Abstract
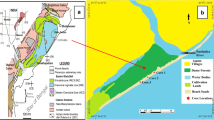
To investigate the dispersal pattern and the fate of dredged materials disposed at a pre-selected disposal site, a field tracer experiment was conducted in the North Passage of the Changjiang Estuary during the 2005 flood season. Three tons of dredged materials were mixed with 2.792 kg of sodium hexachloroiridate (IV) hexahydrate (SHH), which contained the rare earth element tracer iridum (Ir). Sampling was conducted at pre-selected sections of the estuary on the second, third and fourth day after the release of dredged materials. All samples were evaluated by use of neutron activation analysis. The majority of the dredged material was dispersed nearly parallel to the navigation channel and deposited between the channel and the south dike. Only a small quantity of dredged materials entered or crossed the navigation channel, and the back silting ratio in the navigation channel was about 5%. The dredged materials also dispersed southeasterly beyond two dike heads.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Changjiang Water Resources Commission (CWRC), 2004. Changjiang Sediment Bulletin, Changjiang Press, Wuhan, pp 8. (in Chinese)
Chen, J. Y., Zhu, H. F., Dong, Y. F. and Sun, J. M., 1985. Development of the Changjiang Estuary and its submerged delta, Cont. Shelf Res., 4(1–2): 47–56.
Chen, X. and Zong, Y., 1998. Coastal erosion along the Changjiang deltaic shoreline, China: History and prospective, Est. Coast. Shelf Sci., 46(5): 733–742.
Cruz-Motta, J. J. and Collins, J., 2004. Impacts of dredged material disposal on a tropical soft-bottom benthic assemblage, Mar. Pollut. Bull., 48(3–4): 270–280.
Dai, Z. J., Du, J. Z., Chu, A. and Zhang, X. L., 2010. Sediment characteristics in the north branch of the Yangtze Estuary based on radioisotope tracers, Environmental Earth Science, 62(8): 1629–1634.
Gao, S., 2000. A theoretical framework of tracer methods for marine sediment dynamics, Chinese Science Bulletin, 45(15): 1434–1440.
Gao, S., 2009. Grain size trend analysis: Principle and applicability, Acta Sedimentologica Sinica, 27(5): 826–836.
Gao, S. and Collins, M., 1992. Modelling exchange of natural trace sediments between an estuary and adjacent continental shelf, Journal of Sedimentary Petrology, 62(1): 35–40.
Gao, S. and Collins, M. 1995. Net transport direction of sands in a tidal inlet, using foraminiferal tests as natural tracers, Est. Coast. Shelf Sci., 40(6): 681–697.
Guo, J. T., 1995. Study on the sediment transport by the radiation tracer method and probability analysis, Port & Waterway Engineering, (1): 8–12. (in Chinese)
Jin, L., Yu, Z. Y. and He, Q., 2009. On the relationship between maintenance condition of Yangtze Estuary deepwater channel and water & sediment transport from the valley, Port & Waterway Engineering, (1): 91–96. (in Chinese)
Li, J., Shi, W., Shen, H., Xu, H. and Eisma, D., 1993. The bedload movement in the Changjiang Estuary, China Ocean Eng., 7(4): 441–450.
Liu, G. F., Zhu, J. R., Wang, Y. Y., Wu, H. and Wu, J. X., 2011. Tripod measured residual currents and sediment flux: Impacts on the silting of the Deepwater Navigation Channel in the Changjiang Estuary, Est. Coast. Shelf Sci., 93(3): 192–201.
Mulder, T. and Syvitski, J. P. M., 1995. Turbidity current s generated at river mouths during exceptional discharges to the world oceans, J. Geol., 103(3): 285–299.
Noakes, S. E. and Jutte, P. C., 2006. Utilizing gamma isotope tracer to determine sediment source at reef sites near the Charleston ocean dredged material disposal site, Mar. Pollut. Bull., 52(6): 666–673.
Regoli, F., Pellegrini, D., Winston, G. W., Gorbi, S., Giuliani, S., Virno-Lamberti, C. and Bompadre, S., 2002. Application of biomarkers for assessing the biological impact of dredged materials in the Mediterranean: The relationship between antioxidant responses and susceptibility to oxidative stress in the red mullet (Mullus barbatus), Mar. Pollut. Bull., 44(9): 912–922.
Shen, H. T. and Pan, D., 2001. Turbidity Maximum in the Yangtze River Estuary, China Ocean Press, Beijing. (in Chinese)
Simonini, R., Ansaloni, I., Cavallini, F., Graziosi, F., Iotti, M., Massamba N’siala, G., Mauri, M., Montanari, G., Preti, M. and Prevedelli, D., 2005. Effects of long-term dumping of harbor-dredged material on macro-zoobenthos at four disposal sites along the Emilia-Romagna coast (Northern Adriatic Sea, Italy), Mar. Pollut. Bull., 50(12): 1595–1605.
Sun, L. C., 1990. A review of sediment tracer techniques, Port & Waterway Engineering, (7): 18–22. (in Chinese)
Sun, L. C. and Yin, Y., 1994. The tracing of the sediment motion in spoil site of Tianjin Xingang port by Neutron Activation Technique, Journal of Sediment Research, (1): 72–77. (in Chinese)
Wu, J., Liu, J. T., Shen, H. T., and Zhang, S. Y., 2006. Dispersion of disposed dredged slurry in the meso-tidal Changjiang (Yangtze River) Estuary, Est. Coast. Shelf Sci., 70(4): 663–672.
Yin, Y., Chang, N. and Zhong, W., 1992a. A study on sediment movement trends in the Tianjin port spoil ground, Oceanologia et Limnologia Sinica, 23(6): 647–650. (in Chinese)
Yin, Y., Chang, N., Zhong, W., Sun, S., Zhang, W., Chui, H., Chen, S., Feng, Y. and Sun, L., 1992b. Study on technology of tracer sediment by neutron activation analysis, Chinese Science Bulletin, (7): 781–794. (in Chinese)
Yin, Y., Zhong, W., Chang, N., Li, Y. and Fang, Z., 1996. The study on the rule of silt moment in dredge disposal site, Port Engineering Technology, (4): 1–7. (in Chinese)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
The study was financially supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Grant Nos. 50979053 and 50939003) and the Major State Basic Research Development Program of China (973 Program, Grant No. 2010CB429002).
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Liu, Gf., Wu, Hl., Guo, Wh. et al. Dispersal and fate of dredged materials disposed of in the Changjiang Estuary determined by use of an in situ rare earth element tracer. China Ocean Eng 25, 495–506 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13344-011-0040-7
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13344-011-0040-7