Abstract
Introduction
The 2015 Insulin Injection Technique Questionnaire survey involving 13,289 patients included 898 (6.8%) patients in the pediatric age range (≤ 18 years).
Methods
The younger patients included in the questionnaire survey were grouped according to age: Group 1 (G1), 0–6 years, n = 85; Group 2(G2), 7–13, n = 423; Group 3 (G3), 14–18, n = 390. The injection technique was evaluated by means of a questionnaire and nurse assessment.
Results
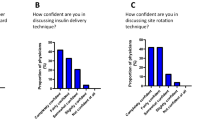
Nurses found lipohypertrophy at injection sites in 41.3, 45.2, and 47.3% of patients in G1, G2, and G3, respectively. Unexpected hypoglycemia was common, ranging from 23.8 to 48.1% of patients, and glucose variability was even more common (61.0% in G1, 45.9% in G2, and 52.5% in G3); both conditions were associated with lipohypertrophy. While increasing numbers of patients were using the recommended 4-mm needles, large percentages still used longer ones (33.3% in G1, 45.9% in G2, and 61.5% in G3). The reuse of needles was also common, ranging from 21.1 to 32.5% in the three age groups. Excessive reuse, defined as using a single needle more than five times, was reported by 9.4–21.8% of patients in the three age group. The percentages of patients who had not received any injection training in the last 12 months ranged from 21.2 to 26.8% in the three groups.
Conclusion
Implications of our study are as follows: (1) pediatric patients should use 4-mm pen needles or 6-mm syringes (inserted at a 45° angle); (2) patients aged ≤ 6 years should always inject into a raised skin fold regardless of which device is used; (3) all patients should rotate sites and use needles only once to avoid lipohypertrophy.
Funding
Becton–Dickinson (BD) diabetes care.
Similar content being viewed by others
Avoid common mistakes on your manuscript.
Introduction
The diagnosis of diabetes (DM) at a young age is always a life-changing event for both patient and family. Along with the diagnosis comes the task of mastering new lifelong habits, one of which involves the administration of insulin. Most pediatric DM patients receive insulin through injections, and it is assumed that they know how to do so properly. Injecting correctly is essential to optimizing both the pharmacokinetics (PK) and pharmacodynamics (PD) of insulin and making PK and PD more consistent from one injection to another [1]. Guidelines and recommendations exist on how to inject correctly [2], but little is known regarding the actual adherence of diabetic pediatric patients to these recommendations.
From February 2014 until June 2015 we administered the Insulin Injection Technique Questionnaire (ITQ) to 13,289 patients from 425 centers in 42 countries [3, 4]. Of these patients, 898 (6.8%) were in the pediatric age range (≤ 18 years). The findings from the ITQ were used to formulate and publish the New Insulin Delivery Recommendations on a worldwide basis [5]. The New Recommendations include sections relevant to pediatric patients, based on published studies on insulin injections in children going back many years.
Here we review the results of the ITQ on pediatric patients, and based on these results of this review we recommend practical steps for improving clinical practice.
Methods
The ITQ study methodology, including language and translations used, validation process, and statistical approach, have been described in two previous publications [3, 6]. A total of 898 pediatric participants with diabetes who had both patient and nurse forms filled out were included in the ITQ database. In the current post hoc analysis we have used the following age-based grouping: Group 1 (G1), 0–6 years (or pre-school); n = 85; Group 2 (G2), 7–13 years (school age), n = 423; Group 3 (G3), 14–18 years (adolescent), n = 390. G2 and G3 were split between age 13 and 14 years since by the latter age over 90% of children (both girls and boys) have one or more secondary sexual characteristics, signifying that they have arrived at puberty [7]. Since subcutaneous tissue (SC) is highly governed by sex hormones, it was felt important to be sure that the adolescent grouping included only patients who had exposure to the hormones of puberty.
The ITQ was conducted according the principles of the Helsinki declaration and subsequent amendments. No patient-identifying information was given to the sponsor, and participants were assured their care would not be affected in any way by their participation, or not. They were put at no risk by the study and did not receive any remuneration to participate. Therefore, ethics committee approval was not required overall, but was obtained whenever requested by local authorities. All participating centers did so voluntarily and without financial incentive.
