Abstract
Sexual fate of the sawfly, Athalia rosae (Hymenoptera: Tenthredinidae) is determined by the complementary sex determination (CSD) mechanism as is the case in honeybees. However, to date, genes involved in sex determination have not been identified in this species. In this study, we attempted to identify orthologs of complementary sex-determiner (csd), feminizer (fem), and doublesex (dsx) from the A. rosae genome, all of which are crucial components of the sex determination cascade in the honeybee. As a result, we identified a sawfly ortholog of dsx (designated as Ardsx). Rapid amplification of cDNA ends (RACE) using total RNA extracted from male and female larvae identified three male-specific variants and three female-specific variants. Comparison between the full-length Ardsx cDNAs and the genomic sequence revealed that exon 5 was differentially spliced between the male- and female-specific variants. RT-PCR analysis demonstrated that Ardsx pre-mRNA was spliced alternatively in a sex-dependent manner at almost all the developmental stages. RNAi-mediated knockdown of Ardsx in males caused severe defects in the reproductive organs and, notably, induced development of the ovipository apparatus containing the dorsal pair of blades and the sheath. These males also showed abnormalities in testes and seminal vesicles and lacked mature sperm. The present study provides the first direct evidence that dsx is essential for sexual development in hymenopteran species.
Similar content being viewed by others
Avoid common mistakes on your manuscript.
Introduction
In several hymenopteran insects, sexual fate is determined by the complementary sex determination (CSD) mechanism, in which heterozygosity at a single locus (the CSD locus) determines femaleness in diploid individuals, while haploid individuals are hemizygous for the CSD locus and thus develop into males (Whiting 1933). The CSD locus was first molecularly identified in the honeybee Apis mellifera and found to be a homolog of transformer (tra) (Beye et al. 2003). The tra gene is known to be a conserved upstream component of the insect sex determination cascade and induces female development by regulating sex-specific alternative splicing of downstream targets such as doublesex (dsx) (Gempe and Beye 2011; Hoshijima et al. 1991). A. mellifera has two copies of tra homologs (Hasselmann et al. 2008). One copy is named complementary sex-determiner (csd) that is the primary signal for femaleness. It activates the other copy, named feminizer (fem), which is more conserved and retains the ancestral function of regulating sex-specific alternative splicing dsx. The csd was considered to have arisen from duplication of the fem gene (Schmieder et al. 2012).
Orthologs of csd and fem have been identified not only in honeybee species but also in bumblebees and ants (Privman et al. 2013; Schmieder et al. 2012). Evolutional analyses demonstrate that the duplication of fem that yielded csd occurred before the divergence of Aculeata species (bees and ants), and also provide evidence that these two genes evolved concertedly through gene conversion. On the basis of these findings, it is supposed that csd likely represents the molecular basis for the CSD mechanism in the Aculeata species and, possibly, in the entire Hymenoptera order.
To verify this hypothesis, it is quite important to know whether hymenopteran species, which are more primitive than Aculeata species, also have csd and fem orthologs. The sawfly, Athalia rosae (Hymenoptera: Tenthredinidae), belongs to the Symphyta infra-order, which is the most primitive infra-order in Hymenoptera (Fig. 1a, b). Adults of this species show significant sexual dimorphisms in their gonads and genitalia (Hatakeyama et al. 1990a, b; Oishi et al. 1995). The male genitalia form a well-organized capsule, in repose retracted within the apical segments of the abdomen, as those reported in other sawfly species (Schulmeister 2003). In particular, the genitalia of females consist of a unique ovipository apparatus with a saw tooth-like structure, which is characteristic for the sawfly species (Ross 1945). Classical genetic analysis demonstrates that sexual fate in this species is also determined by the single-locus CSD system (Naito and Suzuki 1991). The number of alleles at this locus in a field population calculated by random crossing is 40–50 (Fujiwara et al. 2004). However, to date, genes involved in sex determination and sexual differentiation have not been identified in this species.
Identification of a dsx ortholog from A. rosae. Photographs of a last-instar larva (a) and adult male (b) of Athalia rosae. Scale bars indicate 2 mm. A tblastn search of the NCBI database was performed, specifying an A. rosae dataset, using the full amino acid sequence of DSX in Apis mellifera (AmDSX) as a query sequence. Distribution of six blast hits on the query sequence is described. One predicted gene (NCBI accession number XM_012406840.1) showed significant similarities to female-specific AmDSX isoform, AmDSXF1 (c) and male-specific AmDSX isoform, AmDSXM (d)
The whole genome sequencing (WGS) and assembly of Athalia rosae were conducted by the i5K Initiative (Baylor College of Medicine, https://www.hgsc.bcm.edu/arthropods/turnip-sawfly-genome-project) and the assembled data was submitted to the NCBI database in 2013 (GenBank assembly accession number GCA_000344095.1 Aros_1.0). Sequencing depth and coverage are highly sufficient (genome coverage 467.2×), and statistics of the assembly (number of scaffolds 522; number of contigs 7588; contig N50, 51,418; contig L50, 825) shows that the quality of the Athalia rosae genome assembly is good enough for sequence analyses. By using this Athalia rosae WGS data, here, we attempted to identify csd, fem, and dsx orthologs from the A. rosae genome to gain insights into whether the molecular mechanism for the sex determination observed in Aculeata species is conserved in Symphytan species. As a result, we successfully identified a sawfly ortholog of dsx, but failed to find genes homologous to csd and fem in the honeybee, Apis mellifera. The dsx ortholog was designated as Ardsx and its functions in sexual differentiation were assayed by RNAi analysis. Here we provide several lines of evidence that Ardsx is necessary for male development in the sawfly.
