Abstract
Aim
This study aimed to investigate the alteration of circulating CD34+KDR+CD133+ endothelial progenitor cells (EPCs) in patients with newly diagnosed type 2 diabetes and the mechanism of the effect of early intensive insulin therapy.
Methods
In this study, 36 patients with newly diagnosed type 2 diabetes and 22 control subjects matched by age and gender were enrolled. All of the patients with diabetes received intensive insulin therapy. The number of EPCs was assessed by flow cytometry based on the expression of CD34, CD133, and kinase insert domain-containing receptor (KDR).
Results
Levels of circulating CD34+KDR+CD133+ EPCs were higher in patients with diabetes compared to control subjects and significantly decreased after intensive insulin therapy. Levels of vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF), a major contributor to EPC mobilization, were significantly higher in patients with diabetes compared to control subjects, and dramatically decreased after insulin therapy. Importantly, VEGF levels correlated with number of EPCs. Moreover, compared with control subjects, pro-inflammatory cytokines and oxidative stress were significantly higher in patients with diabetes and markedly decreased after intensive insulin therapy.
Conclusions
These results showed that type 2 diabetes is associated with an increase of circulating CD34+KDR+CD133+ EPCs at the onset of diabetes, indicating increased compensatory mobilization. Additionally, early intensive insulin therapy exerts a preserving effect on EPC level partly through improving inflammation status and oxidative stress, thereby implying a putative long-term beneficial effect on vascular integrity via suspending excessive EPC exhaustion.
Clinical Trial Number
NCT03710811.
Similar content being viewed by others
Avoid common mistakes on your manuscript.
Why carry out this study? |
Approximately 463 million people suffer from diabetes worldwide. |
Circulating CD34+KDR+ endothelial progenitor cells (EPCs) correlate with severity of diabetic peripheral arterial disease in patients with type 2 diabetes. |
This study aimed to investigate the alteration of circulating CD34+KDR+CD133+ EPCs in patients with newly diagnosed type 2 diabetes and the mechanism of the effect of early intensive insulin therapy. |
What was learned from the study? |
Type 2 diabetes is associated with an increase of circulating CD34+KDR+CD133+ EPCs at the onset of diabetes. |
Early intensive insulin therapy exerts a preserving effect on CD34+KDR+CD133+ EPC level partly through improving inflammation status and oxidative stress. |
Introduction
Endothelial progenitor cells (EPCs) are immature bone marrow-derived cells which undergo differentiation into endothelial cells and contribute to endothelial repair and angiogenesis [1]. The number of circulating EPCs correlates with cardiovascular risk factors, as well as being an independent predictor of cardiovascular death [2, 3]. Different types of EPCs exist, differing by their maturity, clonogenic potential, and angiogenic effects [4]. In humans, EPCs are primarily identified by the expression of combinations of cell-surface markers, including CD34, CD133, and kinase insert domain-containing receptor (KDR). Although CD34+KDR+ EPCs constitute the major component of the circulating EPC pool, the CD34+KDR+CD133+ EPCs have a more potent vasoregenerative capacity and are mainly mobilized from bone marrow by chemokines and growth factors, such as vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF) [5,6,7].
Diabetic vasculopathy is characterized by high prevalence, early development, and rapid progression. Circulating CD34+KDR+ EPCs were significantly reduced in subjects with impaired glucose tolerance and further decreased in new-onset type 2 diabetes as well [8, 9]. Moreover, the number of circulating CD34+KDR+ EPCs correlates with severity of disease, especially with the degree of diabetic peripheral arterial disease in patients with type 2 diabetes [10, 11]. However, the alteration of CD34+KDR+CD133+ EPCs at the onset of diabetes remains unknown. In addition, in patients with newly diagnosed type 2 diabetes, short-term intensive insulin therapy was shown to achieve long-term glycemic control, and significantly decreases the risk of microvascular complications [12, 13]; however, whether intensive insulin therapy could affect CD34+KDR+CD133+ EPCs is unclear.
