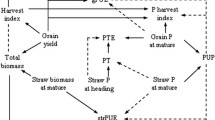
Abstract
Phosphorus (P) deficiency is one of the major limiting factors for rice productivity with only one locus (PSTOL1) available for field based application. A biparental mapping population (F6) derived from two P deficiency tolerant genotypes (Sahbhagi Dhan (SD) (PSTOL1+) and Chakhao Poreiton (CP) (PSTOL1−)), in which, transcriptome data generated from our lab had previously shown existence of diverse mechanisms was used to identify novel regions for better yield under lowland acidic soils. Phenotyping at F4, F5 and F6 generations revealed significant correlation between traits like tiller number at 30 days (TN 30), tiller number at 60 days (TN 60), filled grains (FG), percent spikelet fertility (SF%), panicle number (PN) and grain yield per panicle (GYPP) and also association with better yield/performance under low P acidic soil conditions. Through selected genotyping on a set of forty superior and inferior lines using SSR, candidate gene–based and SNP polymorphic markers, 5 genomic regions associated with various yield-related traits were identified. Marker trait association studies revealed 13 markers significantly associated with yield attributing traits and PUE under lowland acidic field conditions. Chi-square and regression analyses of markers run on the entire population identified seven and six markers for SF% and GYPP, respectively, and two for biological yield with positive allele derived from SD which constitute a novel 1.847-Mb region on chromosome 2 flanked by two markers RM12550 and PR9-2. Expression analysis of 7 candidate genes lying within this region across SD, CP and two low P susceptible rice genotypes has revealed that expression of four genes including SPL4, SPL5, ACA9 and MLO8 is significantly upregulated only in SD under low P conditions. In CP, there is low expression of MLO8 under low P conditions, whereas SPL4, SPL5 and Os02g08120 are downregulated. In the case of the two susceptible genotypes, there is no expression of Os02g08120 either in optimum or limiting conditions. Sequence data across a panel of 3024 rice genotypes also suggests that there is polymorphism for these differentially expressed genes. The genes and underlying markers identified on chromosome 2 will be key to imparting tolerance to low P in diverse genetic backgrounds and for marker-assisted selection for higher yield under lowland acidic conditions.






Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
The data sets supporting the results of this article are included within the article.
References
Ali J, Jewel ZA, Mahender A, Anandan A, Hernandez J, Li Z (2018) Molecular genetics and breeding for nutrient use efficiency in rice. Int J Mol Sci 19:E1762
Bhutia KL, Nongbri EL, Gympad E, Rai M, Tyagi W (2020) In silico characterization, and expression analysis of rice golden 2-like (OsGLK) members in response to low phosphorous. Mol Biol Rep 47:2529
Chen J, Liu Y, Ni J, Wang Y, Bai Y, Shi J, Gan J, Wu Z, Wu P (2011) OsPHF1 regulates the plasma membrane localization of low- and high-affinity inorganic phosphate transporters and determines inorganic phosphate uptake and translocation in rice. Plant Physiol 157:269–278
Chin JH, Lu X, Haefele SM, Gamuyao R, Ismail AM, Wissuwa M, Heuer S (2010) Development and application of gene-based markers for the major rice QTL phosphorus uptake 1. Theor Appl Genet 120:1073–1086
Das S, Tyagi W, Rai M, Yumnam JS (2017) Understanding Fe2+ toxicity and P deficiency tolerance in rice for enhancing productivity under acidic soils. Biotechol Genetic Eng 33:97–117
Delgado M, Zúñiga-Feest A, Almonacid L, Lambers H, Borie F (2015) Cluster roots of Embothrium coccineum (Proteaceae) affect enzyme activities and phosphorus lability in rhizosphere soil. Plant Soil 395:189–200
Dellaporta SL, Wood J, Hicks JB (1983) A plant DNA minipreparation: version II. Plant Mol Biol Rep 1:19–21
Deng Q-W, Luo X-D, Chen Y-L, Zhou Y, Zhang F-T, Biao-Lin Hu B-L, Xie J-K (2018) Transcriptome analysis of phosphorus stress responsiveness in the seedlings of Dongxiang wild rice (Oryza rufipogon Griff.). Biol Res 51:7