Materials and methods
Insect
The wild-type sawflies (Athalia rosae) and several mutant strains cream eye color (cec), short wing (sw), and yellow fat body (yfb), which had been kept at the National Agriculture and Food Research Organization, were used in this study. General biology of A. rosae is described in Oishi et al. (1993). Animals were reared continuously at 25 °C under 16 h light, 8 h dark conditions. The eggs were stored in plastic containers with sufficient humidity, and we used Japanese radish leaves (Sakata no tane) for larval feed. A hydroponic culture kit (Green Farm) was used for cultivation of the Japanese radish leaves. The cec gene is involved in pigmentation of eye, and animals homozygous for cec display cream-eye color (Lee et al. 1998). Adult wings of animals homozygous for sw become atrophied. Animals homozygous for yfb have fat bodies with yellow color (Sawa and Oishi 1989). On the basis of the phenotype of the recessive inheritance trait described above, we discriminated diploid females from fertilized eggs from haploid males from unfertilized eggs.
RNA extraction and RT-PCR
Extraction of total RNA was performed using ISOGEN (Nippon Gene, Tokyo, Japan) according to the protocol provided by the manufacture. A homogenization pestle (Funakoshi) was used for homogenizing samples. Total RNA extracted from samples during embryonic stage to young larval stages (2 days after hatching) were precipitated by addition of 1 μl of glycogen (20 mg/mL, Wako Junyaku) per sample. RT-PCR reactions were performed according to the protocol described previously (Suzuki et al. 2012). The ArEF1-LP and ArEF1-RP primers were used to amplify A. rosae elongation factor-1 alpha (EF-1) (NCBI accession number AB253792) as a positive control for the RT-PCR reaction. The primer sequences utilized in this study are indicated in Table 1. PCR products were analyzed on a 2% agarose gel and visualized with ethidium bromide.
Quantitative real-time RT-PCR
qRT-PCR assays were performed according to the protocol described previously (Suzuki et al. 2012). The ArEF1-LP and ArEF1-RP primers were used to amplify elongation factor-1 alpha (EF-1) as an internal standard for quantification. All primer sequences used in the qRT-PCR assays are listed in Table 2.
Rapid amplification of cDNA ends (RACE)
RACE was performed on the basis of previous protocols (Suzuki et al. 2010), except that the cDNA templates were prepared from whole bodies of pupae. All primer sequences used in RACE are listed in Table 3.
Preparation of dsRNAs
Two sequences conserved between the Ardsx isoforms were amplified with primer pairs ArdsxdsRNAF1-ArdsxdsRNAR1 and ArdsxdsRNAF2-ArdsxdsRNAR2 (Table 4), and they served as a DNA template for double-stranded RNA (dsRNA) synthesis. Each primer contained a T7 promoter site. The dsRNA synthesis was performed according to the protocol described previously (Suzuki et al. 2012).
Injection of dsRNAs into insects
The larvae and pupae were anesthetized by chilling for 30 min in a plastic container placed in an ice bath (Yoshiyama et al. 2013). Individuals receiving injection were left on an ice pack during the injection procedure. Injection was performed using a handmade injection apparatus (Hatakeyama et al. 1990a, b): a fine glass needle, made by pulling a 25-μl Microcaps (Drummond) and cutting the tip, was connected to a 1-ml plastic syringe. dsRNA was injected into the dorsal hemocoel in the second abdominal segment of the larva. Synthesized dsRNA was adjusted to a final concentration of 1 mg/ml, and injected at 3 mg per individual.
Phylogenetic analysis of Ardsx
Multiple alignment analysis of the complete amino acid sequences of Ardsx and known doublesex orthologs was performed using Clustal X 2.0.11 (http://www.softpedia.com/get/Science-CAD/Clustal-X.shtml) with the following settings (pairwise alignment parameters: gap opening penalty 17.00, gap extension penalty 0.2, identity protein weight matrix; multiple alignment parameters: gap opening penalty 17.00, gap extension penalty 0.2, delay divergent cutoff 30%, identity protein weight matrix). Matrices of amino acid p distances were calculated using the program MEGA version 4.0. A comparative phylogenetic tree was produced using the amino acid p distance method and the neighbor-joining algorithm with a bootstrap value of 1000.
Observation of internal and external genital organs
When preparing cuticle specimens of external genitalia, dissection was performed in 70% ethanol. The genitalia were trimmed and then dehydrated in 100% ethanol. The trimmed genitalia were put in a mixed solution of Canada balsam and methyl salicylate on a microscope slide, and covered with a glass coverslip to make cuticle specimens. The specimens were kept at 60 °C for 24 h, and observed under a stereoscope (Olympus SZX 7). To capture images, a CCD camera (Olympus DP 7) mounted on the stereoscope was used. The images were analyzed with CellSens standard software (Olympus). Adult gonads and internal reproductive organs were dissected out immediately after emergence in 1 × PBS. The dissected organs were observed using the stereoscope as described above.
