Abstract
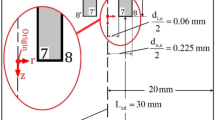
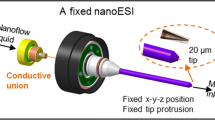
In this work, we propose a novel carbon nanofiber (CNF) emitter for electrospray ionization (ESI)–mass spectrometry (MS) applications. The proposed emitter comprises an array of CNFs around the orifice of a microscale capillary. The electrospray ionization process is simulated using a CFD code based on Taylor–Melcher leaky-dielectric formulations for solving the electrohydrodynamics and volume-of-fluid (VOF) method for tracking the interface. The code is validated for a conventional multiple electrospray emitter and then applied to simulate the CNF emitter model. The modeling results show that under steady state condition, individual cone-jets are established around each of the CNFs resulting in an array of electrosprays. The approach being taken to fabricate the CNF emitter is briefly discussed. Effects of geometrical parameters including aspect ratio of CNFs, total number of CNFs and distribution pattern of the CNFs on the electrospray performance are studied. The influence of operating parameters such as flow rate, potential difference and physical properties of the solvent on the electrospray behavior is thoroughly investigated. The spray current, ‘onset’ potential and jet diameter are correlated with total number and distribution of CNFs and physical properties of the liquid. The correlation results are compared with the available results in the literature. Higher spray current and lower jet diameter indicate that the device can perform equivalent to nanospray emitters while using a micro-scale orifice. This allows higher sample throughput and eliminates potential clogging problem inherent in nano-capillaries.



































Similar content being viewed by others
References
Amekinders JC, Jones C (1999) Multiple jet electrohydrodynamic spraying and applications. J Aerosol Sci 30:969–971
Amirkhani, A, Wetterhall M, Nilsson S, Danielsson R, Bergquist, J (2004) Comparison between different seathless electrospray emitter configurations regarding the performance of nanoscale liquid chromatography-time-of-flight mass spectrometric analysis. J Chromatogr A 1033:257–266
Arscott S, Le Gac S, Druon C, Tabourier P, Rolando C (2004)A planar micro-nib interface for nanoESI-MS microfluidic applications. J Micromech Microeng 14:310–316
Bocanegra R, Barrero A, Loscertales IG, Marquez M (2003) Multiplexing electrosprays emitted from an array of holes. In: 56th annual meeting of the division of fluid dynamics, Bull Am Phys Soc 48
Castellanos A (1998) Basic concepts and equations in electrohydrodynamics. In: Electrohydrodynamics, Springer, Berlin Heidelberg New York
Chhowalla M, Teo KBK, Ducati C, Rupesinghe NL, Amaratunga GAJ, Ferrari AC, Roy D, Robertson, J, and Milne WIJ (2001) Growth process conditions of vertically aligned carbon nanofibers using plasma enhanced chemical vapor deposition. Appl Phys Lett 90:5308
Clegg GA, Dole M (1971) Molecular beams of macroions. 3. Zein and polyvinylpyrrolidone. Biopolymers 10(5):821–826
Cloupeau M, Prunet-Foch B (1989) Electrostatic spraying of liquids in cone-jet mode. J Electrostat 22:135–59
De la Mora FJ, Loscertales IG (1994) The current emitted by highly conducting Taylor cones. J Fluid Mech 260: 155–184
Deng W, Li X, Klemic J, Reed M, Gomez A (2006) Increase of electrospray throughput using multiplexed microfabricated sources for the generation of monodisperse droplets. J Aerosol Sci 37:696–714
Dole M, Mack LL, Hines RL, Mobley RC, Ferguson LD, Alice MB (1968) Molecular beams of macroions. J Chem Phys 49:2240–2249
Duby MH, Deng W, Kim K, Gomez T, Gomez A (2006) Stabilization of monodisperse electrosprays in the multi-jet mode via electric field enhancement. J Aerosol Sci 37(3):306–322
Ebbesen TW, Ajayan PM (1992) Large-scale synthesis of carbon nanofibers. Nature (London) 358:220
Fenn, JB, Mann M, Meng CK, Wong SF, Whitehouse CM(1989) Electrospray ionization for mass spectrometry of large biomolecules. Science 246:64–71
Ganan-Calvo AM (1997) Cone–jet analytical extension of Taylor’s electrostatic solution and the asymptotic universal scaling laws in electrospraying. Phys Rev Lett 79:217–220
Ganan–Calvo AM, Davila J, Barrero A (1997) Current and droplet size in the electrospraying of liquids. Scaling laws. J Aerosol Sci 28:249–275
Griss P, Melin J, Sjodahl J, Rocraade J, Stemme G (2002) Development of micromachined hollow tips for protein analysis based on nanoelectrospray ionization mass spectrometry. J Micromech Microeng 12:682–687
Hartman RPA, Brunner DJ, Camelot DMA, Marijnissen JCM and Scarlett B (1999) Electrohydrodynamic atomization in the cone-jet mode physical modeling of the liquid cone and jet. J Aerosol Sci 30:823–49