In this study, we aimed to evaluate the alteration of CD34+KDR+CD133+ EPCs in patients with newly diagnosed type 2 diabetes and investigate the effect of intensive insulin therapy on these cells. Patients with newly diagnosed type 2 diabetes and control subjects matched by age and gender were enrolled. All of the patients with diabetes received short-term intensive insulin therapy. Blood samples were collected to detect EPCs by flow cytometry based on the expression of CD34, CD133, and KDR.
Methods
Patients and Research Design
In this study, 36 patients with newly diagnosed type 2 diabetes, according to the American Diabetes Association criteria [14], were enrolled from April to September 2017 at Nanjing Drum Tower Hospital Affiliated to Nanjing University Medical School (Nanjing, Jiangsu province, China). A further 22 control subjects who participated in health examinations at the hospital were randomly recruited. Medical history, physical examination, blood biochemistry, and clinical diagnosis were evaluated in all participants. Subjects were excluded from this study for the following reasons: history of taking antihypertensive drugs, hypolipidemic agents, estrogen supplements, herbal drugs, or antioxidants for 3 months before enrolling in the study, medical history of cardiovascular events; acute illness or infection, recent surgery or vascular intervention, ketosis, ketoacidosis, and other diseases requiring continuous medical treatment and cigarette smoking.
Patients with diabetes were treated with continuous subcutaneous insulin infusion by receiving Novolin-R (Novo Nordisk, Bagsvaerd, Denmark) with an insulin pump. Initial insulin dose was adjusted every day depending on the values from the seven-point glucose profile obtained 1 day before and was divided into 50% of basal and 50% of bolus injection. The glycemic control target was defined as fasting plasma glucose below 6.1 mmol/l and prandial plasma glucose below 8.0 mmol/l. Insulin treatment was discontinued 2 weeks later after the target goal was achieved and blood samples were re-collected for further detections.
This study was approved by the Ethics Review Committee of Nanjing Drum Tower Hospital Affiliated to Nanjing University Medical School (No. 2017-068). All patients signed written informed consent before enrollment.
Subjects’ Characteristics
Patients’ height was measured by a portable stadiometer with shoes off, to the nearest centimeter. The weight was measured on a digital scale with identical light clothing on, to the nearest 0.1 kg. BMI was calculated as weight divided by height squared. Blood pressure was measured using a mercury sphygmomanometer after the subject rested for at least 5 min. The mean of three measurements was recorded.
Blood Sample Analysis
Fasting blood samples were collected from the antecubital vein for fasting plasma glucose, insulin, glycosylated hemoglobin (HbA1c), triglycerides (TG), total cholesterol (TC), high-density lipoprotein cholesterol (HDL-C), low-density lipoprotein cholesterol (LDL-C), urea nitrogen, creatinine, and uric acid measurements. The fasting plasma glucose levels were assessed by the hexokinase method using TBA-200FR analyzer (Toshiba Medical Systems, Tokyo, Japan). Insulin concentration was evaluated by a chemiluminescence immunoassay (Cobas e601; Roche, Basel, Switzerland). HbA1c was quantitated by high-performance liquid chromatography (Bio-Rad Laboratories, Inc., Hercules, CA, USA). TG, TC, HDL-C, and LDL-C concentrations were assessed by specific immunoassays (Cobas e601; Roche, Basel, Switzerland). Serum free fatty acids (FFAs) were detected via an enzymatic method (DiaSys Diagnostic Systems GmbH, Holzheim, Germany). Homeostasis model assessment of insulin resistance (HOMA-IR) was derived as follows: [fasting serum insulin (mU/l) × fasting plasma glucose (mmol/l)]/22.5 [15]. Serum 1.5-anhydroglucitol (1.5-AG) was measured using an enzymatic assay kit (GlycoMark, Japan).