Results
Homology-based search of sex-determining genes from Athalia rosae genome
Genetic analysis demonstrates that sexual fate in A. rosae is determined by the single-locus CSD system (Naito and Suzuki 1991). To investigate whether the molecular basis for the sex-determining mechanism of this insect is the same as those reported in honeybee species, a tblastn search of the NCBI database was performed, specifying an A. rosae dataset containing 22,130 of gene models, using the full amino acid sequence of CSD, FEM, and DSX in Apis mellifera as a query sequence. As a result, we were not able to find any sequences with significant homology to CSD and FEM. On the other hand, the tblastn search retrieved one predicted gene (NCBI accession number XM_012406840.1) with significant higher similarity (hit score >200, E value <e−60), when either female (AmDSXF1) or male-specific isoform (AmDSXM) of Apis mellifera DSX served as a query sequence (Fig. 1c, d). Comparison of the predicted protein encoded by the retrieved gene with proteins in the NCBI database using the blastp program indicated that XM_012406840.1 encodes a protein showing high homology to the female-specific DSX isoform (AmDSXF2) of A. mellifera with 54% identity and 69% similarity and also to the female-specific DSX isoform (TcDSXF3) of Tribolium castaneum with 49% identity and 59% similarity. Prediction of conserved protein domains using Pfam demonstrated that the protein encoded by XM_012406840.1 has a DM domain characteristic of the DM superfamily genes containing dsx, mab3, and Dmrt and the oligomerization domain that is characteristic for insect DSX. Taken together, we concluded that the predicted gene (XM_012406840.1) is an A. rosae ortholog of dsx, and hereafter we label this gene “Ardsx”.
Molecular cloning of full-length Ardsx cDNAs from males and females
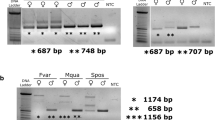
To examine whether the aforementioned genes retrieved by the tblastn searches are transcribed in vivo, we first performed RT-PCR analysis with primers that were designed on the basis of the nucleotide sequence of the predicted gene using cDNAs prepared from male and female pupae. The RT-PCR with primers dsx1 and dsx2 (amplicon size 1025 bp) amplified a DNA fragment whose size was almost similar to the predicted sizes in females (Fig. 2a, lane 2). On the other hand, in males, the same PCR resulted in an amplified product of approximately 1200 bp, which was larger than the expected size (Fig. 2a, lane 1). Similar results were obtained when the RT-PCR was performed with primers dsx1 and dsx7, which were designed to amplify a 1018-bp cDNA fragment (Fig. 2a, lanes 3 and 4). These RT-PCR products were cloned and sequenced. The sequences of the DNA fragments amplified from females were identical to that of XM_012406840.1, while the PCR products obtained from males were found to contain an insertion of 119 bp sequence (Fig. 2b). A blastn search of the A. rosae genome sequence (Version GCA_000344095.1 Aros_1.0) revealed that scaffold 11 contained the region encoding the whole sequence of the aforementioned cDNAs, which spanned at least 15 kb. Comparison between the cDNAs and the genomic DNA sequence demonstrated that the 119-bp fragment was derived from a single intronic sequence. Thus we concluded that inclusion of this intron in the pre-mRNA processing yields male-specific products. This strongly suggests that Ardsx in the sawfly may be sex-differentially spliced like dsx orthologs identified in other insects.
RT-PCR analysis of Ardsx expression in male and female pupae. a RT-PCR for expression pattern analysis of Ardsx mRNAs with primers that were designed on the basis of the nucleotide sequence of the predicted gene (XM_012406840.1) using cDNAs prepared from male and female pupae. Expected size of amplified product using a primer pair dsx1 and dsx2 is 1025 bp, whereas a primer pair dsx1 and dsx7 is expected to amplify 1018 bp of the DNA fragment. The approximate location of the primers (Ardsx1, Ardsx2, and Ardsx3) are described by red arrows in Fig. 3a. The upper panel shows Ardsx expression. The bottom panel shows amplification of the Ar EF-1 alpha (EF-1) transcript, which served as a positive control for RNA extraction and RT-PCR. PCR products were separated on 2% agarose gels and stained with ethidium bromide. Molecular sizes, presented in base pairs, are indicated to the right of each panel. b Comparison of nucleotide sequences of RT-PCR products amplified from male and female larvae. Dashes show alignment gaps. Nucleotides identical between both sexes are shaded black. Numbering is relative to the 5′ end of each of the RT-PCR product
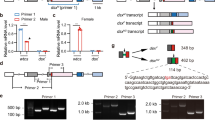
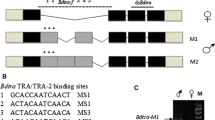
Next, we carried out RACE using total RNA samples purified from whole bodies of female and male pupae to determine the full-length coding and 5′ and 3′ sequences of the Ardsx gene. The 5′ ends of the Ardsx cDNAs determined by RACE were consistent with the 5′ end of the predicted gene XM_012406833.1. In addition, our 5′RACE amplified another two cDNA fragments, which respectively started at 698 and 380 nt upstream of the 5′ end of the predicted gene XM_012406833.1. Because no open reading frame of significant length was identified in these new fragments, we regarded them as 5′ UTRs. The 3′ RACE resulted in a single amplified product with a nucleotide sequence identical to the XM_012406840.1. The nucleotide sequences obtained by the aforementioned RACE showed no difference between males and females. Sex-specific difference was restricted to either presence or absence of the 119-bp sequence described in Fig. 2b. Consequently, Ardsx appeared to yield three male-specific variants (Ardsx M1, Ardsx M2, and Ardsx M3) and three female-specific variants (Ardsx F1, Ardsx F2, and Ardsx F3) (Fig. 3a). The difference among these variants rests entirely in the 5′ UTR, owing to alternative transcription start sites. Comparison between the full-length Ardsx cDNAs and the genomic sequence revealed that exon 5 was differentially spliced between male and female-specific isoforms (Fig. 3a). In the female isoforms, the male-specific 119-bp sequence, which contains a stop codon, was spliced out, causing amino acid sequence difference in the C-terminal region between male and female ArDSX isoforms.
