Abstract
Introduction
This study investigates the cost-effectiveness of insulin degludec versus insulin glargine U100 in patients with type 1 and type 2 diabetes mellitus in Serbia.
Methods
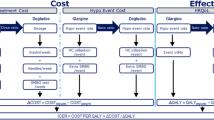
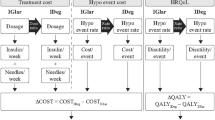
A cost-utility analysis, implementing a simple short-term model, was used to compare treatment costs and outcomes with degludec versus glargine U100 in patients with type 1 (T1DM) and type 2 diabetes (T2DM). Cost-effectiveness was analysed in a 1-year setting, based on data from clinical trials. Costs were estimated from the healthcare payer perspective, the Serbian Health Insurance Fund (RFZO). The outcome measure was the incremental cost-effectiveness ratio (ICER) or cost per quality-adjusted life-year (QALY) gained.
Results
Degludec is highly cost-effective compared with glargine U100 for people with T1DM and T2DM in Serbia. The ICERs are estimated at 417,586 RSD/QALY gained in T1DM, 558,811 RSD/QALY gained in T2DM on basal oral therapy (T2DMBOT) and 1,200,141 RSD/QALY gained in T2DM on basal-bolus therapy (T2DMB/B). All ICERs fall below the commonly accepted thresholds for cost-effectiveness in Serbia (1,785,642 RSD/QALY gained). In all three patient groups, insulin costs are higher with degludec than with glargine U100, but these costs are partially offset by savings from a lower daily insulin dose in T1DM and T2DMBOT, a reduction in hypoglycaemic events in all three patient groups and reduced costs of SMBG testing in the T2DM groups with degludec versus glargine U100.
Conclusion
Degludec is a cost-effective alternative to glargine U100 for patients with T1DM and T2DM in Serbia. Degludec may particularly benefit those suffering from hypoglycaemia or where the patient would benefit from the option of flexible dosing.
Funding
Novo Nordisk.
Similar content being viewed by others
Avoid common mistakes on your manuscript.
Introduction
Globally an estimated 415 million people have diabetes, and this is projected to increase to 642 million by 2040 [1]. According to the estimates of the Serbian Institute of Public Health, diabetes affects 12.4% of the adult population in Serbia [2]. Diabetes is a chronic metabolic disorder characterised by high blood sugar levels (hyperglycaemia) and is a leading cause of blindness, end-stage renal failure, heart attack/stroke, non-traumatic amputation and depression [1]. Diabetes and related complications are chief causes of death in most countries, and according to the International Diabetes Federation (IDF), there were an estimated 10,616 diabetes-related deaths in the 20–79 age group in Serbia in 2015 [1].
The treatment of diabetes has a substantial economic impact on national healthcare systems. The treatment of diabetes-related chronic complications accounts for the largest proportion of diabetes direct medical costs [3, 4]. Indirect costs associated with diabetes, such as absenteeism from work and reduced productivity while at work, are also considerable [3]. The most recent published cost data for Serbia are from 2007 [5] and estimate that annual diabetes expenditures were 53,412.96 RSD (or 444.42 EURFootnote 1) per patient. Indirect costs represented 10.39% of total costs, while anti-diabetes drugs and medical devices represented 44% (38.10% and 5.94%, respectively) and hospital and ambulatory costs the remaining 45%.
The aim of diabetes therapy is to keep blood glucose levels within recommended targets and ultimately limit the development of diabetes-related complications [6, 7]. All patients with type 1 diabetes (T1DM) require insulin. Current clinical guidance in Serbia recommends a basal-bolus regimen or for selected individuals continuous subcutaneous insulin infusion (CSII) by means of an external portable insulin pump [8]. Type 2 diabetes (T2DM) is a progressive disease and treatment is intensified with disease progression. A significant proportion of patients with T2DM will eventually need insulin therapy to achieve optimal blood glucose targets [8]. Insulin is the most effective method of reducing blood glucose concentrations; however, despite clear guidance, glycaemic control remains suboptimal (HbA1c > 7.0%) in a substantial number of patients [9, 10]. Key barriers to insulin therapy include fear and risk of hypoglycaemia, weight gain and restrictive treatment regimens [11, 12].
