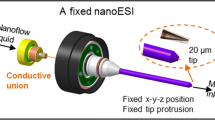
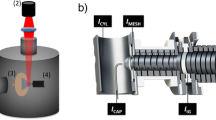
Abstract
Arrays of chemically etched emitters with individualized sheath gas capillaries were developed to enhance electrospray ionization (ESI) efficiency at subambient pressures. By incorporating the new emitter array in a subambient pressure ionization with nanoelectrospray (SPIN) source, both ionization efficiency and ion transmission efficiency were significantly increased, providing enhanced sensitivity in mass spectrometric analyses. The SPIN source eliminates the major ion losses of conventional ESI-mass spectrometry (MS) interfaces by placing the emitter in the first reduced pressure region of the instrument. The new ESI emitter array design developed in this study allows individualized sheath gas around each emitter in the array making it possible to generate an array of uniform and stable electrosprays in the subambient pressure (10 to 30 Torr) environment for the first time. The utility of the new emitter arrays was demonstrated by coupling the emitter array/SPIN source with a time of flight (TOF) mass spectrometer. The instrument sensitivity was compared under different ESI source and interface configurations including a standard atmospheric pressure single ESI emitter/heated capillary, single emitter/SPIN and multi-emitter/SPIN configurations using an equimolar solution of nine peptides. The highest instrument sensitivity was observed using the multi-emitter/SPIN configuration in which the sensitivity increased with the number of emitters in the array. Over an order of magnitude MS sensitivity improvement was achieved using multi-emitter/SPIN compared with using the standard atmospheric pressure single ESI emitter/heated capillary interface.

ᅟ






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Page, J.S., Marginean, I., Baker, E.S., Kelly, R.T., Tang, K., Smith, R.D.: Biases in ion transmission through an electrospray ionization-mass spectrometry capillary inlet. J. Am. Soc. Mass Spectrom. 20, 2265–2272 (2009)
Page, J.S., Kelly, R.T., Tang, K., Smith, R.D.: Ionization and transmission efficiency in an electrospray ionization-mass spectrometry interface. J. Am. Soc. Mass Spectrom. 18, 1582–1590 (2007)
Kebarle, P., Tang, L.: From ions in solution to ions in the gas-phase—the mechanism of electrospray mass spectrometry. Anal. Chem. 65, A972–A986 (1993)
Smith, R.D., Loo, J.A., Edmonds, C.G., Barinaga, C.J., Udseth, H.R.: New developments in biochemical mass-spectrometry-electrospray ionization. Anal. Chem. 62, 882–899 (1990)
Cech, N.B., Enke, C.G.: Practical implications of some recent studies in electrospray ionization fundamentals. Mass Spectrom. Rev. 20, 362–387 (2001)
Kim, T., Udseth, H.R., Smith, R.D.: Improved ion transmission from atmospheric pressure to high vacuum using a multicapillary inlet and electrodynamic ion funnel interface. Anal. Chem. 72, 5014–5019 (2000)
Ibrahim, Y., Tang, K., Tolmachev, A.V., Shvartsburg, A.A., Smith, R.D.: Improving mass spectrometer sensitivity using a high-pressure electrodynamic ion funnel interface. J. Am. Soc. Mass Spectrom. 17, 1299–1305 (2006)
Schneider, B.B., Javaheri, H., Covey, T.R.: Ion sampling effects under conditions of total solvent consumption. Rapid Commun. Mass Spectrom. 20, 1538–1544 (2006)
Pagnotti, V.S., Inutan, E.D., Marshall, D.D., McEwen, C.N., Trimpin, S.: Inlet ionization: a new highly sensitive approach for liquid chromatography/mass spectrometry of small and large molecules. Anal. Chem. 83, 7591–7594 (2011)
Wang, B., Inutan, E., Trimpin, S.: A new approach to high sensitivity liquid chromatography-mass spectrometry of peptides using nanoflow solvent assisted inlet ionization. J. Am. Soc. Mass Spectrom. 23, 442–445 (2012)
Pagnotti, V.S., Chakrabarty, S., Harron, A.F., McEwen, C.N.: Increasing the sensitivity of liquid introduction mass spectrometry by combining electrospray ionization and solvent assisted inlet ionization. Anal. Chem. 84, 6828–6832 (2012)
Page, J.S., Tang, K., Kelly, R.T., Smith, R.D.: Subambient pressure ionization with nanoelectrospray source and interface for improved sensitivity in mass spectrometry. Anal. Chem. 80, 1800–1805 (2008)
Tang, K., Page, J.S., Marginean, I., Kelly, R.T., Smith, R.D.: Improving liquid chromatography-mass spectrometry sensitivity using a subambient pressure ionization with nanoelectrospray (spin) interface. J. Am. Soc. Mass Spectrom. 22, 1318–1325 (2011)
Marginean, I., Kronewitter, S.R., Moore, R.J., Slysz, G.W., Monroe, M.E., Anderson, G., Tang, K., Smith, R.D.: Improving n-glycan coverage using hplc-ms with electrospray ionization at subambient pressure. Anal. Chem. 84, 9208–9213 (2012)
Kelly, R.T., Tolmachev, A.V., Page, J.S., Tang, K., Smith, R.D.: The ion funnel: theory, implementations, and applications. Mass Spectrom. Rev. 29, 294–312 (2010)
Cook, K.D.: Electrohydrodynamic mass-spectrometry. Mass Spectrom. Rev. 5, 467–519 (1986)
Prewett, P.D., Mair, G.L.R.: Focused ion beams from LMIS. pp. 1–332, Research Study Press, Sommeret, UK (1991)