Quantification of EPCs by Flow Cytometry
Peripheral blood mononuclear cells (PBMCs) were isolated with vacutainer cell preparation tubes (CPTs) (Becton Dickinson, Franklin Lakes, NJ, USA) from fasting blood samples. After centrifugation at 1800×g for 30 min, cells in the resulting supernatants were collected, washed with phosphate-buffered saline (PBS), and gradually frozen within 8 h in freezing medium containing 10% dimethyl sulfoxide (DMSO) and 90% fetal bovine serum. Samples were stored in liquid nitrogen until analysis of EPCs.
PBMCs were stained with the following antibodies: fluorescein isothiocyanate (FITC)-labeled anti-CD34 (BD Biosciences, USA), phycoerythrin (PE)-labeled anti-CD133 (Becton Dickinson, Franklin Lakes, NJ, USA), and allophycocyanin (APC)-labeled anti-KDR (Becton Dickinson, Franklin Lakes, NJ, USA). In brief, 100 μl of PBMC samples was incubated at 4 °C for 20 min in the dark with 5 μl of FITC-CD34, 10 μl of PE-CD133, and APC-KDR. Cells labeled with FITC-, PE-, and APC-conjugated isotypic monoclonal antibodies were used as controls to determine the background of fluorescence. After staining, cells were washed in 1 ml PBS and eventually re-suspended in 500 μl PBS. Analysis was then performed within 30 min. Absolute cell numbers were measured using an LSR II Fortessa flow cytometer (Becton Dickinson, Franklin Lakes, NJ, USA); data were analyzed with FACSDiva software (Becton Dickinson, Franklin Lakes, NJ, USA) or FlowJo 9.6.4 software (Tree Star Inc., Ashland, OR, USA). All results from flow cytometry were expressed as number of cells/106 total cytofluorimetric events.
Cytokine Detection and Oxidative Activity Analysis
Serum levels of tumor necrosis factor alpha (TNFα), interferon gamma (IFNγ), and interleukin-1 beta (IL-1β) were determined with a CBA Flex set (BD Biosciences, San Jose, CA). The plasma levels of VEGF, malonyldialdehyde (MDA), glutathione (GSH), and superoxide dismutase (SOD) were respectively determined in duplicate using commercially available ELISA kits according to the manufacturer’s guidelines (USCN Business Co. Ltd., Wuhan, China). The plasma levels of reactive oxygen species (ROS) were determined using the ROS colorimetric assay kit (Nanjing Jiancheng Bioengineering Institute, Nanjing, China).
Statistical Analysis
Data were expressed as mean ± standard deviation (SD) or n (%), unless otherwise specified. Differences in continuous variables were determined by the Student’s t test, paired sample t test, or Mann–Whitney U test, and differences in categorical variables were determined by the χ2 analysis or Fisher’s exact test. Correlation analyses were assessed by Spearman’s rank correlation test. P values < 0.05 were considered statistically significant.
Results
Baseline Characteristics of Study Population
As summarized in Table 1, there were no significant differences in age and sex between patients with type 2 diabetes and controls. Compared with controls, the patients with type 2 diabetes had significantly higher BMI, HbA1c, fasting plasma glucose, fasting insulin, HOMA-IR, TG, TC, FFA, and LDL-C levels. In contrast, HDL-C and 1.5-AG levels were significantly lower in the patients with type 2 diabetes than those of controls. In addition, levels of blood urea nitrogen, creatinine, uric acid, and estimated glomerular filtration rate were not significantly different between the two groups.
After the intensive insulin therapy, patients with type 2 diabetes showed significant decreases in fasting plasma glucose, TG, TC, FFA, and LDL-C levels compared with those before therapy. Although HbA1c level was not decreased, 1.5-AG, a sensitive glycemic marker, which reflects short-term glycemic changes [16], was notably increased in patients with diabetes after intensive insulin therapy. Moreover, HOMA-IR was significantly decreased, while fasting insulin level was not changed.