Insulin degludec (degludec) is a basal insulin analogue with a long duration of action and a distinct, slow absorption mechanism, which results in a flat and stable action profile [13, 14]. It has four times less day-to-day variability in glucose lowering effect than insulin glargine U100 (glargine U100) [15]. Due to its long and stable action profile, degludec allows for flexibility of dosing time. On occasions when administration at the same time of day is not possible, patients can dose their insulin at any time of the day as long as there is a minimum of 8 h between doses [16,17,18].
The efficacy and safety of degludec have been evaluated in a large-scale clinical development programme. The degludec phase 3 clinical trial programme (BEGIN) included more than 9000 patients with T1DM and T2DM [19]. Meta-analyses of the phase 3a clinical trials showed that degludec achieved equivalent reductions in HbA1c with a lower risk of hypoglycaemia versus glargine U100 and at a significantly lower total daily insulin dose compared with glargine U100 in T1DM (12% lower) and T2DM basal oral therapy (10% lower) [20, 21]. Real-world studies confirm the observations from the clinical trials and support the effectiveness of degludec in clinical practice [22, 23].
Due to increasing constraints on healthcare budgets, it is important that new therapies represent good value for the money. Decision-making based on both clinical and economic evidence helps healthcare providers optimise resource use and care for patients with diabetes. Cost-effectiveness models assess the value of interventions by comparing the relative costs and outcomes. An economic analysis typically estimates the difference in cost between one healthcare intervention and an alternative, divided by the difference in health effects, which is termed an incremental cost-effectiveness ratio (ICER). A commonly used effectiveness measure in cost-effectiveness analyses is the quality-adjusted life year (QALY), which measures health as a combination of both duration and health-related quality of life [24]. The incremental cost per additional QALY gained (cost/QALY) allows decision makers to compare across different disease areas to allocate healthcare resources for maximal economic and clinical benefits. A financial threshold is often set at which cost-effectiveness is accepted. In Serbia, there is no officially indicated threshold; however, the level of 3 × GDP per capita suggested by the World Health Organization (WHO) [25] is accepted by the Serbian authorities.
The objective of this study was to evaluate the cost-effectiveness of degludec versus glargine U100 from the healthcare payer perspective in Serbia [Serbian Health Insurance Fund (RFZOFootnote 2)].
Methods
Model Overview
The type of cost-effectiveness analysis used was a cost-utility analysis. Degludec was compared with glargine U100 in three patient populations:
-
T1DM using basal-bolus therapy (T1DM)
-
T2DM using basal oral therapy (T2DMBOT)
-
T2DM using basal-bolus therapy (T2DMB/B)
Glargine U100 was identified as the most appropriate comparator for the cost-utility analysis. Treatment guidelines in Serbia recommend NPH insulin as the first-line insulin treatment for T1DM and T2DM, with a basal insulin analogue considered if after 6 months on NPH there is persisting hypoglycaemia (< 3.5 mmol/l). Thus, degludec should be considered where a basal insulin analogue is indicated.
The model was a simple, transparent, short-term (1-year time horizon) model developed in Microsoft Excel 2010 (Microsoft Corp., Redmond, WA, US) and has been previously published [26]. The short-term model focuses on the impact of important aspects of insulin therapy, such as hypoglycaemia and dosing, and accommodates the treat-to-target trials required by the Food and Drug Administration (FDA) [27]. In treat-to-target trials patients are treated to the same glycaemic target and no differences in HbA1c are expected; thus, there is no rationale for long-term modelling based on HbA1c differences.
Although cost-effectiveness was analysed in a 1-year setting and is based on data from 1-year clinical trials, the model can be replicated for subsequent years, and the outcomes represent the average annual cost-effectiveness in steady state. As the time horizon was 1-year, no discounting was applied.
The model calculated the costs associated with treatment (insulin, needles and SMBG test strips) and hypoglycaemic events (the cost of treating the event and the use of additional SMBG test strips associated with the event). Health-related quality of life (in the form of QALYs) was calculated by applying a disutility per hypoglycaemic event incurred (Fig. 1).