Not every patient responded to every question in the survey. Consequently, there may be a difference in sample size between certain questions or tables. In addition, due to the large numbers of respondents, small differences in results for a number of parameters may achieve statistical significance, but have limited clinical implications.
All results from the ITQ survey data are available in an interactive form on a public website powered by Tableau software [8]. SPSS Statistics software (SPSS Inc., IBM Corp., Armonk, NY, USA) was used to perform the data analysis. Descriptive statistics, frequencies, and rankings were obtained. Chi-squared analysis was performed where appropriate for contingency tables. Log linear analysis and analysis of variance were used for the analysis of individual parameters, and multiple regression and correlation analysis were used for multi-parametric analysis. Two-tailed tests were used in all analyses. The results from each of the 42 countries were initially analyzed independently, and only when the distributions of key demographic parameters (age, sex, body mass index [BMI], and duration of diabetes) were shown to be comparable were all the data pooled into an overall database.
Results
The demographic features of the 898 pediatric patients with DM who completed the questionnaire shown in Table 1 stratified by age group. Of these 898 respondents, 469 (52.2%) were self-injecting adolescents (13–17 years old), 226 (25.2%) were self-injecting children (< 13 years old), and 209 (22.5%) were parents who normally gave injections to the child. The therapies and devices used by the respondents are presented in Table 2. Table 3 provides an outline of the various injection practices according to age group. Table 4 presents the complications reported by patients or observed by nurses, and Table 5 shows the resultant glucose findings, including reported rates of diabetic ketoacidosis (DKA), hyper-and hypoglycemia, and glucose variability.
There was heterogeneity in the three groups in terms of years on insulin and BMI (Table 1). Adolescents (G3) were found to have higher glycated hemoglobin (HbA1c) values (9.3%) than children in the younger age groups (G1 8.6%, G2 8.4%) (p < 0.05). Pen use was lower in G1 than in the other two groups (Table 2). Between 38.5 and 66.7% of pediatric patients used 4-mm pen needles, with large percentages of patients using needles ≥ 5 mm (Table 2). Although the majority of patients claimed to rotate sites, and nurse findings did confirm this, many patients did not perform this rotation correctly (Table 3). Needle reuse rates in the G1, G2, and G3 patients were were 21.1, 30.5, and 32.5%, respectively (Table 3). Skipping injections (any) was reported by 30–35% of patients in G1 and G2, and by 58% of those in G3 (p < 0.05). Up to one-third of patients did not receive site inspections at every clinic visit (Table 3), and approximately one-quarter of patients did not receive any injection training or reminders in the last year (Table 3). Nearly one-half the patients in each group disposed of their used needles into the ordinary rubbish (Table 3). Most did so after recapping, but 1.0–2.5% did not even recap; instead they discarded the unprotected sharp directly into the rubbish. Table 4 shows that lipohypertrophy (LH) was prevalent in the patients of all three groups, with rates of 41.3, 45.2, and 47.3% in G1, G2, and G3, respectively. Those who always injected into an area of LH decreased with increasing age from 40.8 (G1) to 14.9 (G2) to 8.8% (G3). More than one-half of pediatric patients in every group reported having injection pain [5], with the younger the patients, the higher the percentage of those who reported pain, and the more frequently it was reported (Table 4).
We defined glycemic variability as the presence of blood glucose oscillations from < 60 mg/dL (3.3 mM/L) to > 250 mg/dL (13.9 mM/L) at least three times a week in an unpredictable and unexplained fashion and evidence of such a pattern for at least the previous 6 months. (It should be noted that these glucose values were obtained by episodic blood glucose monitoring [BGM] and not by continuous glucose monitoring [CGM] technology.) Table 5 shows that rates of both unexpected hypoglycemia and glucose variability were high in pediatric patients. Both conditions were more common in the youngest patient group. In G1, 48.1% of patients were reported, by their nurse, to have unexpected hypoglycemia and 61.0% were reported to have glucose variability; in G2, these values were 23.8 and 45.9%, respectively, and in G3, they were 24.1 and 52.5%, respectively. Needle length was not related to glucose variability or to HbA1c values.
