Abstract
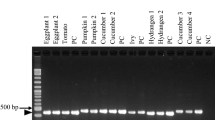
Identifying the causative agent of a disease provides key information for diagnosis and management. Here, we identified the causative agent of a leaf spot disease prevalent in water spinach (Ipomoea aquatica) in Fujian Province, China. Ninety bacterial isolates were recovered from symptomatic leaves of water spinach collected across six growing areas in Fujian Province. Completion of Koch’s postulates confirmed that 60 yellow mucoid isolates were the causative agents of the disease. PCR amplification of 16S ribosomal RNA gene sequences demonstrated that the isolates belonged to the genus Xanthomonas. We then PCR-amplified and sequenced the recA, dnaK, gyrB, and rpoD genes of the isolated pathogens for multilocus sequence analysis. In the resulting phylogenetic tree, the isolated pathogens grouped with X. euvesicatoria pv. perforans strain TC2-1. Biological and chemical tests performed on 60 isolates showed that all of them were positive in hydrogen sulfide, litmus milk, starch hydrolysis and bile-esculin tests, but negative in nitrate reduction, pectinase activity, and oxidase activity tests. The isolates could also cause disease symptoms on tomato (Solanum lycopersicum) leaves and stems but not on pepper (Capsicum annuum) plants. Based on DNA characteristics, physiological and chemical properties, and pathogenicity test results, we propose that the leaf spot disease in water spinach is caused by X. euvesicatoria pv. perforans.




Similar content being viewed by others
Data Availability
All relevant data are within the manuscript and its Supporting Information files.
References
Aiello D, Scuderi G, Vitale A, Firrao G, Polizzi G, Cirvilleri G (2013) A pith necrosis caused by Xanthomonas perforans on tomato plants. Eur J Plant Pathol 137:29–41. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10658-013-0214-7
Araujo ER, Costa JR, Ferreira MASV, Quezado-Duval AM (2016) Widespread distribution of Xanthomonas perforans, and limited presence of X. gardneri in Brazil. Plant Pathol 66:159–168. https://doi.org/10.1111/ppa.12543
Araujo ER, Costa JR, Pontes NC, Quezado-Duval AM (2015) Xanthomonas perforans, and X. gardneri, associated with bacterial leaf spot on weeds in Brazilian tomato fields. Eur J Plant Pathol 143:543–548. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10658-015-0705-9
Bophela KN, Venter SN, Wingfield MJ, Duran A, Tarigan M, Coutinho TA (2019) Xanthomonas perforans: a tomato and pepper pathogen associated with bacterial blight and dieback of Eucalyptus pellita seedlings in Indonesia. Australas Plant Pathol 48:543–551. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13313-019-00657-9
Cerkauskas RF, Koike ST, Azad HR, Lowery DT, Stobbs LW (2006) Diseases, pests, and abiotic disorders of greenhouse-grown water spinach (Ipomoea aquatica) in Ontario and California. Can J Plant Pathol 28:63–70. https://doi.org/10.1080/07060660609507271
Chen LD, Xie X, Shi Y, Chai AL, Li L, Li B (2022) First Report of Leaf Spot on water convolvulus Caused by Stemphylium solani in Yunnan Province. China. Plant Dis 107:3. https://doi.org/10.1094/PDIS-03-22-0689-PDN
Chitsa H, Mtaita T, Tabarira J (2014) Nutrient content of water spinach (Ipomoea aquatica) under different harvesting stages and preservation methods in Zimbabwe. Int J Biol Chem Sci 8:854–861. https://doi.org/10.4314/ijbcs.v8i3.2
Dewanjee S, Joardar S, Bhattacharjee N, Dua TK, Das S, Kalita J, Manna P (2017) Edible leaf extract of Ipomoea aquatica Forsk. (Convolvulaceae) attenuates doxorubicin-induced liver injury via inhibiting oxidative impairment, MAPK activation and intrinsic pathway of apoptosis. Food Chem Toxicol 105:322–336. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.fct.2017.05.002
Dong XZ, Cai MY (2001) Systematical determinative manual of common bacteriology. China, Science Press, Beijing
Frank JA, Reich CI, Sharma S, Weisbaum JS, Wilson BA, Olsen GJ (2008) Critical evaluation of two primers commonly used for amplification of bacterial 16S rRNA genes. Appl Environ Microbiol 74:2461–2470. https://doi.org/10.1128/AEM.02272-07
Goswami MJ, Dutta U, Seema T, Bharali SJ, Yanka H, Tag H, Bharali P, Kakati D (2023) Antioxidant and Antidiabetic Properties of Extracts from Three Underutilized Food Plants of North East India. Chem Biodivers 20(2):e202200718. https://doi.org/10.1002/cbdv.202200718
