Abstract
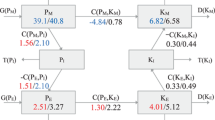
The global energy cycle is a diagnostic metric widely used to gauge the quality of datasets. In this paper, the “Mixed Space-Time Domain” method for diagnosis of energy cycle is evaluated by using newly developed datasets—the Chinese Reanalysis Interim (CRAI) and ECMWF Reanalysis version 5 (ERA5), over a 7-yr period (2010–16) on seasonal and monthly timescales. The results show that the energy components calculated from the two reanalysis datasets are highly consistent; however, some components in the global energy integral from CRAI are slightly larger than those from ERA5. The main discrepancy in the energy components stems from the conversion of baroclinic process, whereas the dominant difference originates from the conversion from stationary eddy available potential energy to stationary eddy kinetic energy (CES), which is caused by systematic differences in the temperature and vertical velocity in low-mid latitudes of the Northern Hemisphere and near the Antarctic, where there exist complex terrains. Furthermore, the monthly analysis reveals that the general discrepancy in the temporal variation between the two datasets also lie mainly in the CES as well as corresponding generation and dissipation rates.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Arpe, K., C. Branković, E. Oriol, et al., 1986: Variability in time and space of energetics from a long series of atmospheric data produced by ECMWF. Contrib. Atmos. Phys., 59, 321–355.
Boer, G. J., and S. Lambert, 2008: The energy cycle in atmospheric models. Climate Dyn., 30, 371–390, DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00382-007-0303-4.
Dee, D. P., S. M. Uppala, A. J. Simmons, et al., 2011: The ERA-Interim reanalysis: Configuration and performance of the data assimilation system. Quart. J. Roy. Meteor. Soc., 137, 553–597, DOI: https://doi.org/10.1002/qj.828.
Dickinson, R. E., 1969: Theory of planetary wave-zonal flow interaction. J. Atmos. Sci., 26, 73–81, DOI: https://doi.org/10.1175/1520-0469(1969)0262.0.CO;2.
Gao, H., L. X. Chen, J. H. He, et al., 2006: Characteristics of zonal propagation of atmospheric kinetic energy at equatorial region in Asia. Acta Meteor. Sinica, 20, 86–94.
Kalnay, E., M. Kanamitsu, R. Kistler, et al., 1996: The NCEP/NCAR 40-year reanalysis project. Bull. Amer. Meteor. Soc., 77, 437–472, DOI: https://doi.org/10.1175/1520-0477(1996)0772.0.CO;2.
Kanamitsu, M., W. Ebisuzaki, J. Woollen, et al., 2002: NCEP-DOE AMIP-II Reanalysis (R-2). Bull. Amer. Meteor. Soc., 83, 1631–1644, DOI: https://doi.org/10.1175/BAMS-83-11-1631.
Kim, Y. H., and M. K. Kim, 2013: Examination of the global Lorenz energy cycle using MERRA and NCEP-reanalysis 2. Climate Dyn., 40, 1499–1513, DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00382-012-1358-4.
Kistler, R., E. Kalnay, W. Collins, et al., 2001: The NCEP-NCAR 50-year reanalysis: Monthly means CD-ROM and documentation. Bull. Amer. Meteor. Soc., 82, 247–268, DOI: https://doi.org/10.1175/1520-0477(2001)0822.3.CO;2.
Li, L. M., A. P. Ingersoll, X. Jiang, et al., 2007: Lorenz energy cycle of the global atmosphere based on reanalysis datasets. Geophys. Res. Lett., 34, 16813, DOI: https://doi.org/10.1029/2007GL029985.
Li, Q. Q., and Q. G. Zhu, 1995: Analysis on the source and sink of kinetic energy of atmospheric 30–60 day period oscillation and the probable causes. Acta Meteor. Sinica, 9, 420–431.
Lorenz, E. N., 1955: Available potential energy and the maintenance of the general circulation. Tellus, 7, 157–167, DOI: https://doi.org/10.3402/tellusa.v7i2.8796.