The 350 patients found to have LH had a mean HbA1c of 9.30% (standard deviation [SD] 2.0%), while the 385 patients without LH had an HbA1c of 8.36% (SD 1.9%); this difference was highly significant (p < 0.001). Of those with LH, 61.1% had unexplained hypoglycemia while of those without LH, 60.0% did not (difference p < 0.001). Similarly, of those with LH, 64.0% had glycemic variability while those without LH, 60.5% did not (difference p < 0.001). Those with LH had more frequent DKA than those without LH (difference p = 0.023). Logistical regression analysis showed that incorrect rotation was the most important factor associated with LH (p < 0.001). The type of insulin did not emerge as a risk factor for LH.
Discussion
This post hoc analysis of the worldwide ITQ results involving 13,289 total patients focuses on the 898 respondents who were in the pediatric age range. The latter cohort was divided into pre-school children (ages 0–6 years, n = 85), school-aged children (ages 7–13, n = 423), and adolescents (ages 14–18, n = 390). These 898 pediatric patients described here represent nearly 7% of the overall ITQ respondents, constituting the largest number ever surveyed on injection practices in the pediatric diabetes patient population. In this paper we not only review the results of the ITQ, but we use the data as a springboard to make recommendations for improving clinical practice.
Our three subgroups had demographic characteristics similar to those seen in other studies of pediatric patients with DM who inject insulin [9]. Notably, the mean HbA1c values were well above target range, especially in the adolescent patients. Country-wide analysis showed that one factor influencing this was the large number of patients who came from Saudi Arabia, where the mean value for HbA1c (9.65%, SD 1.8%) was significantly higher than that for the remaining countries (8.59%, SD 2.0%) (p < 0.001). Nevertheless, the T1D Exchange (which surveys over 70 leading type 1 diabetes mellitus [T1D] clinics in the USA) recently reported similar trends to ours: during childhood mean HbA1c values decreased from 8.3% in 2- to 4-year-olds to 8.1% in 7-year-olds, followed by an increase to 9.2% in 19-year-olds [10]. Among our G3 patients, 58% reported skipping injections (any); this is one possible contributor to the higher HbA1c values in the adolescent patients.
Concerns about how children with DM were injecting have been expressed for decades. In 1991, when needles with a length of 12.7 mm were commonly used, Smith et al. [11] used ultrasound to measure the distance from the skin to the muscle fascia in 32 boys and girls. These researchers found that the subcutaneous layers were much thinner than anticipated and concluded that ‘most boys and some girls who use the perpendicular injection technique may often inject insulin into muscle, and perhaps on occasions into the peritoneal cavity’.
The solution to intramuscular (IM) injections was felt to be the ‘pinch up’. Children were asked to lift a skin fold and inject perpendicularly into it. However, in 1996, Polak showed that a lifted skin fold does not always eliminate the risk of an IM injection, especially in younger, thinner children, even when the shortest needle available at the time (8 mm) was used [12]. Hofman et al. later showed that while a ‘pinch up’ reduced IM insertions in the abdomen, it may paradoxically facilitate IM injections when children use this technique in the thigh [13]. Inadvertent IM insulin injections can lead to increases in insulin absorption (PK) and action (PD). Both can vary considerably, even with mild degrees of exercise [14, 15].
Lo Presti et al. measured the skin and SC fat thickness at various injection sites in 101 children and adolescents with DM (ages 2–17 years) and concluded that the safest strategy for preventing IM injections in children and adolescents at all ages is the use of the the 4-mm needle [9]. Their measurements showed that in the vast majority of children the 4-mm needle is long enough to penetrate the skin but sufficiently short to avoid reaching muscle [16]; however, these authors still recommended use of a pinch-up when the 4-mm needle is used in children aged ≤ 6 years. A South African study found similar SC fat thickness in pediatric populations in that country and drew similar conclusions [17].