Hao YY, Bao WL, Li GL, Gagoshidze Z, Shu HY, Yang Z, Cheng SH, Zhu GP, Wang ZW (2021) The chromosome-based genome provides insights into the evolution in water spinach. Sci Hortic-amsterdam 289:110501. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scienta.2021.110501
Hu M, Li C, Zhou X, Xue Y, Wang S, Hu A, Chen S, Mo X, Zhou J (2021) Microbial Diversity Analysis and Genome Sequencing Identify Xanthomonas perforans as the Pathogen of Bacterial Leaf Canker of Water Spinach (Ipomoea aquatic). Front Microbiol 12:752760. https://doi.org/10.3389/fmicb.2021.752760
Igwenyi IO, Offor CE, Ajah DA, Nwankwo OC, Ukaomah JI, Aja PM (2011) Chemical composition of Ipomea aquatica (Green kangkong). Int J Pharm Bio Sci 2:593–598
Ivey MLL, Strayer AL, Sidhu JK, Minsavage J (2016) Bacterial leaf spot of tomato (Solanum lycopersicum) in Louisiana is caused by Xanthomonas perforans, tomato race 4. Plant Dis 100:1233. https://doi.org/10.1094/PDIS-12-15-1451-PDN
Jalan N, Aritua V, Kumar D, Yu F, Jones JB, Graham JH, Setubal JC, Wang N (2011) Comparative genomic analysis of Xanthomonas axonopodis pv. citrumelo F1, which causes citrus bacterial spot disease, and related strains provides insights into virulence and host specificity. J Bacteriol 193:6342–6357. https://doi.org/10.1128/JB.05777-11
Jalan N, Kumar D, Andrade MO, Yu F, Jones JB, Graham JH, White FF, Setubal JC, Wang, N (2013) Comparative genomic and transcriptome analyses of pathotypes of Xanthomonas citri subsp. citri provide insights into mechanisms of bacterial virulence and host range. BMC Genomics 14:551. https://doi.org/10.1186/1471-2164-14-551
Jardim BR, Kinoti WM, Tran-Nguyen LT, Gambley C, Rodoni B, Constable FE (2021) ‘Candidatus Phytoplasma stylosanthis’, a novel taxon with a diverse host range in Australia, characterised using multilocus sequence analysis of 16S rRNA, secA, tuf, and rp genes. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol 71(1):004589. https://doi.org/10.1099/ijsem.0.004589
Kalyaanamoorthy S, Minh BQ, Wong TKF, von Haeseler A, Jermiin LS (2017) ModelFinder: fast model selection for accurate phylogenetic estimates. Nat Methods 14(6):587–589. https://doi.org/10.1038/nmeth.4285
Kebede M, Timilsina S, Ayalew A, Admassu B, Potnis N, Minsavage GV, Goss EM, Hong JC, Strayer A, Paret M, Jones JB, Vallad GE (2014) Molecular characterization of Xanthomonas strains responsible for bacterial spot of tomato in Ethiopia. Eur J Plant Pathol 140(4):677–688. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10658-014-0497-3
Lange HW, Tancos MA, Carlson MO, Smart CD (2016) Diversity of Xanthomonas campestris isolates from symptomatic Crucifers in New York State. Phytopathology 106:113–122. https://doi.org/10.1094/PHYTO-06-15-0134-R
Leksomboon C, Thaveechai N, Kositratana W (1991) “Bacterial leaf spot of Chinese convolvulus [Ipomoea aquatica],” in Proceedings of the 29th Kasetsart University: Plant Science, (Bangkok: Kasetsart University), 277-283.
Liu PQ, Wei MY, Zhu L, Li BJ (2017) First report of spot blight on water spinach (Ipomoea aquatica) caused by Stagonosporopsis cucurbitacearum in China. Plant Dis 101:838. https://doi.org/10.1094/PDIS-10-16-1485-PDN
Mbega ER, Mabagala RB, Adriko J, Lund OS, Wulff EG, Mortensen CN (2012) Five species of xanthomonads associated with bacterial leaf spot symptoms in tomato from Tanzania. Plant Dis 96:760. https://doi.org/10.1094/PDIS-01-12-0105-PDN
Osdaghi E, Jones JB, Sharma A, Goss EM, Abrahamian P, Newberry EA, Potnis N, Carvalho R, Choudhary M, Paret ML, Timilsina S, Vallad GE (2021) A centenary for bacterial spot of tomato and pepper. Mol Plant Pathol 22(12):1500–1519. https://doi.org/10.1111/mpp.13125
Potnis N, Timilsina S, Strayer A, Shantharaj D, Barak JD, Paret ML, Vallad GE, Jones JB (2015) Bacterial spot of tomato and pepper: diverse Xanthomonas species with a wide variety of virulence factors posing a worldwide challenge. Mol Plant Pathol 16:907–920. https://doi.org/10.1111/mpp.12244
Rademaker JLW, Louws FJ, Schultz MH, Rossbach U, Vauterin L, Swings J, de Bruijn FJ (2005) A comprehensive species to strain taxonomic framework for Xanthomonas. Phytopathology 95:1098–1111. https://doi.org/10.1094/PHYTO-95-1098
Rambaut A, Suchard MA, Xie D, Drummond AJ (2014) Tracer v1.6.0. Available at http:// tree.bio.ed.ac.uk/ software/ tracer/.
