.H., Meng, T.C.: Cysteine S-nitrosylation protects protein-tyrosine phosphatase 1B against oxidation-induced permanent inactivation. J. Biol. Chem. 283(50), 35265–35272 (2008)
Pan, K.T., Chen, Y.Y., Pu, T.H., Chao, Y.S., Yang, C.Y., Bomgarden, R.D., Rogers, J.C., Meng, T.C., Khoo, K.H.: Mass spectrometry-based quantitative proteomics for dissecting multiplexed redox cysteine modifications in nitric oxide-protected cardiomyocyte under hypoxia. Antioxid. Redox Signal. 20(9), 1365–1381 (2014)
Acknowledgments
The authors acknowledge support for this work by the Academia Sinica and a Taiwan National Science Council grant (NSC100-2325-B-001-029) to the Core Facilities for Protein Structural Analysis located at the Institute of Biological Chemistry (IBC), Academia Sinica. The authors also acknowledge the use of Academia Sinica Mass Spectrometry Facilities at IBC.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
ESM 1
(DOCX 6775 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Chou, CC., Chiang, BY., Lin, J.CY. et al. Characteristic Tandem Mass Spectral Features Under Various Collision Chemistries for Site-Specific Identification of Protein S-Glutathionylation. J. Am. Soc. Mass Spectrom. 26, 120–132 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13361-014-1014-9
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13361-014-1014-9