Birkebaek et al. [18] compared the 4- and 6-mm pen needle in lean subjects, both children and adults, with DM. They reported that use of the 4-mm needle led to fewer IM injections, with the levels of leakage equivalent to those of the 6-mm needle. The probability of IM injection with the 6- versus 4-mm needle was dramatically higher in children and adolescents.
At times pediatric patients are obliged to use needles longer than 5 mm due to procurement or reimbursement issues. In this case it is recommended that they inject into a lifted skin fold [19]. When children are obliged to use a needle that is ≥ 6 mm, an additional technique is required, injecting at a 45° angle. Hofman et al. [20] has shown that the use of the 6-mm needle with a 45° angled insertion (essentially depositing insulin at 4 mm from the skin) significantly decreases the risk of IM injection in children and adolescents compared to a straight-in approach. [21].
Based on these findings, the New Insulin Delivery Recommendations state that the 4-mm pen needle ‘should be considered the safest pen needles for adults and children regardless of age, gender, ethnicity and BMI’ [5]. The Recommendations also provide advice on site care, injection site rotation, prevention of complications, alleviation of pain, disposal of used sharps, and the appropriate psychological approach to managing pediatric patients. The adherence of patients to these recommendations was assessed in our ITQ survey.
Despite multiple studies and publications on the safety and efficacy of shorter needles, as well as the presence of national and international guidelines stating that 4-mm pen needles should be first choice in the pediatric patient population, we found that one-third of the patients in G1, comprising the youngest patients with the thinnest SC tissue layers, used needles longer than 4 mm; in G2 and G3, 45.9 and 61.5% of patients, respectively, used needles > 4 mm in length. Given that the ITQ preceded the publication of the New Recommendations, the use of 4-mm pen needles subsequently recommended in the Recommendations is actually fairly encouraging (roughly 67 and 54% of patients in G1 and G2, respectively, used 4-mm pen needles), although there is room for further improvement, especially in G3 patients. The SC layers are much thinner in pediatric patients than in than adults [9]. Thus, the risk with longer needles is that the tip will traverse the SC tissue and deliver an accidental IM dose of insulin. IM injections are a major risk factor for hypoglycemic events, including the unexpected sort which can lead to accidents, third-party interventions, hospitalization, and possible long-term morbidity [15]. These rates of 4-mm needle usage should also be put into context and compared to the overall findings in the ITQ, where roughly 29% of all patients (93% adult) were described by nurses as using the 4-mm needle, a percentage that is much lower than that reported in pediatric patients [3].
It is difficult to be sure of the exact prevalence of LH simply from the results of the ITQ survey. Most participating nurses were not trained to properly examine for LH. Given this caveat, the reported presence of LH in pediatric patients injecting insulin seems to be even higher than that in their adult counterparts [4], being roughly 41–47% across the three age groups. The high percentage of LH in G1 is striking, given that these children had only used insulin for a mean of 2.0 (SD 0.82) years. Not only was LH present in nearly one-half of the pediatric patients responding to the ITQ survey, the practice of injecting into areas with LH was very common in the youngest patients, with 40.8% reporting always to inject into such areas. One possible explanation may simply be the limited injection space on smaller bodies.
Two of the principal factors associated with developing LH are an incorrect rotation of injection sites and the reuse of needles [22, 23]. Excessive reuse is defined as using a single needle more than five times, based on a Spanish study which showed that the relative risk of LH doubled when the needle was used three to five times but went up fivefold when used more than five times [22]. Both incorrect rotation and needle reuse occurred frequently in all three pediatric cohorts in our study and were associated with serious glucose variability/imbalances (Table 5). Just as in the worldwide ITQ, multivariate analysis of the pediatric cohorts showed an association between LH and incorrect site rotation, excessive needle reuse, longer duration of insulin use, and higher number of daily injections. The presence of LH and the practice of injecting into areas of LH were also associated with higher HbA1c values.