Perspective/Viewpoint
All costs were estimated from the healthcare payer perspective, RFZO. The threshold was set at 3 × GDP per capita, as although there are alternative approaches to thresholds for cost-effectiveness of interventions [28], this is an internationally recognised level [25] and is accepted by the Serbian authorities. According to the World Bank statistics for 2016, the GDP per capita in Serbia was 5348.30 USD. Using the exchange rate of 1 USD = 111.29 RSD, the threshold was set at the level of 1,785,642 RSD.
Data Used in the Model
Cost Data
All costs were estimated from the healthcare payer perspective, RFZO.
Direct Treatment Costs
Costs of insulin, needles and SMGB tests were based on official RFZO prices elicited in November 2017. Other costs of treatment (e.g. use of concomitant medication) or other costs resulting from treatment (e.g. long-term outcomes) were assumed to be equivalent in both treatment groups and were therefore not included.
Cost of Hypoglycaemic Events
Resource use associated with non-severe and severe hypoglycaemic events was derived from the clinical trial data. For non-severe events data were obtained from the patient-completed hypoglycaemia safety questionnaire, and for severe events data were obtained from the serious adverse events case reports [29].
The use of additional SMBG tests in the week following a non-severe event was also based on the hypoglycaemia safety questionnaire. Data were not collected on the testing pattern following a severe event; therefore, it was conservatively assumed to be similar to a non-severe hypoglycaemic event.
For patients experiencing severe events it was assumed that all patients who were hospitalised used the ambulance service and that all patients experiencing severe events used glucagon to recover.
Patients suffering a hypoglycaemic event received the same treatment regardless of whether they were on degludec or glargine U100. Therefore, any difference in costs of hypoglycaemia between treatments was due to differences in rates of hypoglycaemia and not the cost per event.
The average costs of hypoglycaemic events are calculated by multiplying the unit cost of the services by the share of patients using that treatment/service (Table 1). It was assumed that a non-severe event would be self-managed and not require any additional resource use; thus, costs relate only to additional SMBG testing.
Clinical Data
Insulin Dose
The daily insulin dose for the degludec and glargine U100 treatment groups was based on the end of trial doses captured from the clinical trial data. The meta-analysis of insulin dose from the clinical trials was the source of the glargine U100 dose and degludec/glargine U100 dose ratio [21]. The degludec dose was calculated using the dose ratio to allow for adjustment of covariate factors such as trial, treatment, antidiabetic therapy at screening, age, sex, region and baseline dose (Table 2).
SMBG Testing
It was assumed that one SMBG test was conducted with every main meal for regimens including bolus insulin (T1DMB/B, T2DMB/B). Three meals per day were assumed.
For SMBG tests related to basal insulin injections, the titration schedule recommended for use with glargine U100 [30] was used to estimate SMBG utilisation for glargine U100. The algorithm recommends seven SMBG tests per week (the dose is adjusted every 3rd day based on the mean of the FPG results over three consecutive days) [31].
Degludec enables patients to titrate, predict and monitor their blood glucose more efficiently [13, 14]. The recommended titration algorithm for degludec is once-weekly adjustment of dose based on the average of two SMBG measurements from the 2 preceding days for patients with T2DM [32]. Thus, the utilisation of SMBG tests related to degludec was assumed to be two tests per week for patients with T2DM.
Hypoglycaemia Event Rates
Real-world hypoglycaemic event rates from a large-scale questionnaire-based study conducted in seven European countries [33] were used as the baseline values for severe and non-severe hypoglycaemic events. These rates provide a better estimation of real-life event rates than those from clinical trials [34], which can be biased in both the selection of patients and the treatment setting. For example, the clinical trials excluded patients with a history of severe hypoglycaemic episodes and anyone considered hypoglycaemia unaware [34,35,36,37,38,39]. The real-world rates were used as the base case event rates in the glargine U100 group (as this is the current treatment on the market); see Table 3. Event rates for the degludec group (Table 3) were calculated using the relative event rates taken from the meta-analysis of hypoglycaemia [20, 21], which were adjusted for trial, type of diabetes, treatment, anti-diabetic therapy at screening, sex and region as fixed factors and age as a continuous covariate. Only rate ratios with a documented statistically significant difference between the treatment arms were used.
Compliance with Ethics Guidelines
This article does not contain any studies with human participants or animals performed by any of the authors.
