Abstract
The objective of the present work was to formulate, optimize, and evaluate transdermal terbutaline sulfate (TBN)-loaded bilosomes (BLS) in gel, compared to conventional oral TBN solution and transdermal gel loaded with free TBN, aiming at evading the hepatic first-pass metabolism. A face-centered central composite design was adopted to observe the effects of different formulation variables on TBN-BLS, and artificial neural network (ANN) modeling was employed to optimize TBN-BLS. TBN-BLS were prepared by a thin film hydration method integrating soybean phosphatidylcholine and cholesterol as a lipid phase and sodium deoxycholate (SDC) as a surfactant with or without the coating of chitosan (CTS). After being subjected to physicochemical characterization, TBN-BLS were enrolled in a histopathological study and pharmacokinetic investigation in a rat model. The optimized TBN chitosan-coated bilosomes (TBN-CTS-BLS) were spherical vesicles (245.13 ± 10.23 nm) with adequate entrapment efficiency (65.25 ± 5.51%) and good permeation characteristics (340.11 ± 22.34 μg/cm2). The TBN-CTS-BLS gel formulation was well-tolerated with no inflammatory signs manifested upon histopathological evaluation. The pharmacokinetic study revealed that the optimized TBN-CTS-BLS formulation successively enhanced the bioavailability of TBN by about 2.33-fold and increased t1/2 to about 6.21 ± 0.24 h as compared to the oral solution. These findings support the prospect use of BLS as active and safe transdermal carrier for TBN in the treatment of asthma.

Graphical Abstract







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Currie GP, Devereux GS, Lee DK, Ayres JG. Recent developments in asthma management. BMJ. 2005;330(7491):585–9.
Sandford AJ, Chagani T, Zhu S, Weir TD, Bai TR, Spinelli JJ, et al. Polymorphisms in the IL4, IL4RA, and FCERIB genes and asthma severity. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2000;106(1):135–40.
Narasimha Murthy S, Hiremath SR. Clinical pharmacokinetic and pharmacodynamic evaluation of transdermal drug delivery systems of salbutamol sulfate. Int J Pharm. 2004;287(1-2):47–53.
Sweetman SC. Martindale: The Complete Drug Reference. 34th ed. london: The Pharmaceutical Press; 2005.
Borgström L, Nyberg L, Jönsson S, Lindberg C, Paulson J. Pharmacokinetic evaluation in man of terbutaline given as separate enantiomers and as the racemate. Br J Clin Pharmacol. 1989;27(1):49–56.
Sayed S, Ibrahim HK, Mohamed MI, El-Milligi MF. Fast-dissolving sublingual films of terbutaline sulfate: formulation and in vitro/in vivo evaluation. Mol Pharm. 2013;10(8):2942–7.
Leferink JG, van den Berg W, Wagemaker-Engels I, Kreukniet J, Maes RA. Pharmacokinetics of terbutaline, a beta 2-sympathomimetic, in healthy volunteers and asthmatic patients. Arzneimittelforschung. 1982;32(2):159–64.
Mutlu GM, Moonjelly E, Chan L, Olopade CO. Laryngospasm and paradoxical bronchoconstriction after repeated doses of beta 2-agonists containing edetate disodium. Mayo Clin Proc. 2000;75(3):285–7.
Nagabhushana S. Harmful effects of aerosolised bronchodilator therapy in bronchiolitis. Indian Pediatr. 2000;37(6):684–7.
Ranade VV. Drug delivery systems. 6. Transdermal drug delivery. J Clin Pharmacol. 1991;31(5):401–18.
Prausnitz MR, Mitragotri S, Langer R. Current status and future potential of transdermal drug delivery. Nat Rev Drug Discov. 2004;3(2):115–24.