Injecting into areas of LH reduces insulin absorption and also raises within-subject uptake variability with a coefficient of variability (CV%) that is three- to fivefold higher than when injecting into normal tissue; therefore, this practice must be avoided [24]. Clearly there is much more that can be done to raise awareness of LH as well as intervene by teaching proper site rotation and limiting needle reuse [25]. Awareness also needs to be raised concerning proper disposal of used (potentially infectious) needles. Nearly one-half of the children in our study disposed of their used sharps directly into the rubbish, with a few of them not even recapping the sharps. Such behavior poses an obvious and easily avoidable public health hazard.
Gentile et al. have recently shown that the more errors made in injection technique the higher the HbA1c value [26]. The science of injection technique has now become an integral part of diabetology. Sustained and concerted efforts, carried out over the past two decades, have ensured that injection technique is now recognized worldwide as an important aspect of insulin therapy. The FIT (Forum for Injection Technique) recommendations released in 2009 and national guidelines from the UK, Ireland, China, Canada, Switzerland, India, and South Africa are evidence of this welcome development [27, 28]. Newer evidence based on the ITQ [3, 4] led to the publication of the New Insulin Delivery Recommendations in 2016 [5]. This international effort was followed by national recommendations in many countries, including India [29].
These guidelines, though comprehensive, do not meet all of the pediatric population’s needs, which are considerably different from those of adults. ‘Pediatric,’ in fact, is also not a homogenous entity as the various age groups have their unique characteristics, with each age group requiring specialized approaches to insulin injection. Infants, toddlers, pre-school children, school-going children, and adolescents differ from each other in their anatomic makeup and neuropsychological development. Therefore, injection technique training needs to be adjusted accordingly for each age group.
The shortest needle currently available in most areas of the world is 4 mm long and is available only with pens [5], while the shortest needle available with syringes is 6 mm long. Although the skin thickness in all children and adolescents (regardless of age, gender, ethnicity, or BMI) is constant (roughly 2 mm), the thickness of SC tissue varies. Even with a 4-mm needle, the risk of an IM injection when the needle is inserted perpendicular to the skin exceeds 20% in 2- to 6-year-olds; in comparison, this risk is < 5% in 7- to 13-year-olds and only 2.4% in adolescents [9].
Hence, the 4-mm needle is recommended for all children and adolescents. Injections in children aged ≤ 6 years should be made with the 4-mm needle inserted perpendicularly into a skin fold, while older children do not need to raise a skin fold. If a 4-mm needle is not available, 5-mm needles may be used with a lifted skin fold, while needles 6 mm or longer require the additional use of a 45° angle. The use of 6-mm needles (i.e., syringe and vials) must be strongly discouraged in children aged ≤ 6 years, unless they consistently use a 45° angle approach to the skin.
The preferred injection sites are the abdomen, thigh, buttocks, and upper arms. Insulin analogs may be injected at any site with similar absorption/action profiles [30]. Conventional (human) insulins, such as regular insulin and neutral protamine hagedorn (insulin N or NPH), show site-specific absorption characteristics [14, 31,31,, 32]. These insulins are absorbed fastest from the abdomen and slowest from the buttocks. Analog insulins (fast-acting and basal) do not show significant inter-site absorption differences.
Physically active children should preferentially receive their daytime injections in the abdomen, as absorption from this site is not influenced by exercise to the extent as when insulin is injected into arms or thighs. Conversely, insulin absorption may be much faster if the injection is delivered into an exercising arm or thigh. However, compelling studies on this area are still lacking. Injections at bed time can be safely administered in the thigh, as chances of unexpected physical activity are minimal—with due care to avoid inadvertent IM insulin deposition due to thinner SC tissue in the lateral thigh. Another option is to use the buttock as injection site; the buttock has the largest amount of SC fat and its use as injection site reduces the number of injections into the more commonly used abdomen, thigh, and arm sites.