Domingo C, Lalanne E, Catalá MM, Pla E, Reig-Valiente JL, Talón M (2016) Physiological basis and transcriptional profiling of three salt-tolerant mutant lines of rice. Front Plant Sci 7:1462
Dutta SS, Tyagi W, Pale G, Pohlong J, Aochen C, Pandey A, Pattanayak A, Rai M (2018) Marker–trait association for low-light intensity tolerance in rice genotypes from Eastern India. Mol Genet Genomics 293:1493–1506
Florez-Sarasa I, Lambers H, Wang X, Finnegan PM, Ribas-Carbo M (2014) The alternative respiratory pathway mediates carboxylate synthesis in white lupin cluster roots under phosphorus deprivation. Plant Cell Environ 37:922–928
Gamuyao R, Hyoun CJ, Pariasca TJ, Pesaresi P, Catausan S, Dalid-Gasper C, Slamet-Loedin I, Tecson-Mendoza EM, Wissuwa M, Heuer S (2012) The protein kinase PSTOL1 from traditional rice confers tolerance of phosphorus deficiency. Nature 488:535–539
Gong YM, Guo ZH, He LY, Li JS (2011) Identification of maize genotypes with high tolerance or sensitivity to phosphorus deficiency. J Plant Nutr 34:1290–1302
Guo M, Ruan W, Li C, Huang F, Zeng M, Liu Y, Yu Y, Ding X, Wu Z, Mao C, Yi K, Wu P, Mo X (2015) Integrative comparison of the role of the PHOSPHATE RESPONSE1 subfamily in phosphate signaling and homeostasis in rice. Plant Physiol 168:1762–1776
He G, Luo X, Tian F, Li K, Zhu Z, Su W, Qian X, Fu Y, Wang X, Sun C, Yang J (2006) Haplotype variation in structure and expression of a gene cluster associated with a quantitative trait locus for improved yield in rice. Genome Res 16:618–626
He Q, Wang F, Wang Y, Lu H, Yang Z, Lv Q, Mao C (2019) Molecular control and genetic improvement of phosphorus use efficiency in rice. Mol Breeding 39:162
Hedley MJ, Kirk GJD, Santos MB (1994) Phosphorus efficiency and the forms of soil phosphorus utilized by upland rice cultivars. Plant Soil 158:53–62
Heuer S, Gaxiola R, Schilling R, Herrera-Estrella L, Lopez-Arredondo D, Wissuwa M, Delhaize E, Rouached H (2017) Improving phosphorus use efficiency: a complex trait with emerging opportunities. Plant J 90:868–885
Huang XH, Wei XH, Sang T, Zhao Q, Feng Q (2010) Genome-wide association studies of 14 agronomic traits in rice landraces. Nat Genet 42:961–967
Huda KKM, Yadav S, Banu MSA, Trivedi DK, Tuteja N (2013) Genome-wide analysis of plant-type II Ca2+ ATPases gene family from rice and Arabidopsis: potential role in abiotic stresses. Plant Physiol Biochem 65:32–47
Ismail AM, Heuer S, Thomson MJ, Wissuwa M (2007) Genetic and genomic approaches to develop rice germplasm for problem soils. Plant Mol Biol 65:547–570
Jewel ZA, Jauhar AJ, Pang Y, Li Z (2019) Identification of quantitative trait loci associated with nutrient use efficiency traits, using SNP markers in an early backcross population of rice (Oryza sativa L.). Int J Mol Sci 20:900
Jia HF, Ren HY, Gu MY, Zhao JN, Sun SB, Zhang X, Chen J, Wu P, Xu G (2011) The phosphate transporter gene OsPht1; 8 is involved in phosphate homeostasis in rice. Plant Physiol 156:1164–1175
Kumar A, Dixit S, Ram T, Yadav RB, Mishra KK, Mandal NP (2014) Breeding high-yielding drought-tolerant rice: genetic variations and conventional and molecular approaches. J Exp Bot 65:6265–6278
Li Y, Zhang J, Zhang X, Fan H, Gu M, Qu H (2015) Phosphate transporter OsPht1;8 in rice plays an important role in phosphorus redistribution from source to sink organs and allocation between embryo and endosperm of seeds. Plant Sci 230:23–32
Liu F, Wang Z, Ren H, Chenjia S, Li Y, Ling H-Q, Wu C, Lian X, Wu P (2010) OsSPX1 suppresses the function of OsPHR2 in the regulation of expression of OsPT2 and phosphate homeostasis in shoots of rice. Plant J 62:508–517
Liu F, Xu Y, Jiang H, Jiang C, Du Y, Gong C, Wang W, Zhu S, Han G, Cheng B (2016) Systematic identification, evolution and expression analysis of the Zea mays PHT1 gene family reveals several new members involved in root colonization by arbuscular mycorrhizal fungi. Int J Mol Sci 17:930
Lopez-Arredondo DL, Leyva-Gonzalez MA, Gonzalez-Morales SI, Lopez-Bucio J, Herrera-Estrella L (2014) Phosphate nutrition: improving low-phosphate tolerance in crops. Annu Rev Plant Biol 65:95–123
