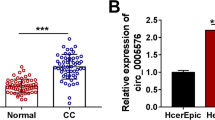
Abstract
The purpose of this study was to investigate the role of circ_0000119 on CC progression and its molecular mechanism. The expression levels of circ_0000119, miR-433-3p, and p21-activated kinase 2 (PAK2) in CC tissues and cell lines were measured by quantitative real-time polymerase chain reaction (qRT-PCR). Cell proliferation was assessed using 3-(4,5)-dimethylthiahiazo (-z-y1)-3,5-di-phenytetrazoliumromide (MTT) assay, 5-Ethynyl-2'-deoxyuridine (EdU) assay and colony formation assay. Cell cycle and apoptosis were assessed by flow cytometry. Cell migration and invasive ability were examined by Transwell assays. Downstream binding targets of circ_0000119 were predicted by online bioinformatics tools and confirmed by dual luciferase reporter gene assay, RNA immunoprecipitation (RIP) assay, and RNA pull-down assay. The role of circ_0000119/miR-433-3p/PAK2 axis in regulating the CC process was explored by rescue experiments. A xenograft model was constructed to further determine the effect of circ_0000119 on CC tumor growth in vivo. Immunohistochemistry (IHC) assay was conducted for Ki67 expression. Circ_0000119 was aberrantly upregulated in CC tissues and cell lines. Knockdown of circ_0000119 inhibited CC cell proliferation, cell cycle progress, migration, invasion, and promoted apoptosis of CC cells. MiR-433-3p was a binding target of circ_0000119, and PAK2 was a downstream gene of miR-433-3p. MiR-433-3p inhibition reversed the inhibitory effect of silencing circ_0000119 on CC progression. In addition, PAK2 overexpression reversed the effect of miR-433-3p on CC progression. PAK2 expression was regulated by circ_0000119 and miR-433-3p. Moreover, circ_0000119 knockdown reduced tumor growth of CC in vivo. Circ_0000119 was upregulated in CC, and circ_0000119 knockdown suppressed CC malignant development through the miR-433-3p/PAK2 axis.







Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
The data sets used and/or analyzed during the current study are available from the corresponding author on reasonable request.
References
Ali Syeda Z, Langden SSS, Munkhzul C, Lee M, Song SJ (2020) Regulatory mechanism of MicroRNA expression in cancer. Int J Mol Sci 21:1723
Arbyn M, Weiderpass E, Bruni L, de Sanjose S, Saraiya M, Ferlay J et al (2020) Estimates of incidence and mortality of cervical cancer in 2018: a worldwide analysis. Lancet Glob Health 8:e191–e203
Bai Y, Li X (2020) hsa_circ_0008285 facilitates the progression of cervical cancer by targeting miR-211-5p/SOX4 Axis. Cancer Manag Res 12:3927–3936
Bak RO, Mikkelsen JG (2014) miRNA sponges: soaking up miRNAs for regulation of gene expression. Wiley Interdiscip Rev RNA 5:317–333
Bi J, Liu H, Dong W, Xie W, He Q, Cai Z et al (2019) Circular RNA circ-ZKSCAN1 inhibits bladder cancer progression through miR-1178-3p/p21 axis and acts as a prognostic factor of recurrence. Mol Cancer 18:133
Bolha L, Ravnik-Glavac M, Glavac D (2017) Circular RNAs: biogenesis, function, and a role as possible cancer biomarkers. Int J Genomics 2017:6218353
Burd EM (2003) Human papillomavirus and cervical cancer. Clin Microbiol Rev 16:1–17
Cao L, Wang M, Dong Y, Xu B, Chen J, Ding Y et al (2020) Circular RNA circRNF20 promotes breast cancer tumorigenesis and Warburg effect through miR-487a/HIF-1alpha/HK2. Cell Death Dis 11:145
Coniglio SJ, Zavarella S, Symons MH (2008) Pak1 and Pak2 mediate tumor cell invasion through distinct signaling mechanisms. Mol Cell Biol 28:4162–4172
Ding L, Zhao Y, Dang S, Wang Y, Li X, Yu X et al (2019) Circular RNA circ-DONSON facilitates gastric cancer growth and invasion via NURF complex dependent activation of transcription factor SOX4. Mol Cancer 18:45
Hou XK, Mao JS (2020) Long noncoding RNA SNHG14 promotes osteosarcoma progression via miR-433-3p/FBXO22 axis. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 523:766–772
Huang A, Zheng H, Wu Z, Chen M, Huang Y (2020) Circular RNA-protein interactions: functions, mechanisms, and identification. Theranostics 10:3503–3517
Jay C, Nemunaitis J, Chen P, Fulgham P, Tong AW (2007) miRNA profiling for diagnosis and prognosis of human cancer. DNA Cell Biol 26:293–300