Ganem-Quintanar A, Silva-Álvarez M, Álvarez-Román R, Casas-Alancaster N, Cázares-Delgadillo J, Quintanar-Guerrero D, et al. Design and evaluation of a self-adhesive naproxen-loaded film prepared from a nanoparticle dispersion. J Nanosci Nanotechnol. 2006;6(9-10):3235–41.
Murthy SN, Hiremath SR. Physical and chemical permeation enhancers in transdermal delivery of terbutaline sulphate. AAPS PharmSciTech. 2001;2(1):E-TN1.
Panigrahi L, Pattnaik S, Ghosal SK. The effect of pH and organic ester penetration enhancers on skin permeation kinetics of terbutaline sulfate from pseudolatex-type transdermal delivery systems through mouse and human cadaver skins. AAPS PharmSciTech. 2005;6(2):E167–73.
Lee EH, Kim A, Oh YK, Kim CK. Effect of edge activators on the formation and transfection efficiency of ultradeformable liposomes. Biomaterials. 2005;26(2):205–10.
Honeywell-Nguyen PL, Bouwstra JA. Vesicles as a tool for transdermal and dermal delivery. Drug Discov Today Technol. 2005;2(1):67–74.
Shukla A, Mishra V, Kesharwani P. Bilosomes in the context of oral immunization: development, challenges and opportunities. Drug Discov Today. 2016;21(6):888–99.
Janga KY, Tatke A, Balguri SP, Lamichanne SP, Ibrahim MM, Maria DN, et al. Ion-sensitive in situ hydrogels of natamycin bilosomes for enhanced and prolonged ocular pharmacotherapy: in vitro permeability, cytotoxicity and in vivo evaluation. Artif Cells Nanomed Biotechnol. 2018;46(sup1):1039–50.
Hasanovic A, Hollick C, Fischinger K, Valenta C. Improvement in physicochemical parameters of DPPC liposomes and increase in skin permeation of aciclovir and minoxidil by the addition of cationic polymers. Eur J Pharm Biopharm. 2010;75(2):148–53.
Li L, Zhang Y, Han S, Qu Z, Zhao J, Chen Y, et al. Penetration Enhancement of Lidocaine Hydrochlorid by a Novel Chitosan Coated Elastic Liposome for Transdermal Drug Delivery. J Biomed Nanotechnol. 2011;7(5):704–13.
Takka S, Gürel A. Evaluation of chitosan/alginate beads using experimental design: formulation and in vitro characterization. AAPS PharmSciTech. 2010;11(1):460–6.
El-Mahrouk GM, El-Gazayerly ON, Aboelwafa AA, Taha MS. Chitosan lactate wafer as a platform for the buccal delivery of tizanidine HCl: in vitro and in vivo performance. Int J Pharm. 2014;467(1-2):100–12.
Kang ML, Cho CS, Yoo HS. Application of chitosan microspheres for nasal delivery of vaccines. Biotechnol Adv. 2009;27(6):857–65.
Thanou M, Verhoef JC, Junginger HE. Chitosan and its derivatives as intestinal absorption enhancers. Adv Drug Deliv Rev. 2001;50(Suppl 1):S91–101.
Nagarwal RC, Singh PN, Kant S, Maiti P, Pandit JK. Chitosan coated PLA nanoparticles for ophthalmic delivery: characterization, in-vitro and in-vivo study in rabbit eye. J Biomed Nanotechnol. 2010;6(6):648–57.
Smith J, Wood E, Dornish M. Effect of chitosan on epithelial cell tight junctions. Pharm Res. 2004;21(1):43–9.
He W, Guo X, Xiao L, Feng M. Study on the mechanisms of chitosan and its derivatives used as transdermal penetration enhancers. Int J Pharm. 2009;382(1-2):234–43.
Bangham AD, Standish MM, Watkins JC. Diffusion of univalent ions across the lamellae of swollen phospholipids. J Mol Biol. 1965;13(1):238–52.