CD34+KDR+CD133+ EPCs are Increased in Patients with Newly Diagnosed Type 2 Diabetes and Reversed After Therapy
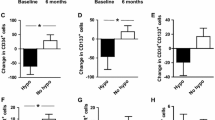
Compared with control subjects, circulating CD34+ cells, CD133+ cells, CD34+CD133+ cells, and CD34+KDR+ cells significantly decreased in patients with newly diagnosed diabetes, and remained unchanged after intensive insulin therapy (Table 1 in the supplementary material). Importantly, the circulating CD34+KDR+CD133+ EPC count was significantly higher in the diabetic group compared to the control group (35 ± 4 vs. 16 ± 2, P < 0.01; Fig. 1). After the intensive insulin therapy, the circulating CD34+KDR+CD133+ EPC count significantly decreased in the diabetic group, as compared to baseline values (15 ± 2 vs. 35 ± 4, P < 0.01, Fig. 1).
a Representative identification of circulating CD34+KDR+CD133+ EPCs. After gating lymphocytes and monocytes in the FSC versus SSC morphologic plot, total CD34+ cells were identified and were then examined for expression of CD133 and KDR. b Circulating CD34+KDR+CD133+ EPCs for control subjects and patients with newly diagnosed type 2 diabetes. Data are mean ± standard error. **P < 0.01 vs. control group. ##P < 0.01 vs. T2DM baseline
Intensive Insulin Therapy Reverses Elevation of VEGF Level in Patients with Newly Diagnosed Type 2 Diabetes
The serum VEGF level in the diabetic group was significantly higher than that in the control group (29.2 ± 4.9 vs.17.9 ± 4.6, P < 0.01; Fig. 2a). After the insulin therapy, the serum VEGF level was remarkably reduced, as compared with baseline values (21.0 ± 3.6 vs. 29.2 ± 4.9, P < 0.01; Fig. 2a). Moreover, in all subjects, the CD34+KDR+CD133+ EPC count was positively correlated with the serum VEGF level (r = 0.392, P = 0.002; Fig. 2b).
Intensive Insulin Therapy Decreases Inflammation and Oxidative Stress in Patients with Diabetes
Pro-inflammatory cytokines were significantly higher in patients with diabetes (TNFα 18.9 ± 1.4 vs. 15.7 ± 2.1, P < 0.01; IL-1β 14.2 ± 5.1 vs. 9.41 ± 1.9, P < 0.05; IFNγ 16.1 ± 3.1 vs. 11.7 ± 3.3, P < 0.05, Table 2) compared to control subjects, and markedly decreased after therapy compared with baseline values (TNFα 17.1 ± 1.6 vs.18.9 ± 1.4, P = 0.009; IL-1β 10.9 ± 1.4 vs.14.2 ± 5.1, P < 0.001; IFNγ 13.3 ± 3.4 vs.16.1 ± 3.1, P < 0.01, Table 2).
Markers of oxidative stress were further detected in all subjects. The serum levels of ROS (2242.9 ± 444.2 vs. 1211.4 ± 510.1, P < 0.01, Table 2) and MDA (8.1 ± 2.4 vs. 4.8 ± 1.2, P < 0.01, Table 2) in the diabetic group were remarkably higher compared to those of the control group, and were significantly decreased after intensive insulin therapy (ROS 1542.0 ± 265.5 vs. 2242.9 ± 444.2, P < 0.01; MDA 5.7 ± 0.8 vs. 8.1 ± 2.4, P < 0.01). In contrast, the serum levels of SOD (81.8 ± 9.1 vs. 103.5 ± 3.3, P < 0.01, Table 2) and GSH (202.1 ± 14.3 vs. 266.3 ± 23.5, P < 0.01, Table 2) in the diabetic group were significantly lower compared to the control group, and were notably restored after intensive insulin therapy (SOD 97.9 ± 6.1 vs. 81.8 ± 9.1, P < 0.01; GSH 237.7 ± 11.9 vs. 202.1 ± 14.3, P < 0.01).