Utility Data
QALYs were calculated by subtracting a disutility [40] per hypoglycaemic event experienced from the baseline health utility. Disutilities associated with hypoglycaemic events were obtained from a large-scale TTO study [40], which reported a disutility of 0.0565 for a severe event (with no significant difference between daytime and nocturnal severe events) and disutilities of 0.0041 and 0.0067 for non-severe daytime and non-severe nocturnal events, respectively (a significant difference in utility was demonstrated for nocturnal vs. daytime non-severe events) [40]. The disutility per hypoglycaemic event was multiplied by the number of events observed in each treatment group.
In addition, the analysis included an estimate of the utility benefit for the option of flexible dosing time with degludec. Boye et al. [41] reported a utility benefit of 0.006 associated with dosing flexibility; therefore, for degludec an extra utility gain of + 0.006 was applied to the QALY benefit.
Sensitivity Analyses
One-way and probabilistic sensitivity analyses were conducted to assess the impact of varying key assumptions and outcomes used in the base case analysis (Table 4).
Results
Costs
In T1DM, total costs are estimated at 185,627.84 RSD per patient per year in the degludec group and 173,637.52 per patient per year in the glargine U100 group, with the majority representing pharmacy costs. The total cost per patient per year is 11,990.32 RSD higher in the degludec group than in the glargine U100 group (6.9% higher costs), largely because of the increase in insulin costs. The costs of hypoglycaemic events are similar for degludec and glargine U100 since only the non-severe nocturnal events showed a statistically significant difference between the two treatments, and the severe and daytime events were unchanged.
In T2DMBOT, the total cost per patient per year in the degludec group (101,270.97 RSD) is 15,042.55 RSD (17.4%) higher than in the glargine U100 group (86,228.42 RSD per patient per year). The difference in cost is due to the increased cost for insulin and the lower costs of SMBG testing and non-severe nocturnal and severe hypoglycaemic events in the degludec group. Lower costs of hypoglycaemia are driven by the significant reduction in the number of severe hypoglycaemic events with degludec vs. glargine U100 in this patient group.
In T2DMB/B, the total cost per patient per year in the degludec group (285,584.00 RSD) is 45,912.88 (19.2%) higher than in the glargine U100 group (239,671.12 RSD per patient per year), caused primarily by a higher spend for insulin partly offset against a lower spend on SMBG and lower costs of non-severe daytime and nocturnal hypoglycaemia. The higher incremental cost for this group is driven mainly by the slightly higher dose of basal insulin required in the degludec arm of the clinical trial. In the T2DMB/B clinical trial [14], high insulin doses were observed in both the degludec and glargine U100 treatment arms. The high doses observed in the trial are not expected to be representative of a real-world setting for patients initiating a basal-bolus regimen as the trial mainly recruited patients who were already uncontrolled on an intensive basal-bolus regimen or uncontrolled on a pre-mixed insulin regimen. In a recent real-world study of degludec, the daily basal and bolus insulin doses in patients with T2DM (75% on a basal-bolus regimen) were considerably lower than those in the clinical trial [23].
Average total costs for the three treatment groups are presented in Table 5.
Incremental Cost-Effectiveness
Degludec is a highly cost-effective treatment option versus glargine U100 in patients with T1DM as part of a basal-bolus insulin regimen with an estimated ICER of 417,586.27 RSD/QALY gained. The result is primarily driven by the significantly lower dose required, QALY gains due to significantly fewer non-severe nocturnal hypoglycaemic events versus glargine U100 and the opportunity to use flexible dosing when needed. This result falls well beneath the cost-effectiveness threshold in Serbia of 1,785,642 RSD/QALY gained.
In T2DMBOT degludec is also highly cost-effective (558,811.00 RSD/QALY gained), driven by cost savings from a significantly lower dose, a significant reduction in severe hypoglycaemia and the potential for once-weekly SMBG testing. Due to the significantly fewer nocturnal and severe hypoglycaemic events in this group and the opportunity to use a flexible dosing time when needed, degludec is associated with a QALY gain versus glargine U100.
In the T2DMB/B setting, degludec is cost-effective with an ICER of 1,200,140.55 RSD/QALY gained, which falls below commonly accepted cost-effectiveness threshold. Degludec is associated with significantly fewer non-severe daytime and nocturnal events, which results in a QALY gain versus glargine U100.
