Abstract
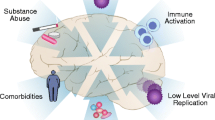
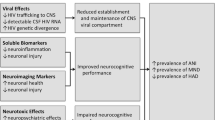
The world’s sustained commitment to the HIV/AIDS response and to reaching the 2030 Sustainable Development Goal (SDG) of “ending AIDS” as a public health issue is indicated by the ambitious 95-95-95 targets for all relevant populations. Neurological conditions of AIDS (neuroAIDS) are the most significant and severe central nervous system complication associated with HIV infection in which viral antigens can enter in the brain by breaching the blood brain barrier and cause dementia, neuroinflammation and encephalopathy. The prevalence of neuroAIDS is 10–50% in people with advanced HIV disease, whereas 5–25% in people on ART. Currently, MRI, CT and other tools are used to diagnose the neuroAIDS/ HIV-associated dementia and antiretroviral therapy is widely used to treat the neuroAIDS. In spite of many advanced tools and pathogenesis of neuroAIDS, developing therapeutics remains a formidable challenge. Long acting cabotegravir type of therapeutics is an advanced stage of research which shows good results for the treatment of neuroAIDS. Therefore, here we are discussing the recent insights of the pathogenesis, possible therapeutics and current strategies and treatment to overcome the neuroAIDS.

Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
The authors confirm that the data supporting the findings of this study are available within the article.
References
Alirezaei M, Watry DD, Flynn CF, Kiosses WB, Masliah E, Williams BR, Kaul M, Lipton SA, Fox HS. Human immunodeficiency virus-1/surface glycoprotein 120 induces apoptosis through RNA-activated protein kinase signaling in neurons. J Neurosci. 2007;27(41):11047–55. https://doi.org/10.1523/JNEUROSCI.2733-07.2007.
Arseniou S, Arvaniti A, Samakouri M. HIV infection and depression. Psychiatry Clin Neurosci. 2015;68:96–109. https://doi.org/10.1111/pcn.12097.
Atluri VS, Pilakka-Kanthikeel S, Samikkannu T, Sagar V, Kurapati KR, Saxena SK, Yndart A, Raymond A, Ding H, Hernandez O, et al. Vorinostat positively regulates synaptic plasticity genes expression and spine density in HIV infected neurons: role of nicotine in progression of HIV-associated neurocognitive disorder. Mol Brain. 2014;7:37. https://doi.org/10.1186/1756-6606-7-37.
Aung HL, Siefried KJ, Gates TM, Brew BJ, Mao L, Carr A, Cysique LA. Meaningful cognitive decline is uncommon in virally suppressed HIV, but sustained impairment, subtle decline and abnormal cognitive aging are not. eClinicalMedicine (part of the lancet discovery science). 2023;56. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.eclinm.2022.101792.
Barry M, Mulcahy F, Back DJ. Antiretroviral therapy for patients with HIV disease. Br J Clin Pharmacol. 1998;45(3):221–8. https://doi.org/10.1046/j.1365-2125.1998.00673.x.
Butovsky O, Weiner HL. Microglial signatures and their role in health and disease. Nat Rev Neurosci. 2018;19(10):622–35. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41583-018-0057-5.
Dahal S, Chitti SV, Nair MP, Saxena SK. Interactive effects of cocaine on HIV infection: implication in HIV-associated neurocognitive disorder and neuroAIDS. Front Microbiol. 2015;6:931. https://doi.org/10.3389/fmicb.2015.00931.
Eilbott DJ, Peress N, Burger H, LaNeve D, Orenstein J, Gendelman HE, Seidman R, Weiser B. Human immunodeficiency virus type 1 in spinal cords of acquired immunodeficiency syndrome patients with myelopathy: expression and replication in macrophages. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989;86(9):3337–41. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.86.9.3337.
Filippi CG, Ulug AM, Ryan E, Ferrando SJ, van Gorp W. Diffusion tensor imaging of patients with HIV and normal-appearing white matter on MR images of the brain. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol. 2001;22(2):277–83.
Fu K, Harrell R, Zinski K, Um C, Jaklenec A, Frazier J, Lotan N, Burke P, Klibanov AM, Langer R. A potential approach for decreasing the burst effect of protein from PLGA microspheres. J Pharm Sci. 2003;92(8):1582–91. https://doi.org/10.1002/jps.10414.