Higuera FJ (2004) Current/flow–rate characteristic of an electrospray with a small meniscus. J Fluid Mech 513:239–46
Hirt CW, Nichols BD (1981) Volume of fluid (VOF) method for the dynamics of free boundaries. J Comput Phys 39:201–225
Hofmann S, Ducati C, Kleinsorge B, and Robertson J (2003) Low-temperature growth of carbon nanofibers by plasma-enhanced chemical vapor deposition. Appl Phys Lett 83:135–137
Hofmann S, Ducati C, Kleinsorge B, Robertson J (2003) Direct growth of aligned carbon nanofiber field emitter arrays onto plastic substrates. Appl Phys Lett 83(22):4661–4663
Huberman MN, Beynon JC, Cohen E, Goldin DS, Kidd PW, Zafran S (1968) Present status of colloid microthruster technology. J Spacecr Rockets 5:1319–1324
J Liu, KW Ro, R Nayak, DR Knapp (2006) Monolithic column plastic microfluidic device for peptide analysis using electrospray from a channel opening on the edge of the device. Int J Mass Spectrom (in press)
Jian L, Kyung WR, Mark B, and Knapp DR (2004) Electrospray Ionization with a pointed carbon fiber emitter. Anal Chem 76:3599–3606
Kaiser S, Kyritsis DC, Dobrowolski P, Long MB, Gomez A (2003) The electrospray and combustion at the mesoscale. J Mass Spectrom 51(1):42–49
Kim JS, Knapp DR (2001) Microfabrication of polydimethylsiloxane electrospray ionization emitters. J Chromatogr A 924:137–145
Melcher J R (1981) Continuum electromechanics. MIT Press, Cambridge
Melechko AV, McKnight TE, Hensley DK, Guillorn MA, Borisevich AY, Merkulov VI, Lowndes DH, Simpson ML (2003) Large scale synthesis of high-aspect-ratio rigid vertically aligned carbon nanofibers. Nanotechnology 14:1029–1035
Merkulov VI, Lowndes DH, Wei YY, Eres G, and Voelkl E (2000) Patterned growth of individual and multiple vertically aligned carbon nanofibers. Appl Phys Lett 76:3555
Regele JD, Papac MJ, Rickard MJA, Dunn-Rankin D (2002) Effects of capaillary spacing on EHD spraying from an array of cone jets. J Aerosol Sci 33:1471–1479
Ren ZF, Huang ZP, Xu JW, Wang JH, Bush P, Siegal MP, Provencio PN (1998) Synthesis of large arrays of well-aligned carbon nanofibers on thermoplastic. Science 282:1105–1107
Rulison AJ, Flagan R (1993) Scale-up of electrospray atomization using linear arrays of Taylor cones. Rev Sci Instrum 64:683–686
Ryu K, Kang M, Kim Y, Jeon H (2003) Low temperature growth of carbon nanotube by plasma-enhanced chemical vapor deposition using nickel catalyst. Jpn J Appl Phys 42:3578–3581
Saville DA (1997) Electrohydrodynamcis: the Taylor–Melcher leaky dielectric model. Annu Rev Fluid Mech 29:27–64
Schultz GA, Corso TN (2000) Proceedings of the 47th ASMS Conference on mass spectrometry and allied topics, Long Beach
Sen AK, Darabi J, Knapp DR, Liu J (2006) Modeling and characterization of a carbon fiber emitter for electrospray ionization. J Micromech Microeng 16:620–630
Tang K, Lin Y, Matson DW, Kim T, Smith RD (2001) Generation of multiple electrosprays using microfabricated emitter arrays for improved mass spectrometric sensitivity. Anal Chem 73:1658–1663
Thess A, Lee R, Nikolaev DH, Petit P, Robert J, Xu C, Lee YH, Kim SG, Rinzler AG, Colbert DT, Scuseria GE, Tomanek D, Fischer JE, Smalley RE (1996) Crystalline ropes of metallic carbon nanofibers. Science 273: 483
Trapp O, Pearce EW, Kimmel JR, Yoon OK, Zuleta IA, Zare RN (2005) A soft on-column metal coating procedure for robust seathless electrospray emitters used in capillary electrophoresis-mass spectrometry. Electrophoresis 26:1358–1365
Wang XQ, Desai A, Tai YC, Licklider L, Lee TD (1999) Polymer based electrospray chips for mass spectrometry. In: Proceedings of the IEEE micro electro mechanical systems (MEMS), Orlando, pp 523–528
Wang YX, Cooper JW, Lee CS, DeVoe DL (2004) Efficient electrospray ionization from polymer microchannels using integrated hydrophobic membranes. Lab Chip 4:363–367
Yoon SS, Heister SD, Epperson JT, Sojka PE (2001) Modeling multi-jet mode electrostatic atomization using boundary element methods. J Electrostatics 50(2):91–108
Zeleny J (1914) Phys Rev 3:69–91
Zeleny J (1917) Phys Rev 10:1–6
Acknowledgments
Supported in part by a grant from the University of South Carolina Research and Productive Scholarship Fund, NIH grant CA86285 and the NHLBI proteomics Initiative via contract N01-HV-28181 (D.R.K.).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Sen, A.K., Darabi, J. & Knapp, D.R. Simulation and parametric study of a novel multi-spray emitter for ESI–MS applications. Microfluid Nanofluid 3, 283–298 (2007). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10404-006-0122-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10404-006-0122-7