Luo XD, Liu J, Dai LF, Zhang FT, Wan Y, Xie JK (2017) Linkage map construction and QTL identification of P-deficiency tolerance in Oryza rufipogon Griff. at early seedling stage. Euphytica 213:96
Lynch JP (2011) Root phenes for enhanced soil exploration and phosphorus acquisition: tools for future crops. Plant Physiol 156:1041–1104
Mahender A, Swamy BPM, Anandan A, Ali J (2019) Tolerance of iron-deficient and -toxic soil conditions in rice. Plants 8:31
Mansueto L, Fuentes RR, Borja FN, Detras J, Abriol-Santos JM, Chebotarov D, Sanciangco M, Palis K, Copetti D, Poliakov A, Dubchak I, Solovyev V, Wing RA, Hamilton RS, Mauleon R, McNally KL, Alexandrov N (2017) Rice SNP-Seek Database update: new SNPs, indels, and queries. Nucleic Acids Res 45(D1):D1075–D1081
Marschner P (2012) Mineral nutrition of higher plants, third edn. Academic Press Inc., San Diego
Niu YF, Chai RS, Jin GL, Wang H, Tang CX, Zhang YS (2013) Responses of root architecture development to low phosphorus availability: a review. Ann Bot 112:391–408
Rao R, Neeraja CN, Srikanth B, Subrahmanyam D, Swamy KN, Rajesh K, Vijayalakshmi P, Kiran TV, Sailaja N, Revathi P, Rao PR, Rao LVS, Surekha K, Babhu VR, Voleti SR (2018) Identification of rice landraces with promising yield and the associated genomic regions under low nitrogen. Sci Rep 8:9200
Reddy VS, Ali GS, Reddy AS (2002) Genes encoding calmodulin-binding proteins in the Arabidopsis genome. J Biol Chem 277:9840–9852
Rose TJ, Wissuwa M (2016) Rethinking internal phosphorus utilization efficiency: a new approach is needed to improve PUE in grain crops. Adv Agron 116:185–217
Schiøtt M, Romanowsky SM, Baekgaard L, Jakobsen MK, Palmgren MG, Harper JF (2004) A plant plasma membrane Ca2+ pump is required for normal pollen tube growth and fertilization. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 101:9502–9507
Singh H, Singh H, Deshmukh RK, Singh A, Singh AK, Gaikwad K, Sharma TR, Mohapatra T, Singh NK (2010) Highly variable SSR markers suitable for rice genotyping using agarose gels. Mol Breed 25:359–364
Singh D, Singh NP, Chauhan SK, Singh P (2011) Developing aluminium tolerant crop plants using biotechnological tools. Curr Sci 100:1807–1814
Swamy BPM, Ahmed HU, Henry A, Mauleon R, Dixit S, Vikram P, Tilatto R, Satish B, Verulkar SB, Perraju P, Mandal NP, Variar M, Robin S, Chandrababu R, Singh ON, Dwivedi JL, Das SP, Mishra KK, Yadaw RB, Aditya TL, Karmakar B, Satoh K, Moumeni A, Kikuchi S, Leung H, Kumar A (2013) Genetic, physiological, and gene expression analyses reveal that multiple QTL enhance yield of rice mega-variety IR64 under drought. PLoS One 8:e62795
Tiwari KK, Singh A, Pattnaik S, Sandhu M, Kaur S, Jain S, Tiwari S, Mehrotra S, Anumalla M, Samal R, Bhardwaj J, Dubey N, Sahu V, Kharshing GA, Zeliang PK, Sreenivasan K, Kumar P, Parida SK, Mithra SVA, Rai V, Tyagi W, Agrawal PK, Rao AR, Pattanayak A, Chandel G, Singh AK, Bisht IS, Bhat KV, Rao GJN, Khurana JP, Singh NK, Mohapatra T (2015) Identification of a diverse mini-core panel of Indian rice germplasm based on genotyping using microsatellite markers. Plant Breed 134:164–171
Tyagi W, Rai M (2017) Root transcriptome of two acidic soil adapted Indica rice genotypes suggest diverse and complex mechanism of low phosphorus tolerance. Protoplasma 254:725–736
Tyburski J, Dunajska-Ordak K, Skorupa M, Tretyn A (2012) Role of ascorbate in the regulation of the Arabidopsis thaliana root growth by phosphate availability. J Bot 2012:1–11
Uexküll HR, Mutert E (1995) Global extent, development and economic impact of acid soils. Plant Soil 171:1–15
USDA (2018) https://www.fas.usda.gov/data/world-agricultural-production. Accessed 9 March 2019
Walder F, Brulé D, Koegel S, Wiemken A, Boller T, Courty P-E (2015) Plant phosphorus acquisition in a common mycorrhizal network: regulation of phosphate transporter genes of the Pht1 family in sorghum and flax. New Phytol 205:1632–1645
Wang Y, Itaya A, Zhong X, Wu Y, Zhang J, van der Knaap E, Olmstead R, Qi Y, Ding B (2011) Function and evolution of a microRNA that regulates a Ca2+-ATPase and triggers the formation of phased small interfering RNAs in tomato reproductive growth. Plant Cell 23:3185–3203