Gandhi N, Saiyed ZM, Napuri J, Samikkannu T, Reddy PV, Agudelo M, Khatavkar P, Saxena SK, Nair MP. Interactive role of human immunodeficiency virus type 1 (HIV-1) clade-specific Tat protein and cocaine in blood-brain barrier dysfunction: implications for HIV-1-associated neurocognitive disorder. J Neurovirol. 2010;16(4):294–305. https://doi.org/10.3109/13550284.2010.499891.
Geretti AM, Harrison L, Green H, Sabin C, Hill T, Fearnhill E, Pillay D, Dunn D. Resistance UKCGoHD: Effect of HIV-1 subtype on virologic and immunologic response to starting highly active antiretroviral therapy. Clin Infect Dis. 2009;48(9):1296–305. https://doi.org/10.1086/598502.
Hemelaar J. The origin and diversity of the HIV-1 pandemic. Trends Mol Med. 2012;18(3):182–92. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.molmed.2011.12.001.
Hogan C, Wilkins E. Neurological complications in HIV. Clin Med (Lond). 2011;11(6):571–5. https://doi.org/10.7861/clinmedicine.11-6-571.
Kaul M, Lipton SA. Chemokines and activated macrophages in HIV gp120-induced neuronal apoptosis. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1999;96(14):8212–6. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.96.14.8212.
Kaul M, Zheng J, Okamoto S, et al. HIV-1 infection and AIDS. Consequences for the central nervous system. Cell Death Differ. 2005;12:878–92. https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.cdd.4401623.
Kincer LP, Schnell G, Swanstrom R, Miller MB, Spudich S, Eron JJ, Price RW, Joseph SB. HIV-1 is Transported into the Central Nervous System by Trafficking Infected Cells. Pathog Immun 2022, 7(2):131–142. https://doi.org/10.20411/pai.v7i2.524. eCollection 2022.
Kumar S, Maurya VK, Dandu HR, Bhatt ML, Saxena SK. Global perspective of novel therapeutic strategies for the management of neuroAIDS. Biomol Concepts. 2018;9(1):33–42. https://doi.org/10.1515/bmc-2018-0005.
Langford D, Hurford R, Hashimoto M, Digicaylioglu M, Masliah E. Signalling crosstalk in FGF2-mediated protection of endothelial cells from HIV-gp120. BMC Neurosci. 2005;6:8. https://doi.org/10.1186/1471-2202-6-8.
Liberto GD, Egervari K. Neurodegenerative phagocytes mediate synaptic stripping in Neuro-HIV. Brain. 2022;145(8):2730–41.
Lipton SA, Gendelman HE. Seminars in medicine of the Beth Israel Hospital, Boston. Dementia associated with the acquired immunodeficiency syndrome. N Engl J Med. 1995 6;332(14):934 – 40. doi: https://doi.org/10.1056/NEJM199504063321407.
Marzolini C, Mueller R, Li-Blatter X, Battegay M, Seelig A. The brain entry of HIV-1 protease inhibitors is facilitated when used in combination. Mol Pharm. 2013;10(6):2340–9. https://doi.org/10.1021/mp300712a.
Microglial phagocytosis of live neurons. Nat Rev Neurosci. 2014;15(4):209–16. https://doi.org/10.1038/nrn3710.
Minagar A, Commins D, Alexander JS, Hoque R, Chiappelli F, Singer EJ, Nikbin B, Shapshak P. NeuroAIDS: characteristics and diagnosis of the neurological complications of AIDS. Mol Diagn Ther. 2008;12(1):25–43. https://doi.org/10.1007/BF03256266.
Reddy PV, Pilakka-Kanthikeel S, Saxena SK, Saiyed Z, Nair MP. Interactive Effects of Morphine on HIV infection: role in HIV-Associated Neurocognitive Disorder. AIDS Res Treat. 2012;2012:953678. https://doi.org/10.1155/2012/953678. Epub 2012 May 20.
Sakai M, Higashi M, Fujiwara T, Uehira T, Shirasaka T, Nakanishi K, Kashiwagi N, Tanaka H, Terada H, Tomiyama N. MRI imaging features of HIV-related central nervous system diseases: diagnosis by pattern recognition in daily practice. Jpn J Radiol. 2021;39(11):1023–38. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11604-021-01150-4.
