Abstract
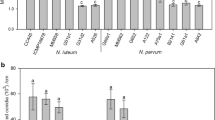
This study investigated the susceptibility of the most common rootstock and scion varieties used in New Zealand grapevine nurseries and vineyards to Botryosphaeriaceae species. A total of six rootstocks and six scion varieties were inoculated with mycelium of three isolates each of the most common Botryosphaeriaceae species (Neofusicoccum luteum, N. parvum and N. australe) recovered from New Zealand grapevine nurseries. Overall results showed that all isolates produced necrotic lesions on all varieties but susceptibility varied significantly (P < 0.001) with 5C and SO4 being the most susceptible of the rootstock varieties, and Merlot and Pinot noir being the most susceptible of the scions. Pathogenicity also varied significantly (P < 0.001) between species with N. parvum being the most virulent among three species tested. This study has further shown that different isolates of the three species have different levels of virulence providing evidence that these pathogens are genetically diverse. These results have significant implications for the New Zealand grapevine industry as the use of resistant varieties is not a possible option at present since none of the common varieties are resistant to these pathogens.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Alaniz S, García-Jiménez J, Abad-Campos P, Armengol J (2010) Susceptibility of grapevine rootstocks to Cylindrocarpon liriodendri and C. macrodidymum. Sci Hortic 125(3):305–308
Amponsah NT, Jones EE, Ridgway HJ, Jaspers MV (2011) Identification, potential inoculum sources and pathogenicity of botryosphaeriaceous species associated with grapevine dieback disease in New Zealand. Eur J Plant Pathol 131:467–482
Arauz LF, Sutton TB (1990) Effect of interrupted wetness periods on spore germination and apple infection by Botryosphaeria obtusa. Phytopathology 80:1218–1220
Baskarathevan J, Jaspers MV, Jones EE, Ridgway HJ (2012) Identification, incidence and distribution of botryosphaeriaceous species in New Zealand vineyards. Eur J Plant Pathol 132:549–560
Billones-Baaijens R, Ridgway HJ, Jones EE, Cruickshank RH, Jaspers MV (2013a) Prevalence and distribution of Botryosphaeriaceae species in New Zealand grapevine nurseries. Eur J Plant Pathol 135:175–185
Billones-Baaijens R, Ridgway HJ, Jones EE, Jaspers MV (2013b) Inoculum sources of Botryosphaeriaceae species in New Zealand grapevine nurseries. Eur J Plant Pathol 135:159–174
Billones-Baaijens R, Jones EE, Ridgway HJ, Jaspers MV (2013c) Pathogenicity affected by assay parameters during grapevine infection studies with Botryosphaeriaceae nursery isolates. Plant Pathol. doi:10.1111/ppa.12051
Burgess TI, Barber PA, St J. Hardy GE (2005) Botryosphaeria spp. associated with eucalypts in Western Australia, including the description of Fusicoccum macroclavatum sp. nov. Australas Plant Pathol 34(4):557–567
Eskalen A, Gubler WD, Khan A (2001) Rootstock susceptibility to Phaeomoniella chlamydospora and Phaeoacremonium spp. Phytopathol Mediterr 40(Supplement):S433–S438
Feliciano AJ, Eskalen A, Gubler WD (2004) Differential susceptibility of three grapevine cultivars to Phaeoacremonium aleophilum and Phaeomoniella chlamydospora in California. Paper presented at the Research papers, short notes and abstracts based on presentations at the third international workshop on grapevine trunk diseases, Christchurch, New Zealand, 1–2 February 2003
Gimenez-Jaime A, Aroca A, Raposo R, Garcia-Jimenez J, Armengol J (2006) Occurrence of fungal pathogens associated with grapevine nurseries and the decline of young vines in Spain. J Phytopathol 154(10):598–602
Jackson D, Schuster D (1994) The production of grapes and wine in cool climates. Gypsum Press, United Kingdom