Al-Mahallawi AM, Khowessah OM, Shoukri RA. Nano-transfersomal ciprofloxacin loaded vesicles for non-invasive trans-tympanic ototopical delivery: in-vitro optimization, ex-vivo permeation studies, and in-vivo assessment. Int J Pharm. 2014;472(1-2):304–14.
González-Rodríguez M, Arroyo C, Cózar-Bernal M, González-R P, León J, Calle M, et al. Deformability properties of timolol-loaded transfersomes based on the extrusion mechanism. Statistical optimization of the process. Drug Dev Ind Pharm. 2016;42(10):1683–94.
González-Rodríguez ML, Barros LB, Palma J, González-Rodríguez PL, Rabasco AM. Application of statistical experimental design to study the formulation variables influencing the coating process of lidocaine liposomes. Int J Pharm. 2007;337(1-2):336–45.
Guinedi AS, Mortada ND, Mansour S, Hathout RM. Preparation and evaluation of reverse-phase evaporation and multilamellar niosomes as ophthalmic carriers of acetazolamide. Int J Pharm. 2005;306(1-2):71–82.
Abdelbary AA, AbouGhaly MH. Design and optimization of topical methotrexate loaded niosomes for enhanced management of psoriasis: application of Box–Behnken design, in-vitro evaluation and in-vivo skin deposition study. Int J Pharm. 2015;485(1-2):235–43.
Al-mahallawi AM, Abdelbary AA, Aburahma MH. Investigating the potential of employing bilosomes as a novel vesicular carrier for transdermal delivery of tenoxicam. Int J Pharm. 2015;485(1-2):329–40.
Ahad A, Aqil M, Kohli K, Sultana Y, Mujeeb M, Ali A. Formulation and optimization of nanotransfersomes using experimental design technique for accentuated transdermal delivery of valsartan. Nanomedicine. 2012;8(2):237–49.
Mahmoud MO, Aboud HM, Hassan AH, Ali AA, Johnston TP. Transdermal delivery of atorvastatin calcium from novel nanovesicular systems using polyethylene glycol fatty acid esters: Ameliorated effect without liver toxicity in poloxamer 407-induced hyperlipidemic rats. J Control Release. 2017;254:10–22.
Wang Y, Wang S, Shi P. Transcriptional transactivator peptide modified lidocaine-loaded nanoparticulate drug delivery system for topical anesthetic therapy. Drug Deliv. 2016;23(9):3193–9.
Aboud HM, Hassan AH, Ali AA, Abdel-Razik AH. Novel in situ gelling vaginal sponges of sildenafil citrate-based cubosomes for uterine targeting. Drug Deliv. 2018;25(1):1328–39.
Günther F, Fritsch S. Neuralnet: Training of neural networks. The R Journal. 2010;2(1):30–8.
Elkomy MH, Elmenshawe SF, Eid HM, Ali AM. Topical ketoprofen nanogel: artificial neural network optimization, clustered bootstrap validation, and in vivo activity evaluation based on longitudinal dose response modeling. Drug Deliv. 2016;23(9):3294–306.
Ueda N, Nakano R. Estimating expected error rates of neural network classifiers in small sample size situations: a comparison of cross-validation and bootstrap. Neural Networks. Proceedings., IEEE International Conference on, IEEE. 1995;1:101–4.
Elkomy MH, El Menshawe SF, Eid HM, Ali AM. Development of a nanogel formulation for transdermal delivery of tenoxicam: a pharmacokinetic-pharmacodynamic modeling approach for quantitative prediction of skin absorption. Drug Dev Ind Pharm. 2017;43(4):531–44.
Elkomy MH, El-Menshawe SF, Ali AA, Halawa AA, El-Din ASGS. Betahistine dihydrochloride transdermal delivery via optimized thermosensitive gels: percutaneous absorption evaluation using rat growth as a biomarker. Drug Deliv Transl Res. 2018;8(1):165–77.