Samikkannu T, Rao KV, Gandhi N, Saxena SK, Nair MP. Human immunodeficiency virus type 1 clade B and C Tat differentially induce indoleamine 2,3-dioxygenase and serotonin in immature dendritic cells: implications for neuroAIDS. J Neurovirol. 2010;16(4):255–63. https://doi.org/10.3109/13550284.2010.497809.
Sarma A, Das MK. Nose to brain delivery of antiretroviral drugs in the treatment of neuroAIDS. Mol Biomed. 2020;1(1):15. https://doi.org/10.1186/s43556-020-00019-8.
Saxena SK, Tiwari S, Nair MP. Nanotherapeutics: emerging competent technology in neuroAIDS and CNS drug delivery. Nanomed (Lond). 2012;7(7):941–4. https://doi.org/10.2217/nnm.12.63.
Saxena SK, Tiwari S, Nair MP. A global perspective on HIV/AIDS. Science. 2012;337(6096):798. https://doi.org/10.1126/science.337.6096.798.
Saylor D, Dickens AM, Sacktor N, Haughey N, Slusher B, Pletnikov M, Mankowski JL, Brown A, Volsky DJ, McArthur JC. HIV-associated neurocognitive disorder–pathogenesis and prospects for treatment. Nat Rev Neurol. 2016;12(4):234–48. https://doi.org/10.1038/nrneurol.2016.27.
Singer EJ, Valdes-Sueiras M, Commins D, Levine A. Neurologic presentations of AIDS. Neurol Clin. 2010;28(1):253–75. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ncl.2009.09.018.
Suwanwelaa N, Phanuphak P, Phanthumchinda K, Suwanwela NC, Tantivatana J, Ruxrungtham K, Suttipan J, Wangsuphachart S, Hanvanich M. Magnetic resonance spectroscopy of the brain in neurologically asymptomatic HIV-infected patients. Magn Reson Imaging. 2000;18(7):859–65. https://doi.org/10.1016/s0730-725x(00)00173-9.
Thakur KT, Boubour A, Saylor D, Das M, Bearden DR, Birbeck GL. Global HIV neurology. A comprehensive review. AIDS. 2019;33(2):163–84. https://doi.org/10.1097/QAD.0000000000001796.
Trezza C, Ford SL, Spreen W, Pan R, Piscitelli S. Formulation and pharmacology of long-acting cabotegravir. Curr Opin HIV AIDS. 2015;10(4):239–45. https://doi.org/10.1097/COH.0000000000000168.
Trujillo J, Jaramillo-rangel G, Ortega-martinez M, et al. International NeuroAIDS: prospects of HIV-1 associated neurological complications. Cell Res. 2005;15:962–9.
UNAIDS. Understanding fast-track accelerating action to end the AIDS epidemic by 2030. UNAIDS. 2014 https://www.unaids.org/sites/default/files/media_asset/201506_JC2743_Understanding_FastTrack_en.pdf. Accessed 08 June 2023.
Wang Y, White MG, Akay C, Chodroff RA, Robinson J, Lindl KA, Dichter MA, Qian Y, Mao Z, Kolson DL, et al. Activation of cyclin-dependent kinase 5 by calpains contributes to human immunodeficiency virus-induced neurotoxicity. J Neurochem. 2007;103(2):439–55. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1471-4159.2007.04746.x.
Wong HL, Chattopadhyay N, Wu XY, Bendayan R. Nanotechnology applications for improved delivery of antiretroviral drugs to the brain. Adv Drug Deliv Rev. 2010;62(4–5):503–17. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.addr.2009.11.020.
Acknowledgements
The authors are grateful to the Vice Chancellor, King George’s Medical University (KGMU) Lucknow, for the encouragement for this work. The authors have no other relevant affiliations or financial involvement with any organization or entity with a financial interest in or financial conflict with the subject matter or materials discussed in the manuscript apart from those disclosed.
Funding
We have not received any specific funding for this work.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that there is no conflict of interests.
Additional information
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Saxena, S.K., Sharma, D., Kumar, S. et al. Understanding HIV-associated neurocognitive and neurodegenerative disorders (neuroAIDS): enroute to achieve the 95-95-95 target and sustainable development goal for HIV/AIDS response. VirusDis. 34, 165–171 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13337-023-00830-1
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13337-023-00830-1