Sensitivity Analysis
Extensive sensitivity analyses demonstrate that the results are robust and largely insensitive to changes in input parameters (results presented in supplementary table).
Key parameters that influenced the ICER values were hypoglycaemia rates (T1DM, T2DMBOT, T2DMB/B), insulin doses (T1DM, T2DMBOT) and the number of SMBG tests used weekly by patients (T2DMBOT, T2DMB/B).
For T1DM, the ICER remains below the cost-effectiveness threshold in all scenarios tested in one-way sensitivity analyses. ICERs range between 297,452 RSD/QALY gained and 1,179,023 RSD/QALY gained. Rates of non-severe hypoglycaemia are influential on the ICER in this group. When the annual number of non-severe daytime events is reduced to 36.16 using data from Donnelly et al. [34], the ICER increases to 997,799 RSD/QALY gained. Conversely, when the annual number of non-severe nocturnal events is increased to 20.80 using data from Ericsson et al. [44], the ICER is reduced to 404,428 RSD/QALY gained. The insulin dose ratio also has an impact on the ICER, but even under an extreme assumption of equal dosing of basal insulin, degludec remains highly cost-effective (720,507 RSD/QALY gained). If the utility gain from flexibility is excluded, the ICER is still within commonly accepted thresholds (527,896 RSD/QALY gained).
Similarly for T2DMBOT, the favourable cost-effectiveness results are invariant to changes in most of the input parameters. ICERs range between 294,932 and 1,955,556 RSD/QALY gained. The number of SMBG tests per week is influential on the ICER in this setting, but degludec is still cost-effective (1,004,600 RSD/QALY gained) even under the strict assumption of no reductions in SMBG testing in the degludec group. Insulin dose ratio and utility gain from flexibility also have an impact on the results, but ICERs fall below the commonly accepted threshold even with extreme assumptions (919,928 and 719,091 RSD/QALY gained respectively). Varying the rates of hypoglycaemia has an impact on the ICER in this group reflecting the large benefits in terms of reduced hypoglycaemia with degludec versus glargine U100. Drawing on higher event rates for non-severe events generates highly cost-effective results for degludec versus glargine U100; conversely, using lower event rates for severe hypoglycaemic events, e.g. from Ratner [20], increases the ICER to 1,955,556.24 RSD/QALY gained, which is just above the commonly accepted threshold.
For T2DMB/B the parameter that has the most influence on the ICER is the rate of hypoglycaemia. Varying the rate of non-severe hypoglycaemia has an impact on the ICER in this group due to the significant reduction of non-severe events with degludec versus glargine U100. ICERs range between 980,305 and 3,636,384 RSD/QALY gained, with low rates of non-severe hypoglycaemia generating the higher ICERs. In all other scenarios analysed the ICERs are below the commonly accepted threshold (range 938,549–1,513,491 RSD/QALY gained), indicating that degludec is a cost-effective therapeutic option in this group.
Probabilistic Sensitivity Analysis
To capture the uncertainty of the results caused by statistical uncertainty with respect to the parameter inputs, probabilistic sensitivity analysis has been conducted. The probabilistic sensitivity analyses have each been run with 1000 iterations.
The cost-effectiveness acceptability curves show that at a willingness-to-pay threshold of 2,048,112 RSD/QALY gained, the probability that degludec is cost-effective relative to glargine U100 is 77.5, 97.3 and 85.7% for T1DM, T2DMBOT and T2DMB/B, respectively (Fig. 2).
Discussion
There are limited data on the cost-effectiveness of treatments for diabetes in Serbia. With an increasing number of insulin formulations available, economic as well as clinical evidence is essential for healthcare providers to maximise healthcare with constrained budgets.
This simple, short-term economic evaluation demonstrates that degludec is likely to be considered highly cost-effective compared with glargine U100 for people with T1DM and T2DM in Serbia. All ICERs fall below the commonly accepted thresholds for cost-effectiveness in Serbia.