Table 3 shows that failure to ever inspect injection sites was < 12% in all three pediatric groups, which is up to fourfold higher than that in the entire ITQ population. This large difference seems to show that caregivers are already doing a better job inspecting injection sites in children and adolescents that adult DM patients. These young patients should be taught to inspect sites themselves prior to injection, but to disinfect only if required. Insulin should be administered with clean hands, on clean sites. Injections must not be given in areas of LH, infection, ulceration, or inflammation.
Injection site rotation, both inter-site and intra-site, must be performed diligently. We recommend moving from one injection to the next within a site by approximately 1 cm (a finger-width) in a predetermined pattern to avoid repeat injections at the same location. Larger sites, such as the abdomen and thigh, may also be divided into four quadrants. At each clinical visit, injection sites must be inspected and palpated for evidence of LH. Children with LH should be counseled not to inject into LH sites, to rotate injections correctly over larger zones, and not to reuse needles. Those who switch injections from areas of LH to normal tissue should initially adjust their insulin doses downward and then titrate as guided by BGM or CGM, subsequently reviewing their injection site health/glucose control regularly.
Limitations of the Study
An important limitation of our data is that the results are based on surveys completed by patients/families and may be subject to recall bias, especially regarding recall of injection education, which may have occurred months or years earlier, and physical examinations of injection sites at clinical visits. We have attempted to mitigate this bias by including a nurse questionnaire which asked many of the same questions, in an attempt to verify, or not, the patients’ answers.
Most of those who answered the ITQ questionnaires were pediatric patients giving themselves injections. Nevertheless 22.5% of responders were parents, answering for their children, and it is unclear what their level of training/knowledge was. Third parties who give injections may not always be parents but may also be school nurses and staff, relatives, among others. It is important that these third parties have a sound knowledge of good injection technique, especially when managing DM in younger children who should not be expected to know the correct technique.
Conclusion
In summary, our ITQ survey reveals worrying rates of LH, poor injection rotation, excessive needle reuse, and incorrect needle length choices in all three pediatric patient populations studied. All of these issues can be addressed through targeted education by caregivers and proper habit formation by patients. Pediatric patients in all age groups should use 4-mm pen needles, with or without pinch-up but always with the needle perpendicular to the skin surface, or 6-mm syringes, with injection at a 45° angle. They should rotate sites correctly so as to avoid injecting into areas of LH. Professionals should inspect injection sites and provide targeted, individualized instruction on a regular basis. Psychological approaches vary by age group, but all are based on empathy, encouragement, firmness and, increasing autonomy. These education-based interventions should result in fewer unexpected hypoglycemic reactions and less glucose variability. None of these challenges require large outlays of money or huge changes in the healthcare system. They are best attained by the creation of awareness, a reassessment of our training techniques, and the provision of appropriate educational tools.
Change history
29 October 2018
In the original publication, fourth author name was incorrectly published as Asthma Deeb in author group.
References
Guerci B, Sauvanet JP. Subcutaneous insulin: pharmacokinetic variability and glycemic variability. Diabetes Metab. 2005;31:4S7–24.
Frid A, Hirsch L, Gaspar R, et al. New injection recommendations for patients with diabetes. Diabetes Metab. 2010;36[Suppl 2]:S3–18.
Frid A, Hirsch L, Menchior A, Morel D, Strauss K. Worldwide injection technique questionnaire study: population parameters and injection practices. Mayo Clinic Proc. 2016;91:1212–23.
Frid A, Hirsch L, Menchior A, Morel D, Strauss K. Worldwide injection technique questionnaire study: injecting complications and role of the professional. Mayo Clinic Proc. 2016;91:1224–30.
Frid A, Kreugel G, Grassi G, et al. New insulin delivery recommendations. Mayo Clinic Proc. 2016;91:1231–55.
Kalra S, Mithal A, Sahay R, et al. Indian injection technique study: population characteristics and injection practices. Diabetes Ther. 2017;8(3):637–57. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13300-017-0243-x.
Susman E, Houts R, Steinberg L, et al. Longitudinal development of secondary sexual characteristics in girls and boys between ages 9½ and 15½ years. Arch Pediatr Adolesc Med. 2010;164(2):166–73. https://doi.org/10.1001/archpediatrics.2009.261.