Discussion
In this study, our data showed that patients with newly diagnosed type 2 diabetes have significantly higher levels of circulating CD34+KDR+CD133+ EPCs, VEGF, oxidative stress, and inflammation. Increased levels of VEGF correlated with circulating CD34+KDR+CD133+ EPCs in these patients. Moreover, short-term intensive insulin therapy restored EPCs level through attenuating oxidative stress, inflammation, and VEGF level.
Our data firstly showed that circulating CD34+CD133+KDR+ EPCs were notably higher in the patients with newly diagnosed type 2 diabetes compared to controls. Among the CD34+KDR+ EPC pools, CD133+ immature EPCs are recently mobilized from bone marrow and have a more potent vasoregenerative capacity [5]. Importantly, the level of CD34+KDR+CD133+ EPCs is associated with the degree of endothelial damage, and the elevation of CD34+KDR+CD133+ EPCs represents the ability to perform neoangiogenesis and maintain the homeostasis of vascular endothelium [17]. Therefore, increased circulating CD34+KDR+CD133+ EPCs at the onset of diabetes may indicate a compensatory EPC mobilization from bone marrow into peripheral blood to improve the early vessel defect. Although appearing beneficial on first sight, this effect may be impaired after exhaustion of CD34+KDR+CD133+ EPCs during long-term hyperglycemia, thereby accelerating the development of microvascular and macrovascular complications. In support of this notion, levels of CD34+KDR+CD133+ EPCs were found to be significantly lower in patients with a long history of type 2 diabetes [18]. Importantly, our results further demonstrated that intensive insulin therapy significantly decreased circulating CD34+KDR+CD133+ EPCs in patients with newly diagnosed type 2 diabetes, indicating a protective role in preventing the excessive exhaustion of CD34+KDR+CD133+ EPCs. Indeed, intensive insulin therapy was shown to achieve long-term glycemic control and significantly decreased the risk of microvascular complications in patients with newly diagnosed type 2 diabetes [12, 13]. Notably, to exclude the effects of medications on circulating CD34+KDR+CD133+ EPCs and to elucidate the alteration of these cells at the onset of type 2 diabetes, we enrolled drug-naïve patients with newly diagnosed diabetes other than patients with long-standing diabetes in this study. Adding another long-standing diabetic group will better clarify the change in course of circulating CD34+CD133+KDR+ EPCs.
Another major finding of this study is that VEGF levels were increased in patients with newly diagnosed type 2 diabetes and were positively correlated with circulating CD34+KDR+CD133+ EPCs. During angiogenesis or for repairing injured blood vessel, EPCs have to be mobilized from the bone marrow to the peripheral blood. VEGF is a cytokine that plays a key role in EPC mobilization [6]. CD34+KDR+CD133+ immature EPCs, which mobilized form bone marrow [5], are tightly regulated by VEGF [6, 7, 19]. In agreement with previous studies, our data showed that EPCs correlated with VEGF levels; thus a higher level of VEGF may contribute to the increased number of CD34+KDR+CD133+ EPCs in patients with newly diagnosed type 2 diabetes. Of note, VEGF expression was shown to be upregulated by oxidative stress [20, 21], while inflammatory cytokines, such as TNF, could promote oxidative stress through inducing the generation of ROS by mitochondria [22,23,24]. In this study, activated oxidative stress was observed in patients with newly diagnosed type 2 diabetes, and was characterized by higher levels of ROS and MDA and lower levels of GSH and SOD. Furthermore, levels of pro-inflammatory cytokines, such as TNFα, IL-1β, and IFNγ, were found to be significantly higher in patients with newly diagnosed type 2 diabetes, and notably reduced after intensive insulin therapy. Thus, inflammation and oxidative stress may contribute to increased VEGF and subsequent EPCs at the onset of diabetes. Additionally, early intensive insulin therapy exerts a preserving effect on VEGF level partly through improving inflammation status and oxidative stress.