In all three patient groups, insulin costs are higher with degludec than with glargine U100, but these costs are partially offset by savings from a lower daily insulin dose in T1DM and T2DMBOT, a reduction in hypoglycaemic events in all three patient groups and reduced costs of SMBG testing in the T2DM groups, with degludec versus glargine U100. For degludec, the longer half-life and the corresponding long flat insulin profile in steady state [15] and lower variability over the day compared with glargine U100 [45] mean that patients are able to titrate, predict and monitor their blood glucose more efficiently. Consequently, degludec can be monitored with less frequent SMBG testing in patients with T2DM. The titration algorithm for degludec is once-weekly adjustment of dose based on the average of two SMBG measurements from the 2 preceding days for patients with T2DM [46]. The concept of fewer SMBG tests per week is supported by a phase 3b trial, which examined different scenarios of SMBG testing in patients with T2DM. The trial demonstrated that degludec was effective and well tolerated using only one SMBG test per week to titrate the insulin dose compared with titration based on three consecutive pre-breakfast SMBG values in patients with T2DM [47]. No statistically significant differences in HbA1c, body weight, hypoglycaemia or any other safety parameters were observed between the two titration algorithms [47].
An important aspect to consider, especially for chronic diseases such as diabetes mellitus, is the quality of life of patients. With degludec higher gains in health-related quality of life (HRQoL) were observed [48]. Incremental QALY gains with degludec versus glargine U100 in all three groups are associated with the reduction in hypoglycaemic events and the opportunity to use flexible dosing when needed. The current analysis included an estimate of the utility benefit of a flexible dosing time with degludec. This additional utility was not captured in the clinical studies and therefore a utility gain of 0.006 for degludec related to flexible dosing was assumed based on the study by Boye et al. [41]. This can be seen as a conservative estimate as a large time trade-off study demonstrated that flexible once-daily injection was associated with a 0.016 higher utility versus a fixed time of injection [43].
Extensive sensitivity analyses show that the results are robust and invariant to changes in most of the input parameters. In all three patients groups the ICER remained below the threshold of 1,785,642 RSD in all scenarios tested, except when low rates of non-severe hypoglycaemia were applied in the T2DMB/B setting and low rates of severe hypoglycaemia applied in the T2DMBOT setting. PSA shows that there is a high probability that degludec will be cost-effective versus glargine U100 in all three patient groups.
Hypoglycaemia can have a major impact on patients’ lives affecting employment, driving, relationships, travel and leisure activities. Severe episodes can result in serious clinical sequelae such as physical (e.g. fractures, head injuries), neurological (e.g. convulsions/seizures, paralysis, coma) and cardiac (e.g. arrhythmia, cardiac failure) morbidity, as well as death in some extreme cases [49, 50]. Furthermore, recurrent episodes, whether severe or non-severe, can lead to the development of impaired awareness of hypoglycaemia; this can be problematic as it means that patients are less able to recognise their symptoms and take remedial action. A recent non-interventional, prospective-cohort survey conducted across 2004 sites in 24 countries, including Serbia, investigated the prevalence of hypoglycaemia [51]. The study included 27,585 patients with insulin-treated diabetes and reported a higher frequency of hypoglycaemia than previously reported, with marked variation across geographic regions. Overall rates of hypoglycaemia in Eastern Europe were 66.9 events/person/year for T1DM and 23.7 events/person/year for T2DM, with the highest rates in T2DM observed in Russia and Eastern Europe. Data from this study also show that hypoglycaemia has a major impact on patients and their behaviour [52]. In Eastern Europe 51.7% T1DM and 40.6% T2DM patients reduced their insulin dose in response to hypoglycaemia, which could compromise glycaemic control, and high proportions increased blood glucose monitoring (75.5% T1DM and 71.9% T2DM).
Hypoglycaemia and the fear of hypoglycaemia act as barriers to timely initiation and intensification of insulin and remain the major limiting factors for achieving target levels of glucose control in insulin-treated patients with diabetes [53, 54]. Poor glycaemic control is associated with serious long-term complications, including cardiovascular disease, renal disease, retinopathy, amputation, depression and neuropathy [55, 56].
