Abstract
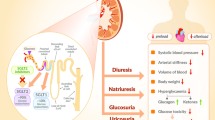
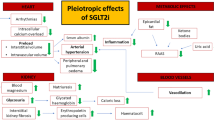
In recent years, successive reports have been made on large-scale cardiovascular outcome trials using novel hypoglycemic drugs. Their results have shown that sodium–glucose cotransporter 2 (SGLT2) inhibitors are hypoglycemic drugs that could potentially greatly improve the heart failure-related outcomes in type 2 diabetes patients with a high cardiovascular risk. Further analyses have subsequently been performed from various perspectives, and SGLT2 inhibitors with their class effect have been indicated to be potentially useful for heart failure in type 2 diabetes patients with extensive clinical background. As a result, a clear concept has globally emerged with SGLT2 inhibitors as drugs of choice in clinical practice to prevent heart failure in type 2 diabetes patients. Further studies are needed to examine the next research topics on heart failure prevention using SGLT2 inhibitors, including their detailed pharmacological mechanism of action and their effectiveness and safety against heart failure in patients regardless of diabetes status. This paper outlines (1) the current evidence of heart failure prevention by SGLT2 inhibitors based on the results of recent large-scale cardiovascular outcome trials and (2) future research topics on their further applications in clinical practice.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Seferovic PM, Petrie MC, Filippatos GS, Anker SD, Rosano G, Bauersachs J, et al. Type 2 diabetes mellitus and heart failure: a position statement from the Heart Failure Association of the European Society of Cardiology. Eur J Heart Fail. 2018;20(5):853–72.
Marx N. Heart failure: an underestimated therapeutic target in diabetes. Cardiovasc Endocrinol Metab. 2018;7(1):10–2.
Marwick TH, Ritchie R, Shaw JE, Kaye D. Implications of underlying mechanisms for the recognition and management of diabetic cardiomyopathy. J Am Coll Cardiol. 2018;71(3):339–51.
Dunlay SM, Givertz MM, Aguilar D, Allen LA, Chan M, Desai AS, et al. Type 2 diabetes mellitus and heart failure: a scientific statement from the American Heart Association and the Heart Failure Society of America: this statement does not represent an update of the 2017 ACC/AHA/HFSA heart failure guideline update. Circulation. 2019;140(7):e294–e324.
Iribarren C, Karter AJ, Go AS, Ferrara A, Liu JY, Sidney S, et al. Glycemic control and heart failure among adult patients with diabetes. Circulation. 2001;103(22):2668–733.
Boonman-de Winter LJ, Rutten FH, Cramer MJ, Landman MJ, Liem AH, Rutten GE, et al. High prevalence of previously unknown heart failure and left ventricular dysfunction in patients with type 2 diabetes. Diabetologia. 2012;55(8):2154–62.
Udell JA, Cavender MA, Bhatt DL, Chatterjee S, Farkouh ME, Scirica BM. Glucose-lowering drugs or strategies and cardiovascular outcomes in patients with or at risk for type 2 diabetes: a meta-analysis of randomised controlled trials. Lancet Diabetes Endocrinol. 2015;3(5):356–66.
Kannel WB, McGee DL. Diabetes and cardiovascular disease. The Framingham study. JAMA. 1979;241(19):2035–8.
Khan SS, Butler J, Gheorghiade M. Management of comorbid diabetes mellitus and worsening heart failure. JAMA. 2014;311(23):2379–80.
Bugger H, Abel ED. Molecular mechanisms of diabetic cardiomyopathy. Diabetologia. 2014;57(4):660–71.
Turnbull FM, Abraira C, Anderson RJ, Byington RP, Chalmers JP, Duckworth WC, et al. Intensive glucose control and macrovascular outcomes in type 2 diabetes. Diabetologia. 2009;52(11):2288–98.
Eurich DT, Weir DL, Majumdar SR, Tsuyuki RT, Johnson JA, Tjosvold L, et al. Comparative safety and effectiveness of metformin in patients with diabetes mellitus and heart failure: systematic review of observational studies involving 34,000 patients. Circ Heart Fail. 2013;6(3):395–402.