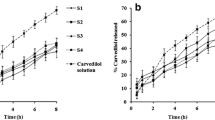
Aboud HM, Ali AA, El-Menshawe SF, Elbary AA. Nanotransfersomes of carvedilol for intranasal delivery: formulation, characterization and in vivo evaluation. Drug Deliv. 2016;23(7):2471–81.
Bancroft JD, Gamble M. Theory and practice of histological techniques: Elsevier Health Sci. 2008.
Nilsson HT, Persson CG, Persson K, Tegner K, Ryrfeldt A. The metabolism of terbutaline in dog and rat. Xenobiotica. 1973;3(9):615–23.
Dominguez-Romero JC, Garcia-Reyes JF, Martinez-Romero R, Martinez-Lara E, Del Moral-Leal ML, Molina-Diaz A. Detection of main urinary metabolites of beta2-agonists clenbuterol, salbutamol and terbutaline by liquid chromatography high resolution mass spectrometry. J Chromatogr B Anal Technol Biomed Life Sci. 2013;923-924:128–35.
El-Badry M, Fetih G, Fathalla D, Shakeel F. Transdermal delivery of meloxicam using niosomal hydrogels: in vitro and pharmacodynamic evaluation. Pharm Dev Technol. 2015;20(7):820–6.
Abu Hashim II, Abo El-Magd NF, El-Sheakh AR, Hamed MF, Abd El-Gawad AEH. Pivotal role of Acitretin nanovesicular gel for effective treatment of psoriasis: ex vivo-in vivo evaluation study. Int J Nanomedicine. 2018;13:1059–79.
Salem HF, Kharshoum RM, Sayed OM, Abdel Hakim LF. Formulation design and optimization of novel soft glycerosomes for enhanced topical delivery of celecoxib and cupferron by Box-Behnken statistical design. Drug Dev Ind Pharm. 2018;44(11):1871–84.
Sun Y, Peng Y, Chen Y, Shukla AJ. Application of artificial neural networks in the design of controlled release drug delivery systems. Adv Drug Deliv Rev. 2003;55(9):1201–15.
Ahmed TA. Preparation of transfersomes encapsulating sildenafil aimed for transdermal drug delivery: Plackett–Burman design and characterization. J Liposome Res. 2015;25(1):1–10.
Avadhani KS, Manikkath J, Tiwari M, Chandrasekhar M, Godavarthi A, Vidya SM, et al. Skin delivery of epigallocatechin-3-gallate (EGCG) and hyaluronic acid loaded nano-transfersomes for antioxidant and anti-aging effects in UV radiation induced skin damage. Drug Deliv. 2017;24(1):61–74.
Manca ML, Zaru M, Manconi M, Lai F, Valenti D, Sinico C, et al. Glycerosomes: a new tool for effective dermal and transdermal drug delivery. Int J Pharm. 2013;455(1-2):66–74.
Abdelbary AA, Abd-Elsalam WH, Al-Mahallawi AM. Fabrication of novel ultradeformable bilosomes for enhanced ocular delivery of terconazole: In vitro characterization, ex vivo permeation and in vivo safety assessment. Int J Pharm. 2016;513(1-2):688–96.
Salama HA, Mahmoud AA, Kamel AO, Abdel Hady M, Awad GA. Brain delivery of olanzapine by intranasal administration of transfersomal vesicles. J Liposome Res. 2012;22(4):336–45.
Dora CP, Singh SK, Kumar S, Datusalia AK, Deep AJ. Development and characterization of nanoparticles of glibenclamide by solvent displacement method. Acta Pol Pharm. 2010;67(3):283–90.
Aziz DE, Abdelbary AA, Elassasy AI. Investigating superiority of novel bilosomes over niosomes in the transdermal delivery of diacerein: in vitro characterization, ex vivo permeation and in vivo skin deposition study. J Liposome Res. 2019;29(1):73–85.