Due to its distinct pharmacological profile degludec is associated with lower rates of hypoglycaemia. In phase 3a clinical trials degludec showed equivalent reductions in HbA1c with a significantly lower rate of hypoglycaemia versus glargine U100 [20, 21]. Degludec was associated with a 17% lower rate of nocturnal non-severe hypoglycaemia in T1DM [21], an 86% lower rate of severe hypoglycaemia and a 36% lower rate of nocturnal non-severe hypoglycaemia in T2DMBOT [20, 21], as well as a 25% lower rate of nocturnal non-severe hypoglycaemia and 17% lower rate of daytime non-severe hypoglycaemia in T2DMB/B [21], compared with glargine U100. Two phase 3b studies, SWITCH 1 and SWITCH 2, investigated the efficacy and safety of degludec in patients with T1DM and T2DM with an increased risk of hypoglycaemia [57, 58]. In these studies equivalent reductions in HbA1c were achieved with degludec with a lower total daily insulin dose at end of trial and with a lower risk of hypoglycaemic episodes versus glargine U100 [57, 58]. The hypoglycaemia benefits of degludec have also been reported in real-world clinical practice, with reductions of up to 90% observed in patients switching to degludec because of problems with hypoglycaemia on glargine U100 or insulin detemir [22].
A limitation of the current economic analysis, common to modelling studies, is the generalisability of clinical trial data to routine clinical practice. The clinical trials included in the meta-analyses used a treat-to-target approach, and insulin was titrated to a predetermined glycaemic target. In contrast, optimal glycaemic control may not be achieved in clinical practice because of non-adherence or poor clinic attendance. However, the sensitivity analyses indicate that the conclusions are robust. Furthermore, real-world studies confirm the observations from the clinical trials and support the effectiveness of degludec in clinical practice. The EUropean TREsiba AudiT (EU_TREAT) is a multinational observational study in the general diabetes population in routine care to assess the effectiveness of degludec [23]. A total of 2550 patients were included in the study (T1DM = 1717, T2DM = 833), and results demonstrated that switching to degludec from other basal insulins significantly improved glycaemic control and reduced the risk of overall, nocturnal and severe hypoglycaemia [23].
The real-world study used for baseline rates of hypoglycaemia [33] was based upon patient recall of hypoglycaemic events and the interpretation of symptoms may be open to bias. The study was designed to maximise the optimum recall period; however, symptoms of hypoglycaemia can be incorrectly interpreted. The uncertainty around hypoglycaemia rates was explored in a number of sensitivity analyses, and whilst hypoglycaemia rates are a key driver of cost-effectiveness outcomes the conclusion that degludec is cost-effective is robust to applying alternative values.
An advantage of the modelling approach used for this economic analysis is its simplicity. This short-term approach focuses on the impact of important aspects of insulin therapy such as hypoglycaemia and dosing and enables economic analysis of new insulins that have been evaluated in treat-to-target trials. This model has been previously used to evaluate the cost-effectiveness of degludec versus glargine U100 in patients with T1DM and T2DM [44, 59,60,61]. An analysis from the UK perspective found that degludec was dominant to glargine U100 in the T1DM and T2DMBOT populations and highly cost-effective in the T2DMB/B population [26]. Similarly, in a Swedish setting degludec was cost-effective versus glargine U100 in all three patient groups [44]. In both cases, results are consistent with those observed in this study.
Conclusion
This short-term economic evaluation indicates that degludec is a cost-effective alternative to glargine U100 for patients with T1DM and T2DM in Serbia. Degludec may particularly benefit those suffering from hypoglycaemia or where the patient would benefit from the additional flexibility.
Notes
1 EUR = 120.185 RSD: Rulebook on the conditions, criteria, method and procedure for placing the medicinal products on the reimbursement list.
Republički fond za zdravstveno osiguranje.
REFERENCES
International Diabetes Federation (IDF). Diabetes atlas, 7th edition, 2015. Available at: http://www.idf.org/idf-diabetes-atlas-seventh-edition.
Institute of Public Health of Serbia. Incidence and mortality from diabetes in Serbia 2013. Institute of Public Health of Serbia “Dr. Milan Jovanović Batut”, Belgrade: 2014. http://www.batut.org.rs/.
American Diabetes Association. Economic costs of diabetes in the US in 2012. Diabetes Care. 2013;36:1033–46.
Jonsson B. Revealing the cost of type II diabetes in Europe. Diabetologia. 2002;45:S5–12.
Biorac N, Jakovljevic M, Stefanovic D, et al. Assessment of diabetes mellitus type 2 treatment costs in the Republic of Serbia. Vojnosanit Pregl. 2009;66:271–6.
Holman RR, Paul SK, Bethel MA, et al. 10-year follow-up of intensive glucose control in type 2 diabetes. N Engl J Med. 2008;359:1577–89.