Insulin Injection Technique Questionnaire (ITQ). ITQ survey data. Tableau Public Adam Young’s Profile website:. http://tabsoft.co/23V6ofi. Accessed 10 Apr 2018.
Lo Presti D, Ingegnosi C, Strauss K. Skin and subcutaneous thickness at injecting sites in children with diabetes: ultrasound findings and recommendations for giving injection. Pediatr Diabetes. 2012;13(7):525–33.
Miller K, Foster N, Beck R, et al. Current state of type 1 diabetes treatment in the US: updated data from the T1D exchange clinic registry. Diabetes Care. 2015;38:971–8. https://doi.org/10.2337/dc15-0078.
Smith CP, Sargent MA, Wilson BP, Price DA. Subcutaneous or intramuscular insulin injections. Arch Dis Child. 1991;66(7):879–82.
Polak M, Beregszaszi M, Belarbi N, et al. Subcutaneous or intra-muscular injections of insulin in children: are we injecting where we think we are? Diabetes Care. 1996;19(12):1434–6.
Hofman PL, Derraik JG, Pinto TE, et al. Defining the ideal injection techniques when using 5-mm needles in children and adults. Diabetes Care. 2010;33(9):1940–4.
Vaag A, Handberg A, Lauritzen L, et al. Variation in absorption of NPH insulin due to Intramuscular injection. Diabetes Care. 1990;13:74–6.
Vaag A, Damgaard Pedersen K, Lauritzen M, Hildebrandt P, Beck-Nielsen H. Intramuscular versus subcutaneous injection of unmodified insulin; consequences for blood glucose control in patients with type 1 diabetes mellitus. Diabetic Med. 1990;7(4):335–42.
Hirsch L, Klaff L, Bailey T, et al. Comparative glycemic control, safety and patient ratings for a new 4 mm\32G insulin pen needle in adults with diabetes. Curr Med Res Opin. 2010;26:1531–41.
Marran K, Segal D. SKINNY—SKIN thickness and needles in the young. S Afr J Child Health. 2014;8(3):92–5. https://doi.org/10.7196/sajch.687.
Birkebaek NH, Solvig J, Hansen B, Jorgensen C, Smedegaard J, Christiansen JS. A 4-mm needle reduces the risk of intramuscular injections without increasing backflow to skin surface in lean diabetic children and adults. Diabetes Care. 2008;31(9):e65.
Strauss K, Hannet I, McGonigle J, et al. Ultra-short (5 mm) insulin needles: trial results and clinical recommendations. Pract Diabetes Int. 1999;16:218–21.
Hofman PL, Derraik JG, Pinto TE, et al. Defining the ideal injection techniques when using 5-mm needles in children and adults. Diabetes Care. 2010;33(9):1940–4.
Hofman PL, Lawton SA, Peart JM, et al. An angled insertion technique using 6-mm needles markedly reduces the risk of intramuscular injections in children and adolescents. Diabet Med. 2007;24(12):1400–5.
Blanco M, Hernández MT, Strauss KW, Amaya M. Prevalence and risk factors of lipohypertrophy in insulin-injecting patients with diabetes. Diabetes Metab. 2013;39(5):445–53.
Ji L, Sun Z, Li Q, et al. Lipohypertrophy in China: prevalence, risk factors, insulin consumption, and clinical impact. Diabetes Technol Ther. 2017;19(1):61–7. https://doi.org/10.1089/dia.2016.0334.
Famulla S, Hövelmann U, Fische A, et al. Insulin injection into lipohypertrophic tissue: blunted and more variable insulin absorption and action and impaired postprandial glucose control. Diabetes Care. 2016;39:1486–92. https://doi.org/10.2337/dc16-0610.
Campinos C, Le Floch JP, Petit C, et al. An effective intervention for diabetic lipohypertrophy: results of a randomized, controlled, prospective multicenter study in France. Diabetes Technol Ther. 2017;19(11):623–32. https://doi.org/10.1089/dia.2017.0165.