Gamero-Castano, M., Aguirre-De-Carcer, I., de Juan, L., de la Mora, J.F.: On the current emitted by taylor cone-jets of electrolytes in vacuo: implications for liquid metal ion sources. J. Appl. Phys. 83, 2428–2434 (1998)
Romero-Sanz, I., de la Mora, J.F.: Energy distribution and spatial structure of electrosprays of ionic liquids in vacuo. J. Appl. Phys. 95, 2123–2129 (2004)
Sheehan, E.W.: Method and apparatus for improved electrospray analysis. USA Patent no. 5,838,002 (1998)
Sheehan, E.W., Willoughby, R.C., Jarrell, J.A., Strand, D.M.: Electrospray for chemical analysis. USA Patent no. 6,278,111 (2001)
Marginean, I., Page, J.S., Tolmachev, A.V., Tang, K., Smith, R.D.: Achieving 50% ionization efficiency in subambient pressure ionization with nanoelectrospray. Anal. Chem. 82, 9344–9349 (2010)
Wilm, M., Mann, M.: Analytical properties of the nanoelectrospray ion source. Anal. Chem. 68, 1–8 (1996)
El-Faramawy, A., Siu, K.W.M., Thomson, B.A.: Efficiency of nano-electrospray ionization. J. Am. Soc. Mass Spectrom. 16, 1702–1707 (2005)
Kelly, R.T., Page, J.S., Zhao, R., Qian, W.-J., Mottaz, H.M., Tang, K., Smith, R.D.: Capillary-based multi nanoelectrospray emitters: improvements in ion transmission efficiency and implementation with capillary reversed-phase LC-ESI-MS. Anal. Chem. 80, 143–149 (2008)
Mao, P., Wang, H.-T., Yang, P., Wang, D.: Multinozzle emitter arrays for nanoelectrospray mass spectrometry. Anal. Chem. 83, 6082–6089 (2011)
Gibson, G.T.T., Mugo, S.M., Oleschuk, R.D.: Nanoelectrospray emitters: trends and perspective. Mass Spectrom. Rev. 28, 918–936 (2009)
Tang, K., Lin, Y.H., Matson, D.W., Kim, T., Smith, R.D.: Generation of multiple electrosprays using microfabricated emitter arrays for improved mass spectrometric sensitivity. Anal. Chem. 73, 1658–1663 (2001)
Gibson, G.T.T., Wright, R.D., Oleschuk, R.D.: Multiple electrosprays generated from a single polycarbonate microstructured fibre. J. Mass Spectrom. 47, 271–276 (2012)
Kelly, R.T., Page, J.S., Tang, K., Smith, R.D.: Array of chemically etched fused-silica emitters for improving the sensitivity and quantitation of electrospray ionization mass spectrometry. Anal. Chem. 79, 4192–4198 (2007)
Kelly, R.T., Page, J.S., Marginean, I., Tang, K., Smith, R.D.: Nanoelectrospray emitter arrays providing interemitter electric field uniformity. Anal. Chem. 80, 5660–5665 (2008)
Su, S., Gibson, G.T.T., Mugo, S.M., Marecak, D.M., Oleschuk, R.D.: Microstructured photonic fibers as multichannel electrospray emitters. Anal. Chem. 81, 7281–7287 (2009)
Kim, W., Guo, M., Yang, P., Wang, D.: Microfabricated monolithic multinozzle emitters for nanoelectrospray mass spectrometry. Anal. Chem. 79, 3703–3707 (2007)
Sen, A.K., Darabi, J., Knapp, D.R.: Simulation and parametric study of a novel multi-spray emitter for esi-ms applications. Microfluid. Nanofluid. 3, 283–298 (2007)
Gomez, A., Bingham, D., de Juan, L., Tang, K.: Production of protein nanoparticles by electrospray drying. J. Aerosol Sci. 29, 561–574 (1998)
Romero-Sanz, I., Bocanegra, R., de la Mora, J.F., Gamero-Castano, M.: Source of heavy molecular ions based on taylor cones of ionic liquids operating in the pure ion evaporation regime. J. Appl. Phys. 94, 3599–3605 (2003)
Deng, W., Gomez, A.: Influence of space charge on the scale-up of multiplexed electrosprays. J. Aerosol Sci. 38, 1062–1078 (2007)
Kelly, R.T., Page, J.S., Luo, Q., Moore, R.J., Orton, D.J., Tang, K., Smith, R.D.: Chemically etched open tubular and monolithic emitters for nanoelectrospray ionization mass spectrometry. Anal. Chem. 78, 7796–7801 (2006)
Acknowledgment
Portions of this research were supported by the National Center for Research Resources (RR18522), National Cancer Institute (1R33CA155252), National Institute of General Medical Sciences Sciences (P41 GM103493-1), the Laboratory Directed Research and Development Program at Pacific Northwest National Laboratory (PNNL), and by the Department of Energy Office of Biological and Environmental Research Genome Sciences Program under the Pan-omics project. All the experiments were performed in the Environmental Molecular Sciences Laboratory, a US Department of Energy (DOE) national scientific user facility located at PNNL in Richland, Washington. PNNL is a multiprogramming national laboratory operated by Battelle for the DOE under contract DE-AC05-76RLO01830.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Figure SM1
Optical image of complete emitter assembly (a). Photomicrograph of a 10-emitter array with individualized sheath gas capillaries (b) (DOCX 4427 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Cox, J.T., Marginean, I., Kelly, R.T. et al. Improving the Sensitivity of Mass Spectrometry by Using a New Sheath Flow Electrospray Emitter Array at Subambient Pressures. J. Am. Soc. Mass Spectrom. 25, 2028–2037 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13361-014-0856-5
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13361-014-0856-5