Crowley MJ, Diamantidis CJ, McDuffie JR, Cameron CB, Stanifer JW, Mock CK, et al. Clinical outcomes of metformin use in populations with chronic kidney disease, congestive heart failure, or chronic liver disease: a systematic review. Ann Intern Med. 2017;166(3):191–200.
Scirica BM, Bhatt DL, Braunwald E, Steg PG, Davidson J, Hirshberg B, et al. Saxagliptin and cardiovascular outcomes in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus. N Engl J Med. 2013;369(14):1317–26.
White WB, Cannon CP, Heller SR, Nissen SE, Bergenstal RM, Bakris GL, et al. Alogliptin after acute coronary syndrome in patients with type 2 diabetes. N Engl J Med. 2013;369(14):1327–35.
McGuire DK, Alexander JH, Johansen OE, Perkovic V, Rosenstock J, Cooper ME, et al. Linagliptin effects on heart failure and related outcomes in individuals with type 2 diabetes mellitus at high cardiovascular and renal risk in CARMELINA. Circulation. 2019;139(3):351–61.
Inagaki N, Yang W, Watada H, Ji L, Schnaidt S, Pfarr E, et al. Linagliptin and cardiorenal outcomes in Asians with type 2 diabetes mellitus and established cardiovascular and/or kidney disease: subgroup analysis of the randomized CARMELINA® trial. Diabetol Int. 2019. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13340-019-00412-x.
Cosentino F, Grant PJ, Aboyans V, Bailey CJ, Ceriello A, Delgado V, et al. 2019 ESC guidelines on diabetes, pre-diabetes, and cardiovascular diseases developed in collaboration with the EASD. Eur Heart J. 2019;41:255–323.
Kristensen SL, Rorth R, Jhund PS, Docherty KF, Sattar N, Preiss D, et al. Cardiovascular, mortality, and kidney outcomes with GLP-1 receptor agonists in patients with type 2 diabetes: a systematic review and meta-analysis of cardiovascular outcome trials. Lancet Diabetes Endocrinol. 2019;7(10):776–85.
Tanaka A, Node K. Clinical application of glucagon-like peptide-1 receptor agonists in cardiovascular disease: lessons from recent clinical cardiovascular outcomes trials. Cardiovasc Diabetol. 2018;17(1):85.
Margulies KB, Hernandez AF, Redfield MM, Givertz MM, Oliveira GH, Cole R, et al. Effects of liraglutide on clinical stability among patients with advanced heart failure and reduced ejection fraction: a randomized clinical trial. JAMA. 2016;316(5):500–8.
Rahmoune H, Thompson PW, Ward JM, Smith CD, Hong G, Brown J. Glucose transporters in human renal proximal tubular cells isolated from the urine of patients with non-insulin-dependent diabetes. Diabetes. 2005;54(12):3427–34.
Inzucchi SE, Zinman B, Wanner C, Ferrari R, Fitchett D, Hantel S, et al. SGLT-2 inhibitors and cardiovascular risk: proposed pathways and review of ongoing outcome trials. Diabetes Vasc Dis Res. 2015;12(2):90–100.
Zinman B, Wanner C, Lachin JM, Fitchett D, Bluhmki E, Hantel S, et al. Empagliflozin, cardiovascular outcomes, and mortality in type 2 diabetes. N Engl J Med. 2015;373(22):2117–288.
Fitchett D, Zinman B, Wanner C, Lachin JM, Hantel S, Salsali A, et al. Heart failure outcomes with empagliflozin in patients with type 2 diabetes at high cardiovascular risk: results of the EMPA-REG OUTCOME(R) trial. Eur Heart J. 2016;37(19):1526–34.
Fitchett D, Butler J, van de Borne P, Zinman B, Lachin JM, Wanner C, et al. Effects of empagliflozin on risk for cardiovascular death and heart failure hospitalization across the spectrum of heart failure risk in the EMPA-REG OUTCOME(R) trial. Eur Heart J. 2018;39(5):363–70.