Gentile S, Strollo F, Della Corte T, Marino G, Guarino G. Insulin related lipodystrophic lesions and hypoglycemia: double standards? Diabetes Metab Syndr. 2018;12(5):813–8. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.dsx.2018.04.023.
Forum for Injection Technique (FIT). FIT recommendations. Available at: http://www.fit4diabetes.com/united-kingdom/fit-recommendations/. Accessed on 10 Apr 2018.
Tandon N, Kalra S, Balhara YP, et al. Forum for injection technique (FIT), India: The Indian recommendations 2.0, for best practice in insulin injection technique, 2015. Indian J Endocrinol Metab. 2015;19(3):317.
Tandon N, Kalra S, Balhara YP, Baruah MP, Chadha M, Chandalia HB, et al. Forum for injection technique and therapy expert recommendations, India: the Indian recommendations for best practice in insulin injection technique, 2017. Indian J Endocrinol Metab. 2017;21(4):600.
Home P. Pharmacokinetics and pharmacodynamics of biosimilar insulins: is clamp technology fit for purpose? Diabetes Care. 2015;38(12):2234–6. https://doi.org/10.2337/dc15-1046.
Frid A, Gunnarson R, Guntner P, Linde P. Effects of accidental intramuscular injection on insulin absorption in IDDM. Diabetes Care. 1988;11:41–5.
Thow J, Johnson A, Fulcher G, Home P. Different absorption of isophane (NPH) insulin from subcutaneous and intramuscular sites suggests a need to reassess recommended insulin injection technique. Diabet Med. 1990;7(3):600–2.
Acknowledgements
Our sincerest thanks go to the participating centers with their doctors and nurses and patients.
Funding
Becton–Dickinson (BD) sponsored this study by reimbursing hospitals for time spent. No healthcare professional or patient received payment for participating in the study and no payments were given to any author for publication of this article. BD is funding Diabetes Therapy’s processing charges for this article.
Authorship
All named authors meet the International Committee of Medical Journal Editors (ICMJE) criteria for authorship for this manuscript. All authors had full access to all of the data in this study and take complete responsibility for the integrity of the data and accuracy of the data analysis.
Disclosures
Laurence J. Hirsch is an employee of BD, a manufacturer of injecting devices. Kenneth W. Strauss is an employee of BD, a manufacturer of injecting devices. All other authors (Sanjay Kalra, Anders Frid, and Asma Deeb) have nothing to disclose.
Compliance with Ethics Guidelines
All procedures performed in studies involving human participants were in accordance with the 1964 Helsinki declaration and its later amendments or comparable ethical standards. No patient-identifying information was obtained, and participants’ care was not affected in any way. Participants were put at no risk by the study and did not receive remuneration to participate. Therefore, ethics committee approval was not generally required; however, it was obtained whenever requested by local authorities.
Data Availability
The datasets generated during and/or analyzed during the current study are available in the Tableau Public Adam Young’s Profile website: http://tabsoft.co/23V6ofi. Accessed 10 September 2018.
Open Access
This article is distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc/4.0/), which permits any noncommercial use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided you give appropriate credit to the original author(s) and the source, provide a link to the Creative Commons license, and indicate if changes were made.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
The original version of this article was revised: In the original publication fourth author name was incorrectly published and this has been updated as 'Asma Deeb'.
Enhanced digital features
To view enhanced digital features for this article go to https://doi.org/10.6084/m9.figshare.7087520.
Rights and permissions
This article is published under an open access license. Please check the 'Copyright Information' section either on this page or in the PDF for details of this license and what re-use is permitted. If your intended use exceeds what is permitted by the license or if you are unable to locate the licence and re-use information, please contact the Rights and Permissions team.
About this article
Cite this article
Kalra, S., Hirsch, L.J., Frid, A. et al. Pediatric Insulin Injection Technique: A Multi-Country Survey and Clinical Practice Implications. Diabetes Ther 9, 2291–2302 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13300-018-0514-1
Received:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13300-018-0514-1