Jiao J, Zhang T, Jiao X, Huang T, Zhao L, Ma D et al (2020) hsa_circ_0000745 promotes cervical cancer by increasing cell proliferation, migration, and invasion. J Cell Physiol 235:1287–1295
Kulcheski FR, Christoff AP, Margis R (2016) Circular RNAs are miRNA sponges and can be used as a new class of biomarker. J Biotechnol 238:42–51
Lee JS, Mo Y, Gan H, Burgess RJ, Baker DJ, van Deursen JM et al (2019) Pak2 kinase promotes cellular senescence and organismal aging. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 116:13311–13319
Li H, Wu X, Cheng X (2016) Advances in diagnosis and treatment of metastatic cervical cancer. J Gynecol Oncol 27:e43
Li X, Yang L, Chen LL (2018) The biogenesis, functions, and challenges of circular RNAs. Mol Cell 71:428–442
Molli PR, Li DQ, Murray BW, Rayala SK, Kumar R (2009) PAK signaling in oncogenesis. Oncogene 28:2545–2555
Okunade KS (2020) Human papillomavirus and cervical cancer. J Obstet Gynaecol 40:602–608
Ou R, Lv J, Zhang Q, Lin F, Zhu L, Huang F et al (2020) circAMOTL1 motivates AMOTL1 expression to facilitate cervical cancer growth. Mol Ther Nucleic Acids 19:50–60
Rong D, Sun H, Li Z, Liu S, Dong C, Fu K et al (2017) An emerging function of circRNA-miRNAs-mRNA axis in human diseases. Oncotarget 8:73271–73281
Sharma S, Deep A, Sharma AK (2020) Current treatment for cervical cancer: an update. Anticancer Agents Med Chem 20:1768–1779
Shen T, Cheng X, Liu X, Xia C, Zhang H, Pan D et al (2019) Circ_0026344 restrains metastasis of human colorectal cancer cells via miR-183. Artif Cells Nanomed Biotechnol 47:4038–4045
Wang L, Tong X, Zhou Z, Wang S, Lei Z, Zhang T et al (2018) Circular RNA hsa_circ_0008305 (circPTK2) inhibits TGF-beta-induced epithelial-mesenchymal transition and metastasis by controlling TIF1gamma in non-small cell lung cancer. Mol Cancer 17:140
Wang YG, Wang T, Ding M, Xiang SH, Shi M, Zhai B (2019) hsa_circ_0091570 acts as a ceRNA to suppress hepatocellular cancer progression by sponging hsa-miR-1307. Cancer Lett 460:128–138
Wang F, Fan M, Cai Y, Zhou X, Tai S, Yu Y et al (2020) Circular RNA circRIMS1 acts as a sponge of miR-433-3p to promote bladder cancer progression by regulating CCAR1 expression. Mol Ther Nucleic Acids 22:815–831
Xu J, Zhang Y, Huang Y, Dong X, Xiang Z, Zou J et al (2020) circEYA1 functions as a sponge of miR-582-3p to suppress cervical adenocarcinoma tumorigenesis via upregulating CXCL14. Mol Ther Nucleic Acids 22:1176–1190
Yao GW, Bai JR, Zhang DP (2019) P21 activated kinase 2 promotes pancreatic cancer growth and metastasis. Oncol Lett 17:3709–3718
Yu T, Wang Y, Fan Y, Fang N, Wang T, Xu T et al (2019) CircRNAs in cancer metabolism: a review. J Hematol Oncol 12:90
Zhang Z, Yang T, Xiao J (2018) Circular RNAs: promising biomarkers for human diseases. EBioMedicine 34:267–274
Zhang J, Guo Y, Ma Y, Wang L, Li W, Zhang M et al (2022) miR-433-3p Targets AJUBA to inhibit malignant progression of glioma. NeuroImmunoModulation 29:44–54
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
J.Z. designed and supervised the study, conducted the experiments and drafted the manuscript. G.C. and L.Z. collected and analyzed the data. J.L. contributed the methodology. J.H. operated the software and edited the manuscript. All authors reviewed the manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Ethics approval and consent to participate
The collection of samples was approved by the Northwest Women’s and Children’s Hospital Ethics Committee.
This animal experiment was performed in strict accordance with the regulations and approved by the Animal Ethics Research Committee of Northwest Women’s and Children’s Hospital.
Consent for publication
Not applicable
Competing interests
The authors declare that they have no conflicts of interest.
Additional information
Communicated by: Maciej Szydlowski
Publisher's note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Materials
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Zhang, J., Chu, G., Zheng, L. et al. Circular RNA circ_0000119 promotes cervical cancer cell growth and migration via miR-433-3p/PAK2 axis. J Appl Genetics 64, 531–543 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13353-023-00772-w
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13353-023-00772-w