Fitchett D, Inzucchi SE, Cannon CP, McGuire DK, Scirica BM, Johansen OE, et al. Empagliflozin reduced mortality and hospitalization for heart failure across the spectrum of cardiovascular risk in the EMPA-REG OUTCOME trial. Circulation. 2019;139(11):1384–95.
Verma S, Mazer CD, Fitchett D, Inzucchi SE, Pfarr E, George JT, et al. Empagliflozin reduces cardiovascular events, mortality and renal events in participants with type 2 diabetes after coronary artery bypass graft surgery: subanalysis of the EMPA-REG OUTCOME(R) randomised trial. Diabetologia. 2018;61(8):1712–23.
Savarese G, Sattar N, Januzzi J, Verma S, Lund LH, Fitchett D, et al. Empagliflozin is associated with a lower risk of post-acute heart failure rehospitalization and mortality. Circulation. 2019;139(11):1458–60.
Kaku K, Lee J, Mattheus M, Kaspers S, George J, Woerle HJ. Empagliflozin and cardiovascular outcomes in asian patients with type 2 diabetes and established cardiovascular disease- results from EMPA-REG OUTCOME((R)). Circ J. 2017;81(2):227–34.
Neal B, Perkovic V, Mahaffey KW, de Zeeuw D, Fulcher G, Erondu N, et al. Canagliflozin and cardiovascular and renal events in type 2 diabetes. N Engl J Med. 2017;377(7):644–57.
Mahaffey KW, Neal B, Perkovic V, de Zeeuw D, Fulcher G, Erondu N, et al. Canagliflozin for primary and secondary prevention of cardiovascular events: results from the CANVAS program (Canagliflozin Cardiovascular Assessment Study). Circulation. 2018;137(4):323–34.
Radholm K, Figtree G, Perkovic V, Solomon SD, Mahaffey KW, de Zeeuw D, et al. Canagliflozin and heart failure in type 2 diabetes mellitus. Circulation. 2018;138(5):458–68.
Figtree GA, Radholm K, Barrett TD, Perkovic V, Mahaffey KW, de Zeeuw D, et al. Effects of canagliflozin on heart failure outcomes associated with preserved and reduced ejection fraction in type 2 diabetes mellitus. Circulation. 2019;139(22):2591–3.
Wiviott SD, Raz I, Bonaca MP, Mosenzon O, Kato ET, Cahn A, et al. Dapagliflozin and cardiovascular outcomes in type 2 diabetes. N Engl J Med. 2019;380(4):347–57.
Furtado RHM, Bonaca MP, Raz I, Zelniker TA, Mosenzon O, Cahn A, et al. Dapagliflozin and cardiovascular outcomes in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus and previous myocardial infarction. Circulation. 2019;139(22):2516–27.
Kato ET, Silverman MG, Mosenzon O, Zelniker TA, Cahn A, Furtado RHM, et al. Effect of dapagliflozin on heart failure and mortality in type 2 diabetes mellitus. Circulation. 2019;139(22):2528–36.
Perkovic V, Jardine MJ, Neal B, Bompoint S, Heerspink HJL, Charytan DM, et al. Canagliflozin and renal outcomes in type 2 diabetes and nephropathy. N Engl J Med. 2019;380(24):2295–306.
McMurray JJV, Solomon SD, Inzucchi SE, Kober L, Kosiborod MN, Martinez FA, et al. Dapagliflozin in patients with heart failure and reduced ejection fraction. N Engl J Med. 2019;381:1995–2008.
Zelniker TA, Wiviott SD, Raz I, Im K, Goodrich EL, Bonaca MP, et al. SGLT2 inhibitors for primary and secondary prevention of cardiovascular and renal outcomes in type 2 diabetes: a systematic review and meta-analysis of cardiovascular outcome trials. Lancet. 2019;393(10166):31–9.
Fitchett DH, Udell JA, Inzucchi SE. Heart failure outcomes in clinical trials of glucose-lowering agents in patients with diabetes. Eur J Heart Fail. 2017;19(1):43–53.