Guo J, Ping Q, Jiang G, Huang L, Tong Y. Chitosan-coated liposomes: characterization and interaction with leuprolide. Int J Pharm. 2003;260(2):167–73.
Zeisig R, Shimada K, Hirota S, Arndt D. Effect of sterical stabilization on macrophage uptake in vitro and on thickness of the fixed aqueous layer of liposomes made from alkylphosphocholines. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1996;1285(2):237–45.
Ammar HO, Mohamed MI, Tadros MI, Fouly AA. Transdermal Delivery of Ondansetron Hydrochloride via Bilosomal Systems: In Vitro, Ex Vivo, and In Vivo Characterization Studies. AAPS PharmSciTech. 2018;19(5):2276–87.
Tokudome Y, Nakamura K, Itaya Y, Hashimoto F. Enhancement of skin penetration of hydrophilic and lipophilic compounds by pH-sensitive liposomes. J Pharm Pharm Sci. 2015;18(3):249–57.
Chaudhary H, Kohli K, Kumar V. Nano-transfersomes as a novel carrier for transdermal delivery. Int J Pharm. 2013;454(1):367–80.
Zhang K, Zhang Y, Li Z, Li N, Feng N. Essential oil-mediated glycerosomes increase transdermal paeoniflorin delivery: Optimization, characterization, and evaluation in vitro and in vivo. Int J Nanomedicine. 2017;12:3521–32.
Aburahma MH. Bile salts-containing vesicles: promising pharmaceutical carriers for oral delivery of poorly water-soluble drugs and peptide/protein-based therapeutics or vaccines. Drug Deliv. 2016;23(6):1847–67.
Mahmood S, Taher M, UKJIjon M. Experimental design and optimization of raloxifene hydrochloride loaded nanotransfersomes for transdermal application. Int J Nanomedicine. 2014;9:4331–46.
Niu M, Tan YN, Guan P, Hovgaard L, Lu Y, Qi J, et al. Enhanced oral absorption of insulin-loaded liposomes containing bile salts: a mechanistic study. Int J Pharm. 2014;460(1-2):119–30.
El Zaafarany GM, Awad GA, Holayel SM, Mortada ND. Role of edge activators and surface charge in developing ultradeformable vesicles with enhanced skin delivery. Int J Pharm. 2010;397(1-2):164–72.
Taveira SF, Nomizo A, Lopez RF. Effect of the iontophoresis of a chitosan gel on doxorubicin skin penetration and cytotoxicity. J Control Release. 2009;134(1):35–40.
Mohsen AM, Asfour MH, Salama AAA. Improved hepatoprotective activity of silymarin via encapsulation in the novel vesicular nanosystem bilosomes. Drug Dev Ind Pharm. 2017;43(12):2043–54.
Chieng YY, Chen SB. Interaction and complexation of phospholipid vesicles and triblock copolymers. J Phys Chem B. 2009;113(45):14934–42.
Mady MM, Darwish MM, Khalil S, Khalil WM. Biophysical studies on chitosan-coated liposomes. Eur Biophys J. 2009;38(8):1127–33.
Singh BP, Menchavez R, Takai C, Fuji M, Takahashi M. Stability of dispersions of colloidal alumina particles in aqueous suspensions. J Colloid Interface Sci. 2005;291(1):181–6.
Moghimipour E, Ameri A, Handali S. Absorption-enhancing effects of bile salts. Molecules. 2015;20(8):14451–73.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
The animal ethical committee of Beni-Suef University approved this protocol.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Electronic supplementary material
ESM 1
(DOCX 256 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
El Menshawe, S.F., Aboud, H.M., Elkomy, M.H. et al. A novel nanogel loaded with chitosan decorated bilosomes for transdermal delivery of terbutaline sulfate: artificial neural network optimization, in vitro characterization and in vivo evaluation. Drug Deliv. and Transl. Res. 10, 471–485 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13346-019-00688-1
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13346-019-00688-1