Abstract
Objective
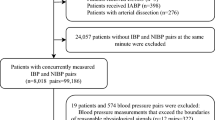
We assessed the agreement between non-invasive (oscillatory) blood pressure (NIBP) measurements and invasive intra-arterial blood pressure (IBP) in the pediatric cardiac critical care unit.
Methods
Children with intra-arterial lines as per standard management protocol were enrolled. NIBP was measured every 4 hourly and the corresponding IBP reading was recorded.
Results
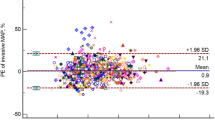
A total of 839 brachial NIBP, 834 IBP femoral (IF), and 137 IBP radial (IR) readings were noted on 45 participants. The mean difference (95% CI) for agreement between NIBP and IF was −2.3 (−27.1, 22.5) mmHg for systolic, 0.9 (−21.3, 23.1) mmHg for diastolic and 0.3 (−23.3, 23.9) mmHg for mean BP. Similar results were found between NIBP and IR and between IF and IR. The interrater agreement [Kappa (95% CI)] was fair between NIBP and IF [0.54 (0.48, 0.61)], and IF and IR [0.62 (0.48, 0.76)] but lower between NIBP and IR [0.37(0.20, 0.55)] when values were classified as hypotensive, normotensive, and hypertensive.
Conclusions
NIBP cannot replace but can supplement IBP in the pediatric cardiac critical care setting.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ward M, Langton JA. Blood pressure measurement. Continue Educ Anesth Crit Care Pain. 2007;7:122–6.
Lehman LW, Saeed M, Talmor D, Mark R, Malhotra A. Methods of blood pressure measurement in the ICU. Crit Care Med. 2013;41:34–40.
Ricci Z, Brogi J, De Filippis S, Caccavelli R, Morlacchi M, Romagnoli S. Arterial pressure monitoring in pediatric patients undergoing cardiac surgery: An observational study comparing invasive and non-invasive measurements. Pediatr Cardiol. 2019;40:1231–7.
Arafat M, Mattoo TK. Measurement of blood pressure in children: recommendations and perceptions on cuff selection. Pediatrics. 1999;104:e30.
Romagnoli S, Ricci Z, Quattrone D, et al. Accuracy of invasive arterial pressure monitoring in cardiovascular patients: An observational study. Crit Care. 2014;30;18:644.
Lin WQ, Wu HH, Su CS, et al. Comparison of continuous noninvasive blood pressure monitoring by TL-300 with standard invasive blood pressure measurement in patients undergoing elective neurosurgery. J Neurosurg Anesthesiol. 2017;29:1–7.
Ribezzo S, Spina E, Di Bartolomeo S, Sanson G. Noninvasive techniques for blood pressure measurement are not a reliable alternative to direct measurement: A randomized crossover trial in ICU. Scientific World Journal. 2014;2014:353628.
Krishna BV, Das S, Sen S. Correlation between blood pressure measurement by non-invasive and invasive methods in critically-ill children. Indian Pediatr. 2018;55:297–300.
de Caen AR, Berg MD, Chameides L, et al. Part 12: Pediatric Advanced Life Support: 2015 American Heart Association Guidelines Update for Cardiopulmonary Resuscitation and Emergency Cardiovascular Care. Circulation. 2015;132:S526–42.
Flynn JT, Kaelber DC, Baker-Smith CM, et al. Clinical practice guideline for screening and management of high blood pressure in children and adolescents. Pediatrics. 2017;140:e20171904.
Flynn JT. Neonatal hypertension: Diagnosis and management. Pediatr Nephrol. 2000;14:332–41.
Joffe R, Duff J, Guerra GG, Pugh J, Joffe AR. The accuracy of blood pressure measured by arterial line and noninvasive cuff in critically ill children. Crit Care. 2016;20:1.
Hayes S, Miller R, Patel A, et al. Comparison of blood pressure measurements in the upper and lower extremities versus arterial blood pressure readings in children under general anesthesia. Med Devices (Auckl). 2019;12:297–303.
Kim WY, Jun JH, Huh JW, Hong SB, Lim CM, Koh Y. Radial to femoral arterial blood pressure differences in septic shock patients receiving high-dose norepinephrine therapy. Shock. 2013;40:527–531.
Holt TR, Withington DE, Mitchell E. Which pressure to believe? A comparison of direct arterial with indirect blood pressure measurement techniques in the pediatric intensive care unit. Pediatr Crit Care Med. 2011;12:e391–4.
Wax DB, Lin HM, Leibowitz AB. Invasive and concomitant noninvasive intraoperative blood pressure monitoring observed differences in measurements and associated therapeutic interventions. Anesthesiology. 2011;115:973–8.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Ethics clearance
Institutional ethics committee; No IEC/HMPCMCE/114/Faculty/11/dated October 1, 2019. Considering the nature of the study, a waiver of informed consent was approved.
Contributors
JT: conceptualized and designed the study, guided and supervise data collection, drafted the manuscript, and approved the final manuscript; SN: conceptualized and designed the study, critical review of the manuscript, and approved the final manuscript; AK; critical inputs for design of the study and manuscript preparation, drafting the manuscript, guided and supervise data collection, and approved the final manuscript; MC; helped in study planning and execution, continued onsite data collection and interpretation, and approved the final manuscript; AP: conceptualized and designed the study, data analysis, critical input for manuscript preparation, and approved the final manuscript.
Funding
None
Competing interest
None stated.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kumar, A., Thacker, J.P., Chaudhary, M. et al. Agreement Between Non-Invasive (Oscillatory) and Invasive Intra-Arterial Blood Pressure in the Pediatric Cardiac Critical Care Unit. Indian Pediatr 58, 643–646 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13312-021-2260-0
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13312-021-2260-0