Ronquist F, Teslenko M, Mark PVD, Ayres DL, Darling A, Hohna S, Larget B, Liu L, Suchard MA, Huelsenbeck JP (2012) Mrbayes 3.2: efficient Bayesian phylogenetic inference and model choice across a large model space. Syst Biol 61(3): 539-542. https://doi.org/10.1093/sysbio/sys029
Ryan RP, Vorhöelter FJ, Potnis N, Jones JB, Van Sluys MA, Bogdanove AJ, Dow JM (2011) Pathogenomics of Xanthomonas: understanding bacterium-plant interactions. Nat Rev Microbiol 9:344–355. https://doi.org/10.1038/nrmicro2558
Schaad NW, Jones JB, Chun W (2001) Laboratory guide for the identification of plant pathogenic bacteria, 3rd edn. The American Phytopathological Society, St. Paul, MN
Song S, Zhang Y, Liu H, Pan CQ, Yang MX, Ding JF, Zhang JH (2019) Isolation and characterization of Xanthomonas euvesicatoria pv. euvesicatoria causing bacterial spot in Physalis pubescens in northeast China. J Plant Pathol 101:361–366
Sophea K, Preston TR (2001) Comparison of biodigester effluent and urea as fertilizer for water spinach vegetable. Livest Res Rural Dev 13:1–13
Tamura K, Stecher G, Kumar S (2021) MEGA11: Molecular evolutionary genetics analysis version 11. Mol Biol Evol 38(7):3022–3027. https://doi.org/10.1093/molbev/msab120
Timilsina S, Jibrin MO, Potnis N, Minsavage GV, Kebede M, Schwartz A, Bart R, Staskawicz B, Boyer C, Vallad GE, Pruvost O, Jones JB, Goss EM (2015) Multilocus sequence analysis of xanthomonads causing bacterial spot of tomato and pepper plants reveals strains generated by recombination among species and recent global spread of Xanthomonas gardneri. Appl Environ Microbiol 81:1520–1529. https://doi.org/10.1128/AEM.03000-14
Timilsina S, Potnis N, Newberry EA, Liyanapathiranage P, Iruegas-Bocardo F, White FF, Goss EM, Jones JB (2020) Xanthomonas diversity, virulence and plant-pathogen interactions. Nat Rev Microbiol 18(8):415–427. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41579-020-0361-8
Triplett LR, Verdier V, Campillo T, Van Malderghem C, Cleenwerck I, Maes M, Deblais L, Corral R, Koita O, Cottyn B, Leach JE (2015) Characterization of a novel clade of Xanthomonas isolated from rice leaves in Mali and proposal of Xanthomonas maliensis sp. nov. Antonie Van Leeuwenhoek 107:869–881. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10482-015-0379-5
Villa JE, Tsuchiya K, Horita M, Natural M, Opina N, Hyakumachi M (2005) Phylogenetic relationships of Ralstonia solanacearum species complex strains from Asia and other continents based on 16S rDNA, endoglucanase, and hrpB gene sequences. J Gen Plant Pahthol 71:39–46. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10327-004-0156-1
Wang YY, Shi YX, Chai AL, Xie XW, Li BJ (2017) Identification of Myrothecium roridum causing leaf spot on water spinach. Acta Phytopathol Sin 1:117–121
Yang UJ, Park TS, Shim SM (2013) Protective effect of chlorophyllin and lycopene from water spinach extract on cytotoxicity and oxidative stress induced by heavy metals in human hepatoma cells. J Toxicol Env Heal 76:1307–1315. https://doi.org/10.1080/15287394.2013.851632
Yaripour Z, Taghavi SM, Osdaghi E, Lamichhane JR (2018) Host range and phylogenetic analysis of Xanthomonas alfalfae causing bacterial leaf spot of alfalfa in Iran. Eur J Plant Pathol 150:267–274. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10658-017-1271-0
Young JM, Park DC, Shearman HM, Fargier E (2008) A multilocus sequence analysis of the genus Xanthomonas. Syst Appl Microbiol 31:366–377. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.syapm.2008.06.004
Yu Y, Chen J, Liu C, Gao Y, Wang JY, Yang YJ, Lu FQ, Huang M, Fang CY, Pan WJ, Yan BH, Wei D, Ni WR, Li HM (2015) Study on occurring characteristics of Albugo ipomoeae-aquaticae on Ipomoea aquatic Forsk and its controlling techniques in Shanghai. China Plant Prot 35:38–42
Acknowledgment
We thank Dr. Jianqiang Li and Dr. Laixin Luo from the Seed Health Centre, China Agricultural University for kindly providing the reference strain X. euvesicatoria pv. perforans XJ1602. We thank Dr. Guokun Liu from Fujian Agriculture and Forestry University, Fuzhou, China for kindly providing technical assistance.
Funding
This work was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (31801696), Fund for Basic Research Projects of Fujian Academy of Agricultural Sciences (CXTD2021004-3, XTCXGC2021011, XTCXGC2021017).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Fan, X., Zheng, H., Luo, H. et al. Xanthomonas euvesicatoria pv. perforans is the causative agent of bacterial leaf spot on Ipomoea aquatica from Fujian Province in China. Australasian Plant Pathol. 52, 327–337 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13313-023-00924-w
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13313-023-00924-w