Wang S, Zhang S, Sun C, Xu Y, Chen Y, Yu C, Qian Q, Jiang DA, Qi Y (2014a) Auxin response factor (OsARF12), a novel regulator for phosphate homeostasis in rice (Oryza sativa). New Phytol 201:91–103
Wang Z, Ruan W, Shi J, Zhang L, Xian D, Yang C, Li C, Wu Z, Liu Y, Yu Y, Shou H (2014b) Rice SPX1 and SPX2 inhibit phosphate starvation responses through interacting with PHR2 in a phosphate-dependent manner. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 111:14953–14958
Watanabe T, Osaki M, Yano H, Rao IM (2006) Internal mechanisms of plant adaptation to aluminium toxicity and phosphorus starvation in tree tropical forages. J Plant Nutr 29:1243–1255
Wege S, Khan GA, Jung JY, Vogiatzaki E, Pradervand S, Aller I, Meyer AJ, Poirier Y (2016) The EXS domain of PHO1 participates in the response of shoots to phosphate deficiency via a root-to-shoot signal. Plant Physiol 170:385–400
White PJ, George TS, Dupuy LX, Karley AJ, Valentine TA, Weisel L, Wishart J (2013) Root traits for infertile soils. Front Plant Sci 4:19
Wissuwa M, Ae N (1999) Molecular markers associated with phosphorus uptake and internal phosphorus-use efficiency in rice. In: Gissel-Nielsen G, Jensen A (eds) Plant nutrition—molecular biology and genetics. Kluwer Academic Publishers, The Netherlands, pp 433–439
Wissuwa M, Yano M, Ae N (1998) Mapping of QTLs for phosphorus deficiency tolerance in rice (Oryza sativa L.). Theor Appl Genet 97:777–783
Wissuwa M, Wegner J, Ae N, Yano M (2002) Substitution mapping of Pup1: a major QTL increasing phosphorus uptake of rice from a phosphorus deficient soil. Theor Appl Genet 105:890–897
Wissuwa M, Kretzschmar T, Rose TJ (2016) From promise to application: root traits for enhanced nutrient capture in rice breeding. J Exp Bot 67:3605–3615
Yamaguchi T, Aharon GS, Sottosanto JB, Blumwald E (2005) Vacuolar Na+/H+ antiporter cation selectivity is regulated by calmodulin from within the vacuole in a Ca2+-and pH-dependent manner. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 102:16107–16112
Yumnam JS, Rai M, Tyagi W (2017a) Allele mining across two low-P tolerant genes PSTOL1 and PupK20-2 reveals novel haplotypes in rice genotypes adapted to acidic soils. Plant Genet Resour-C 15:221–229
Yumnam JS, Rai M, Tyagi W (2017b) In silico characterisation of novel rice transcripts differentially expressed in phosphorus deficient conditions suggests a role of these transcripts in multiple abiotic stresses. Acta Biol Hung 68:398–411
Yun SJ, Kaeppler SM (2001) Induction of maize acid phosphatase activities under phosphorus starvation. Plant Soil 237:109–115
Acknowledgements
Dr. Ng Eng Hwa is acknowledged for facilitating SNP genotyping under CGIAR, HTPG project.
Funding
WT was supported by the grants from Indian Council of Agricultural Research (NAIP; component IV; C30033/415101-036) and Department of Biotechnology, Government of India (BT/566/NE/U-excel/2016/72). KLB was supported by NFST (#201516-NFST-2015-17-ST-3514) from Ministry of Tribal Affairs, University Grant Commission, Government of India.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
MR and WT conceived the research plan and designed the experiments. KLB performed the phenotyping; KLB, ELN and TOS performed the genotyping. TOS and ELN generated the hydroponics and qRT-PCR data, respectively. KLB wrote the draft. KLB, ELN and TOS analyzed the data generated. WT and MR reviewed and edited the paper, providing helpful comments and discussions. All authors read and approved the final manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Ethics approval and consent to participate
Not applicable.
Consent for publication
Not applicable.
Additional information
Communicated by: Izabela Pawłowicz
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Bhutia, K.L., Nongbri, E.L., Sharma, T.O. et al. A 1.84-Mb region on rice chromosome 2 carrying SPL4, SPL5 and MLO8 genes is associated with higher yield under phosphorus-deficient acidic soil. J Appl Genetics 62, 207–222 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13353-020-00601-4
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13353-020-00601-4