This study has several limitations. First, the number of patients was limited and the results need further confirmation in a larger cohort. Second, the function of CD34+KDR+CD133+ EPCs and effect of intensive insulin therapy on vascular function and integrity were not assessed in the present study. Using a mice model, which mimics the effect of intensive insulin therapy on metabolic improvement [25], we aim to determine the causative role of intensive insulin therapy in EPC regulation in the future, accompanied by investigating the vascular integrity and function through analyzing pericyte coverage of vessels, detecting fluorescein-conjugated dextran extravasation, and measuring vessel relaxation and contraction activity in response to stimulus. Of note, when circulating EPCs were detected by flow cytometry, EPCs of whole blood samples were gated in the lymphoid and mononuclear cell populations [26, 27], and many studies isolated the mononuclear cells from whole blood samples before analyzing EPCs [28,29,30,31]. In this study, PBMC were isolated to detect the alteration of CD34+KDR+CD133+ EPCs in patients with newly diagnosed diabetes. Although usage of cell preparation tubes guaranteed the optimal yield of mononuclear cells from the blood samples, it is important to point out that selective depletion caused by PBMC separation before analysis of stem/progenitor cells might exist.
Notwithstanding these limitations, we suggest that our data may have pathophysiological implications. Intensive insulin therapy may be suggested in the early phases after diagnosis of type 2 diabetes in order to suspend excessive CD34+KDR+CD133+ EPC exhaustion and preserve marrow mobilization function longer, thereby causing a long-term beneficial effect on vascular integrity and decreasing the risk of microvascular complications.
Conclusions
Patients with type 2 diabetes were associated with an increase of circulating CD34+KDR+CD133+ EPCs at the onset of diabetes, indicating increased compensatory mobilization. Importantly, early intensive insulin therapy exerts a preserving effect on CD34+KDR+CD133+ EPCs partly through improving oxidative stress and inflammation status, thereby implying a putative long-term beneficial effect on vascular integrity via suspending excessive EPC exhaustion.
Change history
14 March 2022
A Correction to this paper has been published: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13300-022-01227-x
References
Asahara T, Murohara T, Sullivan A, et al. Isolation of putative progenitor endothelial cells for angiogenesis. Science. 1997;275(5302):964–7.
Hill JM, Zalos G, Halcox JP, et al. Circulating endothelial progenitor cells, vascular function, and cardiovascular risk. N Engl J Med. 2003;348(7):593–600.
Werner N, Kosiol S, Schiegl T, et al. Circulating endothelial progenitor cells and cardiovascular outcomes. N Engl J Med. 2005;353(10):999–1007.
Hur J, Yoon CH, Kim HS, et al. Characterization of two types of endothelial progenitor cells and their different contributions to neovasculogenesis. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol. 2004;24(2):288–93.
Friedrich EB, Walenta K, Scharlau J, Nickenig G, Werner N. CD34-/CD133+/VEGFR-2+ endothelial progenitor cell subpopulation with potent vasoregenerative capacities. Circ Res. 2006;98(3):e20-25.
Ye J, Ni P, Kang L, Xu B. Apelin and vascular endothelial growth factor are associated with mobilization of endothelial progenitor cells after acute myocardial infarction. J Biomed Res. 2012;26(6):400–9.
Moore MA, Hattori K, Heissig B, et al. Mobilization of endothelial and hematopoietic stem and progenitor cells by adenovector-mediated elevation of serum levels of SDF-1, VEGF, and angiopoietin-1. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 2001;938:36–45 (discussion 45-37).
Fadini GP, Pucci L, Vanacore R, et al. Glucose tolerance is negatively associated with circulating progenitor cell levels. Diabetologia. 2007;50(10):2156–63.
Fadini GP, Boscaro E, de Kreutzenberg S, et al. Time course and mechanisms of circulating progenitor cell reduction in the natural history of type 2 diabetes. Diabetes Care. 2010;33(5):1097–102.
Tepper OM, Galiano RD, Capla JM, et al. Human endothelial progenitor cells from type II diabetics exhibit impaired proliferation, adhesion, and incorporation into vascular structures. Circulation. 2002;106(22):2781–6.
Fadini GP, Sartore S, Albiero M, et al. Number and function of endothelial progenitor cells as a marker of severity for diabetic vasculopathy. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol. 2006;26(9):2140–6.