Jaspers MV, Bleach CM, Harvey IC (2007) Susceptibility of grapevine rootstocks to Cylindrocarpon disease (Abstract). Phytopathol Mediterr 46(1):114
Keller M (2010) The science of grapevines: anatomy and physiology. Elsevier, Inc., London
Larignon P, Dubos B (2001) The villainy of black dead arm. Wines Vines 82:86–89
Luque J, Martos S, Torres E, Garcia F (2007) Susceptibility of some grapevine varieties and rootstocks commonly used in Spain to decline-associated fungi (Abstract). Phytopathol Mediterr 46(1):118–119
Marchi G (2001) Susceptibility to esca of various grapevine (Vitis vinifera) cultivars grafted on different rootstocks in a vineyard in the province of Siena (Italy). Phytopathol Mediterr 40(1):27–36
Martos S (2008) El decaimiento de la vid: enfermedades de la madera relacionadas con hongos de la familia Botryosphaeriaceae. PhD thesis, Universitat Autònoma de Barcelona, Bellaterra, Spain
Michailides TJ (1991) Pathogenicity, distribution, sources of inoculum, and infection courts of Botryosphaeria dothidea on pistachio. Phytopathology 81(5):566–573
New Zealand Winegrowers Statistical Annual (2010) New Zealand
Pearson RC, Goheen A C (Eds) (1998) Compendium of Grape Diseases. Minenesota, USA: APS Press.
Phillips AJL (2002) Botryosphaeria species associated with diseases of grapevines in Portugal. Phytopathol Mediterr 41(1):3–18
Sakalidis ML, Hardy GES, Burgess TI (2011a) Endophytes as potential pathogens of the baobab species Adansonia gregorii: a focus on the Botryosphaeriaceae. Fungal Ecol 4(1):1–14
Sakalidis ML, St J. Hardy GE, Burgess TI (2011b) Class III endophytes, clandestine movement amongst hosts and habitats and their potential for disease; a focus on Neofusicoccum australe. Australas Plant Pathol 40:510–521
Slippers B, Wingfield MJ (2007) Botryosphaeriaceae as endophytes and latent pathogens of woody plants: diversity, ecology and impact. Fungal Biol Rev 21(2–3):90–106
Taylor A, St J.Hardy GE, Wood P, Burgess T (2005) Identification and pathogenicity of Botryosphaeria species associated with grapevine decline in Western Australia. Australas Plant Pathol 34(2):187–195
Urbez-Torres JR, Leavitt GM, Voegel TM, Gubler WD (2006) Identification and distribution of Botryosphaeria spp. associated with grapevine cankers in California. Plant Dis 90(12):1490–1503
Urbez-Torres JR, Gubler WD (2009) Pathogenicity of Botryosphaeriaceae species isolated from grapevine cankers in California. Plant Dis 93(6):584–592
Urbez-Torres JR, Battany M, Bettiga LJ, Gispert C, McGourty G, Roncoroni J (2010) Botryosphaeriaceae species spore-trapping studies in California vineyards. Plant Dis 94(6):717–724
Urbez-Torres JR (2011) The status of Botryosphaeriaceae species infecting grapevines. Phytopathol Mediterr 50(Supplement):5–45
van Niekerk JM, Crous PW, Groenewald JZ, Fourie PH, Halleen F (2004) DNA phylogeny, morphology and pathogenicity of Botryosphaeria species on grapevines. Mycologia 96(4):781–798
Acknowledgments
We thank New Zealand Winegrowers and Lincoln University for funding this research and the grapevine nurseries for providing us with their valuable plant materials for our research. We also want to thank Brent Richards and Leona Meachen for maintaining our nursery plants throughout the conduct of these experiments.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Billones-Baaijens, R., Jones, E.E., Ridgway, H.J. et al. Susceptiblity of common rootstock and scion varieties of grapevines to Botryosphaeriaceae species. Australasian Plant Pathol. 43, 25–31 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13313-013-0228-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13313-013-0228-9