Structures of the Ardsx splicing variants obtained by RACE and sexual difference in the expression pattern of Ardsx. a Upper panel shows the three male-specific Ardsx transcription variants (Ardsx M1, Ardsx M2, and Ardsx M3) and lower panel indicates three female-specific Ardsx transcription variants (Ardsx F1, Ardsx F2, and Ardsx F3) obtained by RACE. Boxes represent exons and lines are introns. Only exons are drawn to scale. The white regions indicate UTRs. The black regions indicate ORFs. The numbers shown above the box are exon numbers. The number indicated in each region describes the size in base pairs. ATG sites and stop codons are indicated. The red arrows show the approximate position of the primers (Ardsx1, Ardsx2, and Ardsx3) used for RT-PCR analysis illustrated in Fig. 2a. The black arrows indicate the approximate location of the primers (ArdsxFMF1 and ArdsxFMR1) that were used for RT-PCR described in b. b Sexual difference in the expression pattern of Ardsx mRNA was assessed by RT-PCR with primers described in a. Individuals hatched from fertilized eggs served as females, and individuals hatched from parthenogenetic eggs served as males. For embryonic stages, total RNA was extracted from a single egg at day 0, day 1, day 2, day 3, and day 4 after oviposition or parthenogenetic treatment. For larval stages, total RNA was extracted from a single animal at day 0–day 6 after hatching for males, and at day 0–day 7 after hatching for females since the larval period of females was 1 day longer than that of males. Total RNA was also isolated from a pupa at day 7 after pupation and an adult at day 5 after emerging. Bottom panel shows the results of RT-PCR amplification of the EF-1 transcript, which served as a positive control for the RT-PCR reaction. PCR products were analyzed on a 2% agarose gel. Arrows to the left of the gel refer to position of female and male specific-isoforms of Ardsx (Ardsx F1–F3 and Ardsx M1–M3). Molecular sizes, presented in base pairs, are indicated to the right of each panel
Ardsx M1, Ardsx M2, and Ardsx M3 encode the same protein (ArDSXM) of 233 amino acids. Ardsx F1, Ardsx F2, and Ardsx F3 also encode the protein with an identical sequence of 337 amino acids (ArDSXF). ArDSXM and ArDSXF share an N-terminal region of 222 amino acids that encodes a conserved DNA-binding domain called DM domain (or OD1 domain) and part of a conserved dimeriztion domain known as OD2 domain, which is specifically conserved among DSX proteins (Price et al. 2015) (Fig. 4a). Amino acid sequence of the C-terminal part shows difference between ArDSXM and ArDSXF (Fig. 4a).
Amino acid sequence of ArDSX and phylogeny of ArDSX with other insect DSX proteins. a Amino acid sequence comparison between ArDSXF and ArDSXM. Dashes show alignment gaps. Amino acids identical between both proteins are shaded black. The blue and the green lines indicate DM domain and dimerization domain, respectively. b A comparative phylogenetic tree was produced using the complete amino acid sequences of ArDSXF and 14 other known proteins, including DSX beta protein from Daphnia magna (BAJ78308), DSXF1 from Apis mellifera (ABW99105), BmDSXF from Bombyx mori (NP_001036871), DSXF1 from Onthophagus taurus (AEX92939), DSXF proteins from Nasonia vitripennis (NP_001155990), Ostrinia scapulalis (BAJ25852), Antheraea assama (ADL40852), Gnatocerus cornutus (BAW32685), Tribolium castaneum (AFQ62106), Megaselia scalaris (AAK38831), Musuca domestica (AAR23812), Bactrocera tryoni (AAB99948), Ceratitis capitata (AAN63598), and Drosophila melanogaster (NP_001287220). Bootstrap values for 1000 replicate analyses are shown at the branching points. The bar below the tree indicates the branch length representing the mean number of differences (0.05) per residue along each branch
Phylogenetic analysis using the full amino acid sequence of ArDSXF indicated that the identified sequence from A. rosae was grouped with other hymenopteran DSX proteins (Fig. 4b). These results strongly suggest that Ardsx is a dsx ortholog of A. rosae.
Expression analysis of Ardsx
As shown above, exon 5 of Ardsx was differentially spliced between two sexes, resulting in the male-specific insertion of the 119-bp fragment (Fig. 3a). To investigate whether sexual difference in the expression pattern of Ardsx mRNA changes according to the developmental stages, RT-PCR analysis was performed using cDNAs prepared from males and females at the different stages with primers that specifically anneal to the regions flanking the 119-bp fragment (Fig. 3b).