Weng J, Li Y, Xu W, et al. Effect of intensive insulin therapy on beta-cell function and glycaemic control in patients with newly diagnosed type 2 diabetes: a multicentre randomised parallel-group trial. Lancet. 2008;371(9626):1753–60.
UK Prospective Diabetes Study (UKPDS) Group. Intensive blood-glucose control with sulphonylureas or insulin compared with conventional treatment and risk of complications in patients with type 2 diabetes (UKPDS 33). Lancet. 1998;352(9131):837–53.
American Diabetes Association. 2. Classification and diagnosis of diabetes. Diabetes Care. 2017;40(Suppl 1):S11–24.
Xuan Y, Sun LH, Liu DM, et al. Positive association between serum levels of bone resorption marker CTX and HbA1c in women with normal glucose tolerance. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2015;100(1):274–81.
Stickle D, Turk J. A kinetic mass balance model for 1,5-anhydroglucitol: applications to monitoring of glycemic control. Am J Physiol. 1997;273(4 Pt 1):E821-830.
Isner JM, Asahara T. Angiogenesis and vasculogenesis as therapeutic strategies for postnatal neovascularization. J Clin Investig. 1999;103(9):1231–6.
Yue WS, Lau KK, Siu CW, et al. Impact of glycemic control on circulating endothelial progenitor cells and arterial stiffness in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus. Cardiovasc Diabetol. 2011;10:113.
Asahara T, Takahashi T, Masuda H, et al. VEGF contributes to postnatal neovascularization by mobilizing bone marrow-derived endothelial progenitor cells. EMBO J. 1999;18(14):3964–72.
Behl T, Kotwani A. Exploring the various aspects of the pathological role of vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF) in diabetic retinopathy. Pharmacol Res. 2015;99:137–48.
Klettner A, Roider J. Constitutive and oxidative-stress-induced expression of VEGF in the RPE are differently regulated by different mitogen-activated protein kinases. Graefes Arch Clin Exp Ophthalmol. 2009;247(11):1487–92.
Kim YS, Morgan MJ, Choksi S, Liu ZG. TNF-induced activation of the Nox1 NADPH oxidase and its role in the induction of necrotic cell death. Mol Cell. 2007;26(5):675–87.
Schulze-Osthoff K, Bakker AC, Vanhaesebroeck B, Beyaert R, Jacob WA, Fiers W. Cytotoxic activity of tumor necrosis factor is mediated by early damage of mitochondrial functions. Evidence for the involvement of mitochondrial radical generation. J Biol Chem. 1992;267(8):5317–23.
Houstis N, Rosen ED, Lander ES. Reactive oxygen species have a causal role in multiple forms of insulin resistance. Nature. 2006;440(7086):944–8.
Tang W, Tang S, Wang H, Ge Z, Zhu D, Bi Y. Insulin restores UCP3 activity and decreases energy surfeit to alleviate lipotoxicity in skeletal muscle. Int J Mol Med. 2017;40(6):2000–10.
Fadini GP, Tura A, Pacini G, Avogaro A, de Vigili KS. Reduced circulating stem cells associate with excess fasting and post-load NEFA exposure in healthy adults with normal glucose tolerance. Atherosclerosis. 2017;261:117–23.
Fadini GP, Bonora BM, Cappellari R, et al. Acute effects of linagliptin on progenitor cells, monocyte phenotypes, and soluble mediators in type 2 diabetes. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2016;101(2):748–56.
Oikonomou D, Kopf S, von Bauer R, et al. Influence of insulin and glargine on outgrowth and number of circulating endothelial progenitor cells in type 2 diabetes patients: a partially double-blind, randomized, three-arm unicenter study. Cardiovasc Diabetol. 2014;13:137.
Ai S, He Z, Ding R, et al. Reduced vitamin D receptor on circulating endothelial progenitor cells: a new risk factor of coronary artery diseases. J Atheroscler Thromb. 2018;25(5):410–21.