Luo, Z. X., 1994: Effect of energy dispersion on the structure and motion of tropical cyclone. Acta Meteor. Sinica, 8, 51–59.
Marques, C. A. F., A. Rocha, J. Corte-Real, et al., 2009: Global atmospheric energetics from NCEP-reanalysis 2 and ECMWFERA40 reanalysis. Int. J. Climatol., 29, 159–174, DOI: https://doi.org/10.1002/joc.1704.
Marques, C. A. F., A. Rocha, and J. Corte-Real, 2010: Comparative energetics of ERA-40, JRA-25 and NCEP-R2 reanalysis, in the wave number domain. Dyn. Atmos. Oceans, 50, 375–399, DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.dynatmoce.2010.03.003.
Onogi, K., H. Koide, M. Sakamoto, et al., 2005: JRA-25: Japanese 25-year re-analysis project—progress and status. Quart. J. Roy. Meteor. Soc., 131, 3259–3268, DOI: https://doi.org/10.1256/qj.05.88.
Oort, A. H., 1964: On estimates of the atmospheric energy cycle. Mon. Wea. Rev., 92, 483–493, DOI: https://doi.org/10.1175/1520-0493(1964)0922.3.CO;2.
Oort, A. H., and J. P. Peixóto, 1974: The annual cycle of the energetics of the atmosphere on a planetary scale. J. Geophys. Res., 79, 2705–2719, DOI: https://doi.org/10.1029/JC079i018p02705.
Rienecker, M. M., M. J. Suarez, R. Gelaro, et al., 2011: MERRA: NASA’s modern-era retrospective analysis for research and applications. J. Climate, 24, 3624–3648, DOI: https://doi.org/10.1175/JCLI-D-11-00015.1.
Simmons, A. J., and B. J. Hoskins, 1980: Barotropic influences on the growth and decay of nonlinear baroclinic waves. J. Atmos. Sci., 37, 1679–1684, DOI: https://doi.org/10.1175/1520-0469(1980)0372.0.CO;2.
Steinheimer, M., M. Hantel, and P. Bechtold, 2008: Convection in Lorenz’s global energy cycle with the ECMWF model. Tellus A, 60, 1001–1022, DOI: https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1600-0870.2008.00348.x.
Stone, P. H., 1978: Baroclinic adjustment. J. Atmos. Sci., 35, 561–571, DOI: https://doi.org/10.1175/1520-0469(1978)0352.0.CO;2.
Ulbrich, U., and P. Speth, 1991: The global energy cycle of stationary and transient atmospheric waves: Results from ECMWF analyses. Meteor. Atmos. Phys., 45, 125–138, DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01029650.
Uppala, S. M., P. W. KÅllberg, A. J. Simmons, et al., 2005: The ERA-40 re-analysis. Quart. J. Roy. Meteor. Soc., 131, 2961–3012, DOI: https://doi.org/10.1256/qj.04.176.
von Storch, J. S., C. Eden, I. Fast, et al., 2012: An estimate of the Lorenz energy cycle for the world ocean based on the STORM/NCEP simulation. J. Phys. Oceanogr., 42, 2185–2205, DOI: https://doi.org/10.1175/JPO-D-12-079.1.
Zhao, B., and B. Zhang, 2014: Diagnostic study of global energy cycle of the GRAPES global model in the mixed space-time domain. J. Meteor. Res., 28, 592–606, DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s1351-014-3072-0.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Supported by the China Meteorological Administration (CMA) Special Public Welfare Research Fund (GYHY201506002), National Key Research and Development Program of China (2017YFA0604500), CMA Special Project for Developing Key Techniques for Operational Meteorological Forecast (YBGJXM201706), and National Natural Science Foundation of China (41305091).
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zhao, B., Zhang, B., Shi, C. et al. Comparison of the Global Energy Cycle between Chinese Reanalysis Interim and ECMWF Reanalysis. J Meteorol Res 33, 563–575 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13351-019-8129-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13351-019-8129-7