As a result, the amplification product of 269 bp was observed in males at all the examined stages (Fig. 3b). On the other hand, the same RT-PCR amplified the 150-bp DNA fragment in females throughout the examined stages. In females, the 269-bp DNA fragment was weakly detectable until 4 days after hatching. After that, the DNA band gradually disappeared with a concomitant increase in the amplification level of the 150-bp DNA fragment. After cloning of these amplified products and sequencing the cloned DNA, the amplified product of 269 bp corresponded to the male-specific Ardsx isoforms identified by RACE, while the RT-PCR product of 150 bp had a nucleotide sequence identical to that of the corresponding region in the female-specific Ardsx isoforms. These results clearly demonstrate that Ardsx pre-mRNA is spliced alternatively in a sex-dependent manner. However, in females, sex-specificity of the splicing is less accurate until middle larval stages, yielding the male-specific Ardsx in addition to the female-specific Ardsx isoforms.
Functional analysis of Ardsx
In order to analyze the function of Ardsx, we investigated the effects of Ardsx knockdown on sexual developments. Two different dsRNAs (Fig. 5a, Ardsx1 and Ardsx2), both of which targeted to a region common between Ardsx isoforms, were injected into larvae at the wandering stage. qRT-PCR analysis confirmed a significant reduction in Ardsx mRNA level in males and females injected with Ardsx1 (Fig. 5b). Similar results were observed when males and females were injected with Ardsx2 (data not shown). Morphological analysis of adult phenotypes demonstrated that negative control males and females, which were injected with dsRNA targeting the EGFP gene, had normal genital organs as observed in wild-type adult males and females (Fig. 5c, d, g). On the other hand, Ardsx knockdown males (Ardsx KD males) injected with Ardsx1 had external genital organs whose shapes were very similar to those observed in the control females (Fig. 5c). Normal females have external genitalia that contain an ovipository apparatus consisting of two pairs of valvifers, which give rise to the other parts: a saw formed by two pairs of blades (a ventral pair of blades derived from the first valvifers and a dorsal pair of blades derived from the second valvifers); and a sheath composed of a pair of appressed end segments of the second valvifers (Ross 1945) as represented by Fig. 5g. The genitalia observed in the Ardsx KD males contained several imcomplete parts of the ovipository apparatus including the dorsal pair of blades and the sheath, both of which are derived from the second valvifers (Fig. 5e). Differing from the normal female genitalia, Ardsx KD male genitalia lacked the ventral blades but instead contained an abnormal tissue with a saw tooth-like structure. Morphological analysis of internal reproductive organs revealed that these Ardsx KD males showed abnormal (Fig. 5k). Moreover, the seminal ducts looked thicker than those of the control male. The seminal vesicle filled with mature sperms in the control male (Fig. 5j) was not observed in the Ardsx knockdown males (Fig. 5k). Similar morphological abnormalities were observed in Ardsx KD males injected with Ardsx2 (Fig. 5f, l).
Effects of RNAi-mediated knockdown of Ardsx on sexual development. a Schematic diagram of two dsRNAs (Ardsx1 and Ardsx2) targeting Ardsx mRNA. b Quantification of Ardsx mRNA expression 1 day after injection by qRT-PCR. EF-1 served as an internal standard. Error bar standard deviation (SD); *significant differences at the 0.05 level (t test) compared with the control. c Ventral view of the abdominal segments of the negative control male (left), Ardsx knockdown male (middle), and the negative control female (right). Ventral view of the external genitalia in the negative control male (d), Ardsx knockdown male injected either with Ardsx1 (e) or Ardsx2 (f), the negative control female (g), and Ardsx knockdown female injected either with Ardsx1 (h) or Ardsx2 (i). Sa saw, Vb ventral pair of blades, Db dorsal pair of blades, Sh sheaths, S9 ninth sternite, Cu cuspis, He herpe, Pp parapenis, Pv penis valve; *abnormal tissue specifically observed in Ardsx knockdown males. Morphologies of testes and internal reproductive organs dissected out from the control male (j) and Ardsx knockdown male injected either with Ardsx1 (k) or Ardsx2 (l). Ts testis, Sv seminal vesicle, Ag accessory gland
Ardsx knockdown females injected either with Ardsx1 or Ardsx2 were also subjected to the same analyses but their external genitalia showed the same phenotype as those observed in the control females (Fig. 5h, i). All the examined Ardsx KD females had normal ovaries and internal reproductive organs and fertile (data not shown).
These results suggest that expression of Ardsx during the pupal stage is essential for normal sexual development in the male external genitalia and that its expression is also important for testis and seminal vesicle development.