Lev EI, Singer J, Leshem-Lev D, et al. Effect of intensive glycaemic control on endothelial progenitor cells in patients with long-standing uncontrolled type 2 diabetes. Eur J Prev Cardiol. 2014;21(9):1153–62.
Hammer Y, Soudry A, Levi A, et al. Effect of vitamin D on endothelial progenitor cells function. PLoS ONE. 2017;12(5): e0178057.
Acknowledgements
Funding
This work and journal’s Rapid Service Fee was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China Grant Awards (82030026, 81970689, 82070837, 81970704, 81770819, 81703294, 81800752, 81900787, 82000735, 82000775, and 81800719), the National Key Research and Development Program of China (2016YFC1304804 and 2017YFC1309605), the Jiangsu Provincial Key Medical Discipline (ZDXKB2016012), the Key Project of Nanjing Clinical Medical Science, the Jiangsu Provincial Medical Talent (ZDRCA2016062), the Six Talent Peaks Project of Jiangsu Province of China (YY-086), the Scientific Research Project of the Fifth Phase of “333 Project” of Jiangsu Province of China, the Doctor of Entrepreneurship and Innovation Program of Jiangsu Province, the Fundamental Research Funds for the Central Universities (021414380444).
Authorship
All named authors meet the International Committee of Medical Journal Editors (ICMJE) criteria for authorship for this article, take responsibility for the integrity of the work as a whole, and have given their approval for this version to be published.
Author Contributions
Dalong Zhu and Yan Bi conceived and designed the study. Clinical data was collected by Wenjuan Tang, Pengzi Zhang, and Tianwei Gu. Quantification of EPCs by flow cytometry, cytokine detection, and oxidative activity analysis were performed by Wei Zhang, Hongdong Wang, Fangcen Liu, and Xiao Ye. Wei Zhang performed the data analysis and drafted the manuscript. Hongdong Wang contributed to the revision of the manuscript. All authors critically read and approved the final manuscript.
Prior Presentation
This study was presented as a poster at the American Diabetes Association’s 78th Scientific Sessions, June 22–26, 2018 in Orlando, Florida. Poster presentation number 457-P, in category 02-A Complications-Macrovascular-Atherosclerotic Cardiovascular Disease and Human Diabetes. Poster link: https://diabetes.diabetesjournals.org/content/67/Supplement_1/457-P.
Disclosures
Wei Zhang, Hongdong Wang, Fangcen Liu, Xiao Ye, Wenjuan Tang, Pengzi Zhang, Tianwei Gu, Dalong Zhu, and Yan Bi declare that they have nothing to disclose interest.
Compliance with Ethics Guidelines
All recruited participants gave their written informed consent before enrollment. The study (NCT03710811) was registered at ClinicalTrials.gov and was approved by the Ethics Committee of Drum Tower Hospital Affiliated to Nanjing University Medical School (No. 2017-068) and was compliant with the declaration of Helsinki 1964 and its later amendments.
Data Availability
All data generated or analyzed during this study are included in this published article/as supplementary information files.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Additional information
The original online version of this article was revised due to update in text.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
Open Access This article is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License, which permits any non-commercial use, sharing, adaptation, distribution and reproduction in any medium or format, as long as you give appropriate credit to the original author(s) and the source, provide a link to the Creative Commons licence, and indicate if changes were made. The images or other third party material in this article are included in the article's Creative Commons licence, unless indicated otherwise in a credit line to the material. If material is not included in the article's Creative Commons licence and your intended use is not permitted by statutory regulation or exceeds the permitted use, you will need to obtain permission directly from the copyright holder. To view a copy of this licence, visit http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc/4.0/.
About this article
Cite this article
Zhang, W., Wang, H., Liu, F. et al. Effects of Early Intensive Insulin Therapy on Endothelial Progenitor Cells in Patients with Newly Diagnosed Type 2 Diabetes. Diabetes Ther 13, 679–690 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13300-021-01185-w
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13300-021-01185-w