Davies MJ, D'Alessio DA, Fradkin J, Kernan WN, Mathieu C, Mingrone G, Management of Hyperglycemia in Type 2 Diabetes, et al. A Consensus Report by the American Diabetes Association (ADA) and the European Association for the Study of Diabetes (EASD). Diabetes Care. 2018;41(12):2669–701.
Tsutsui H, Isobe M, Ito H, Ito H, Okumura K, Ono M, et al. JCS 2017/JHFS 2017 guideline on diagnosis and treatment of acute and chronic heart failure-digest version. Circ J. 2019;83(10):2084–184.
Verma S, McMurray JJV. The serendipitous story of SGLT2 inhibitors in heart failure. Circulation. 2019;139(22):2537–41.
Farkouh ME, Verma S. Prevention of heart failure with SGLT-2 inhibition: insights from CVD-REAL. J Am Coll Cardiol. 2018;71(22):2507–10.
Lahnwong S, Chattipakorn SC, Chattipakorn N. Potential mechanisms responsible for cardioprotective effects of sodium-glucose co-transporter 2 inhibitors. Cardiovasc Diabetol. 2018;17(1):101.
Lytvyn Y, Bjornstad P, Udell JA, Lovshin JA, Cherney DZI. Sodium glucose cotransporter-2 inhibition in heart failure: potential mechanisms, clinical applications, and summary of clinical trials. Circulation. 2017;136(17):1643–58.
Packer M, Anker SD, Butler J, Filippatos G, Zannad F. Effects of sodium-glucose cotransporter 2 inhibitors for the treatment of patients with heart failure: proposal of a novel mechanism of action. JAMA Cardiol. 2017;2(9):1025–9.
Verma S, Rawat S, Ho KL, Wagg CS, Zhang L, Teoh H, et al. Empagliflozin increases cardiac energy production in diabetes: novel translational insights into the heart failure benefits of SGLT2 inhibitors. JACC Basic Transl Sci. 2018;3(5):575–87.
Tanaka A, Node K. Emerging roles of sodium-glucose cotransporter 2 inhibitors in cardiology. J Cardiol. 2017;69(3):501–7.
Packer M. Lessons learned from the DAPA-HF trial concerning the mechanisms of benefit of SGLT2 inhibitors on heart failure events in the context of other large-scale trials nearing completion. Cardiovasc Diabetol. 2019;18(1):129.
Januzzi JL Jr, Butler J, Jarolim P, Sattar N, Vijapurkar U, Desai M, et al. Effects of canagliflozin on cardiovascular biomarkers in older adults with type 2 diabetes. J Am Coll Cardiol. 2017;70(6):704–12.
Verma S, Garg A, Yan AT, Gupta AK, Al-Omran M, Sabongui A, et al. Effect of empagliflozin on left ventricular mass and diastolic function in individuals with diabetes: an important clue to the EMPA-REG OUTCOME Trial? Diabetes Care. 2016;39(12):e212–e213213.
Nassif ME, Windsor SL, Tang F, Khariton Y, Husain M, Inzucchi SE, et al. Dapagliflozin effects on biomarkers, symptoms, and functional status in patients with heart failure with reduced ejection fraction: the DEFINE-HF trial. Circulation. 2019;140(18):1463–76.
Paulus WJ, Tschope C. A novel paradigm for heart failure with preserved ejection fraction: comorbidities drive myocardial dysfunction and remodeling through coronary microvascular endothelial inflammation. J Am Coll Cardiol. 2013;62(4):263–71.
Butler J, Hamo CE, Filippatos G, Pocock SJ, Bernstein RA, Brueckmann M, et al. The potential role and rationale for treatment of heart failure with sodium-glucose co-transporter 2 inhibitors. Eur J Heart Fail. 2017;19(11):1390–400.
Acknowledgements
The authors would like to thank Ms. Aya Yamada (Saga University) for her excellent support. This work was partly supported by Taiju Life Social Welfare Foundation.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
About this article
Cite this article
Tanaka, A., Node, K. Promising roles of sodium–glucose cotransporter 2 inhibitors in heart failure prevention and treatment. Diabetol Int 11, 252–260 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13340-020-00445-7
Received:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13340-020-00445-7