Discussion
Despite the previous finding that sexual fate in A. rosae is determined by the single-locus CSD system (Naito and Suzuki 1991), we could not find genes showing significant homology to csd and fem in the A. rosae genome, both of which are core components for the honeybee CSD system. The csd was considered to have arisen from duplication of the fem gene (Schmieder et al. 2012) that is a tra homolog found in honeybees and other Aculeata species (Privman et al. 2013; Schmieder et al. 2012). To date, the tra gene has been identified not only in hymenopteran species but also in dipteran and coleopteran species. On the other hand, several previous studies and recent genome-wide analysis in a wide range of insect species revealed that tra shows a distinctly patchy distribution among insects (Geuverink and Beukeboom 2014). For example, no tra homologs have been identified in lepidopteran insects including Bombyx mori, Danaus plexippus, and Heliconius melpomene (Geuverink and Beukeboom 2014; Mita et al. 2004). One of the coleopteran species, Tribolium castaneum, carries a tra ortholog (Shukla and Palli 2012), while the tra gene has to date not been found in the genome of coleopteran Dendroctonus ponderosae (Geuverink and Beukeboom 2014). Mengenilla moldrzyki that belongs to Strepsiptera, which is a sister order of the Coleoptera, appeared to lack a tra homolog (Geuverink and Beukeboom 2014). The most interesting pattern of tra distribution is seen in the Diptera genus. The tra gene is found in brachycera species including D. melanogaster, while several mosquito species, which belong to a basal dipteran lineage, do not possess tra (Geuverink and Beukeboom 2014). These facts imply multiple independent losses or recruitment of tra into the sex determination cascade. It would be possible that A. rosae, which belongs to the most primitive infra-order in Hymenoptera, may not possess tra orthologs. It is well known that upstream components of the sex determination cascade are highly evolutionarily labile (Wilkins 1995). For example, in mosquito species, Aedes aegypti and Anopheles gambiae, maleness is determined by a dominant Y chromosome-linked M factor, but the gene encoding the M factor is completely different between these two species. Nix, which is a distant homolog of tra-2, functions as an M factor in A. aegypti, while Yob, which seemed to encode a short amino acid protein that may contain a helix-loop-helix motif, acts as an M factor in A. gambiae (Hall et al. 2015; Krzywinska et al. 2016). In the sawfly, a gene responsible for the CSD system might be different from those identified in multiple Aculeata species. However, we cannot rule out the possibility that our homology-based search using the tblastn program provided by NCBI may be inappropriate for identifying tra orthologs such as csd and fem from the A. rosae genome because of its less conserved sequences among groups.
In this paper, we provided several lines of evidence that a homolog of the dsx gene, named Ardsx, is also present in the A. rosae genome (Figs. 1c, d, 4b), and showed that Ardsx is transcribed into sex-specific mRNA isoforms as a result of sex-specific alternative splicing (Figs. 2, 3). The Ardsx mRNAs produced in males and females encode polypeptides sharing common N-terminal sequences but differing in C-terminal sequences (Fig. 4a), similar to the dsx orthologs identified in the honeybee and other multiple insect species. Concerning this point, it is presumed that Ardsx would take a splicing pattern similar to the honeybee dsx (Amdsx), but the following two points are significantly different: (1) Ardsx does not have a female-specific exon. In A. mellifera, the single female-specific exon in Amdsx F1 is skipped in the male variant (Amdsx M), resulting in the final two exons being shared between Amdsx F1 and Amdsx M (Cho et al. 2007). Similar sex-specific splicing pattern is reported in B. mori dsx (Suzuki et al. 2001). In A. rosae, the male-specific Ardsx contained a stop codon located in the middle of exon 5, while the region of 119 bp including the stop codon is skipped in the female-specific Ardsx isoforms (Fig. 3a). In other words, Ardsx has a female-specific intron. (2) In all the dsx orthologs so far characterized, skipping of an exon including a female-specific stop codon is seen only in males, whereas in A. rosae, skipping of the partial exonic region that includes the male-specific stop codon occurs in females (Fig. 3a). These findings may imply that the regulatory mechanism of sex-specific splicing of Ardsx may be different from that of Amdsx.
Ardsx knockdown adult males had several parts of the ovipository apparatus including the dorsal pair of blades and the sheath, both of which are derived from the second valvifers (Fig. 5e, f). These results indicate that development of the dorsal pair of blades and the sheath in males is repressed by the expression of ArDSXM and its expression is essential for development of the male genitalia. Differing from the normal ovipository apparatus, Ardsx KD male genitalia lacked the ventral pair of blades, which are derived from the first valvifers (Fig. 5e, f). In D. melanogaster, one of two isoforms of Abdominal-B (Abd-B), Abd-Bm, is present only in the female genital primordium, whereas the other isoform, Abd-Br, is present only in the male genital primordium (Casares et al. 1997; Duncan 1996). Concerted action of these two isoforms either with DSXM or DSXF is important for the appropriate sexual development of genital primordium (Sánchez et al. 2001). A previous study demonstrated that knockdown of Abd-B in A. rosae females caused a malformed ovipositor and these females could not lay eggs, while ovaries and internal reproductive organs were normal in appearance (Hatakeyama et al., unpublished data). If Abd-B in A. rosae also produces abdominal segment-specific isoforms like Abd-Bm and Abd-Br, then Abd-Bm in A. rosae may be able to facilitate the development of the ovipository apparatus including the dorsal pair of blades and the sheath without the help of ArDSXF since these organs were observed in Ardsx knockdown adults with almost complete phenotypes; whereas, concerted action of ArDSXF with Abd-Br may be necessary for the development of the ventral pair of blades. It is further postulated that ArDSXM together with Abd-Bm represses the development of the ovipository apparatus, resulting in the formation of the ninth sternite covering the copulatory organ (“9S” in Fig. 5d), and that ArDSXM plus Abd-Br promotes the development of the male copulatory organs. These hypotheses can explain the reason why the Ardsx knockdown males had the ovipository apparatus, which lacked the ventral pair of blades but instead had the abnormal tissue with a saw tooth-like structure. It would be expected that Abd-Br alone was not able to induce the development either of the ventral pair of blades or the copulatory organs, resulting in the formation of the abnormal tissue in Ardsx knockdown males. If so, then the knockdown of Ardsx should also cause some morphological defects in the ventral pair of blades in Ardsx knockdown females. However, the Ardsx knockdown females exhibited normal phenotype in their ovipository apparatus (Fig. 5h, i). One possible explanation for these results is that insufficient level of knockdown of endogenous Ardsx F expression might allow normal development of the ventral blades in the Ardsx knockdown females. Null mutation of Ardsx induced by gene targeting using TALEN and CRISPR/Cas9 will be helpful to further understand the importance of Ardsx functions for the development of the ovipository apparatus.
Effects of Ardsx knockdown on the development of internal reproductive organs seemed relatively weak. Male-to-female sex reversal such as partial ovary formation and egg production was not seen in the Ardsx knockdown males. Ardsx knockdown females were phenotypically normal and had normal fertility. In D. melanogaster, males homozygous for dsx loss-of-function mutant alleles contain gonads with spermatogenic and undifferentiated germ cells, and asexual gonads were rarely observed (Orssaud and Laugé 1982; Steinmann-Zwicky 1994). Similarly, ArDSXM may be required for sperm maturation in A. rosae. Thus, knockdown of Ardsx in males caused incomplete spermatogenesis, resulting in absence of mature sperm. Taken together with the findings that in D. melanogaster several genes such as fruitless (fru), intersex (ix), and hermaphrodite (her) act independently or dependently to regulate some aspects of sexual differentiation, we suppose that Ardsx function is not only required for the proper sexual development for the internal reproductive organs but other factors also act as a downstream regulator in the sex determination cascade in A. rosae.
The most notable result in this study is that knockdown of Ardsx caused ectopic formation of the ovipository apparatus containing the dorsal pair of blades and the sheath in males, both of which showed almost complete phenotype (Fig. 5e, f). This finding would seem to imply that formation of several parts of the ovipository apparatus represent the default state and do not require the expression of Ardsx. Hymenoptera is the most basal lineage in the phylogeny of holometabolous insects (superorder Endopterygota), being an outgroup to Diptera, Lepidoptera, and Coleoptera (Savard et al. 2006; Trautwein et al. 2012; Misof et al. 2014; Peters et al. 2014). The dsx gene in Daphnia magna that belongs to cladocera species, which are the closest relatives to the insects, is expressed predominantly in males and only required for male development (Kato et al. 2011). These findings lead to the inference that female sexual development might occur by default in ancestral insect species. To examine whether this hypothesis is correct or not, it will be important to reveal functions of dsx orthologs in other hymenopteran species.
References
Beye M, Hasselmann M, Fondrk MK, Page RE, Omholt SW (2003) The gene csd is the primary signal for sexual development in the honeybee and encodes an SR-type protein. Cell 114:419–429
Casares F, Sánchez L, Guerrero I, SanchezHerrero E (1997) The genital disc of Drosophila melanogaster. 1. Segmental and compartmental organization. Dev Genes Evol 207:216–228
Cho S, Huang ZY, Zhang J (2007) Sex-specific splicing of the honeybee doublesex gene reveals 300 million years of evolution at the bottom of the insect sex-determination pathway. Genetics 177:1733–1741
Duncan I (1996) How do single homeotic genes control multiple segment identities? BioEssays 18:91–94
Fujiwara Y, Akita K, Okumura W, Kodaka T, Tomioka K, Naito T (2004) Estimation of allele numbers at the sex-determining locus in a field population of the turnip sawfly (Athalia rosae). J Hered 95:81–84
Gempe T, Beye M (2011) Function and evolution of sex determination mechanisms, genes and pathways in insects. BioEssays 33:52–60
Geuverink E, Beukeboom LW (2014) Phylogenetic distribution and evolutionary dynamics of the sex determination genes doublesex and transformer in insects. Sex Dev 8:38–49
Hall AB, Basu S, Jiang X, Qi Y, Timoshevskiy VA, Biedler JK, Sharakhova MV, Elahi R, Anderson MA, Chen XG, Sharakhov IV, Adelman ZN, Tu Z (2015) A male-determining factor in the mosquito Aedes aegypti. Science 2348:1268–1270
Hasselmann M, Gempe T, Schiott M, Nunes-Silva CG, Otte M, Beye M (2008) Evidence for the evolutionary nascence of a novel sex determination pathway in honeybees. Nature 454:519–522
Hatakeyama M, Nakamura T, Kim KB, Sawa M, Naito T, Oishi K (1990a) Experiments inducing prospective polar body nuclei to participate in embryogenesis of the sawfly Athalia rosae (Hymenoptera). Roux’s Arch Dev Biol 198:389–394
Hatakeyama M, Sawa M, Oishi K (1990b) Ovarian development and vitellogenesis in the sawfly, Athalia rosae ruficornis Jakovlev (Hymenoptera, Tenthredinidae). Invertebr Reprod Dev 17:237–245
Hoshijima K, Inoue K, Higuchi I, Sakamoto H, Shimura Y (1991) Control of doublesex alternative splicing by transformer and transformer-2 in Drosophila. Science 252:833–836
Kato Y, Kobayashi K, Watanabe H, Iguchi T (2011) Environmental sex determination in the branchiopod crustacean Daphnia magna: deep conservation of a Doublesex gene in the sex-determining pathway. PLoS Genet 7:e1001345
Krzywinska E, Dennison NJ, Lycett GJ, Krzywinski J (2016) A maleness gene in the malaria mosquito Anopheles gambiae. Science 353:67–69
Lee JM, Hashino Y, Hatakeyama M, Oishi K, Naito T (1998) Egg deposition behavior in the haplodiploid sawfly Athalia rosae ruficornnis Jakovlev (Hymenoptera: Symphyta: Tenthredinidae). J Insect Behav 11:419–428
Misof B, Liu S, Meusemann K, Peters RS, Donath A et al (2014) Phylogenomics resolves the timing and pattern of insect evolution. Science 346:763–767
Mita K, Kasahara M, Sasaki S, Nagayasu Y, Yamada T et al (2004) The genome sequence of silkworm, Bombyx mori. DNA Res 11:27–35
Naito T, Suzuki H (1991) Sex determination in the sawfly, Athalia rosae ruficornis (Hymenoptera): occurrence of triploid males. J Hered 82:101–104
Oishi K, Sawa M, Hatakeyama M, Kageyama Y (1993) Genetics and biology of the sawfly, Athalia rosae (Hymenoptera). Genetica 88:119–127
Oishi K, Sawa M, Hatakeyama M (1995) Developmental biology of the sawfly, Athalia rosae (Hymenoptera). Proc Arthropod Embryol Soc Jpn 30:1–8
Orssaud L, Laugé G (1982) Etude histologique de l’appareil genital du mutant d’intersexualité doublesex (dsx) de Drosophila melanogaster Meigen (diptere: Drosophilidae). Int J Insect Morphol Embryol 11:53–67
Peters RS, Meusemann K, Petersen M, Mayer C, Wilbrandt J et al (2014) The evolutionary history of holometabolous insects inferred from transcriptome-based phylogeny and comprehensive morphological data. BMD Evol Biol 14:52
Price DC, Egizi A, Fonseca DM (2015) The ubiquity and ancestry of insect doublesex. Sci Rep 5:13068
Privman E, Wurm Y, Keller L (2013) Duplication and concerted evolution in a master sex determiner under balancing selection. Proc Biol Sci 280:20122968
Ross HH (1945) Sawfly genitalia: terminology and study techniques. Entomol News 10:261–265
Sánchez L, Gorfinkiel N, Guerrero I (2001) Sex determination genes control the development of the Drosophila genital disc, modulating the response to Hedgehog, Wingless and Decapentaplegic signals. Development 128:1033–1043
Savard J, Tautz D, Richards S, Weinstock GM, Gibbs RA, Werren JH, Tettelin H, Lercher MJ (2006) Phylogenomic analysis reveals bees and wasps (Hymenoptera) at the base of the radiation of Holometabolous insects. Genome Res 16:1334–1338
Sawa M, Oishi K (1989) Studies on the sawfly, Athalia rosae (Insecta, Hymenoptera, Tenthredinidae). III. Fertilization by sperm injection. Zool Sci 6:557–563
Schmieder S, Colinet D, Poirié M (2012) Tracing back the nascence of a new sex-determination pathway to the ancestor of bees and ants. Nat Commun 3:895
Schulmeister S (2003) Genitalia and terminal abdominal segments of male basal Hymenoptera (Insecta): morphology and evolution. Org Divers Evol 3:253–279
Shukla JN, Palli SR (2012) Sex determination in beetles: production of all male progeny by parental RNAi knockdown of transformer. Sci Rep 2:602
Steinmann-Zwicky M (1994) Sex determination of the Drosophila germ line: tra and dsx control somatic inductive signals. Development 120:707–716
Suzuki MG, Ohbayashi F, Mita K, Shimada T (2001) The mechanism of sex-specific splicing at the doublesex gene is different between Drosophila melanogaster and Bombyx mori. Insect Biochem Mol Biol 31:1201–1211
Suzuki MG, Imanishi S, Dohmae N, Asanuma M, Matsumoto S (2010) Identification of a male-specific RNA binding protein that regulates sex-specific splicing of Bmdsx by increasing RNA binding activity of BmPSI. Mol Cell Biol 30:5776–5786
Suzuki MG, Suzuki K, Aoki F, Ajimura M (2012) Effect of RNAi-mediated knockdown of the Bombyx mori transformer-2 gene on the sex-specific splicing of Bmdsx pre-mRNA. Int J Dev Biol 56:693–699
Trautwein MD, Wiegmann BM, Beutel R, Kjer KM, Yeates DK (2012) Advances in insect phylogeny at the dawn of the postgenomic era. Annu Rev Entomol 57:449–468
Whiting PW (1933) Selective fertilization and sex determination in Hymenoptera. Science 78:537–538
Wilkins AS (1995) Moving up the hierarchy: a hypothesis on the evolution of a genetic sex determination pathway. BioEssays 17:71–77
Yoshiyama N, Tojo K, Hatakeyama M (2013) A survey of the effectiveness of non-cell autonomous RNAi throughout development in the sawfly, Athalia rosae (Hymenoptera). J Insect Physiol 59:400–407
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by a Japan Society for the Promotion of Science (JSPS) KAKENHI Grant-in-Aid for Scientific Research (B) (Grant no. 26292172). It was also supported, in part, by a JSPS KAKENHI Grant-in-Aid for Challenging Exploratory Research (Grant no. 15K14892).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
Open Access This article is distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/), which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided you give appropriate credit to the original author(s) and the source, provide a link to the Creative Commons license, and indicate if changes were made.
About this article
Cite this article
Mine, S., Sumitani, M., Aoki, F. et al. Identification and functional characterization of the sex-determining gene doublesex in the sawfly, Athalia rosae (Hymenoptera: Tenthredinidae). Appl Entomol Zool 52, 497–509 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13355-017-0502-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13355-017-0502-3