Nathan DM, Cleary PA, Backlund JY, et al. Intensive diabetes treatment and cardiovascular disease in patients with type 1 diabetes. N Engl J Med. 2005;353:2643–53.
Ministry of Health of the Republic of Serbia. National clinical guidelines for management of diabetes mellitus. The Republic Expert Comittee for development and implementation of a good clinical practice guide.
de Pablos-Velasco P, Parhofer KG, Bradley C, et al. Current level of glycaemic control and its associated factors in patients with type 2 diabetes across Europe: data from the PANORAMA study. Clin Endocrinol (Oxf). 2014;80:47–56.
Giugliano D, Maiorino MI, Bellastella G, et al. Efficacy of insulin analogs in achieving the hemoglobin A1c target of < 7% in type 2 diabetes: meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials. Diabetes Care. 2011;34:510–7.
Davies M, Gagliardino J, Gray L, et al. Real-world factors affecting adherence to insulin therapy in patients with type 1 or type 2 diabetes mellitus: a systematic review. Diabet Med. 2013;30:512–24.
Peyrot M, Rubin RR, Lauritzen T, et al. Resistance to insulin therapy among patients and providers: results of the cross-national diabetes attitudes, wishes, and needs (DAWN) study. Diabetes Care. 2005;28:2673–9.
Heise T, Nosek L, Bottcher SG, et al. Ultra-long-acting insulin degludec has a flat and stable glucose-lowering effect in type 2 diabetes. Diabetes Obes Metab. 2012;14:944–50.
Haahr H, Heise T. A review of the pharmacological properties of insulin degludec and their clinical relevance. Clin Pharmacokinet. 2014;53:787–800.
Heise T, Hermanski L, Nosek L, et al. Insulin degludec: four times lower pharmacodynamic variability than insulin glargine under steady-state conditions in type 1 diabetes. Diabetes Obes Metab. 2012;14:859–64.
Meneghini L, Atkin SL, Gough SC, et al. The efficacy and safety of insulin degludec given in variable once-daily dosing intervals compared with insulin glargine and insulin degludec dosed at the same time daily: a 26-week, randomized, open-label, parallel-group, treat-to-target trial in individuals with type 2 diabetes. Diabetes Care. 2013;36:858–64.
Mathieu C, Hollander P, Miranda-Palma B, et al. Efficacy and safety of insulin degludec in a flexible dosing regimen vs insulin glargine in patients with type 1 diabetes (BEGIN: flex T1): a 26-week randomized, treat-to-target trial with a 26-week extension. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2013;98:1154–62.
European Medicines Agency. Tresiba® (insulin degludec) Summary of Product Characteristics. Available at: http://www.ema.europa.eu/docs/en_GB/document_library/EPAR_-_Product_Information/human/002498/WC500138940.pdf.
Wangnoo SK, Chowdhury S, Rao PV. Treating to target in type 2 diabetes: the BEGIN trial programme. J Assoc Phys India. 2014;62:21–6.
Ratner R, Gough SC, Mathieu C, et al. Hypoglycaemia risk with insulin degludec compared with insulin glargine in type 2 and type 1 diabetes: a pre-planned meta-analysis of phase 3 trials. Diabetes Obes Metab. 2013;15:175–84.
Vora J, Christensen T, Rana A, et al. Insulin degludec versus insulin glargine in type 1 and type 2 diabetes mellitus: a meta-analysis of endpoints in phase 3a trials. Diabetes Ther. 2014;5:435–46.
Evans M, McEwan P, Foos V. Insulin degludec early clinical experience: does the promise from the clinical trials translate into clinical practice—a case-based evaluation. J Med Econ. 2015;18:96–105.
Siegmund T, Tentolouris N, Knudsen ST, et al. A European, multicentre, retrospective, non-interventional study (EU-TREAT) of the effectiveness of insulin degludec after switching basal insulin in a population with type 1 or type 2 diabetes. Diabetes Obes Metab. 2017. https://doi.org/10.1111/dom.13149.
Sassi F. Calculating QALYs, comparing QALY and DALY calculations. Health Policy Plan. 2006;21:402–8.
Macroeconomics and health: investing in health for economic development. Report of the Commission on Macroeconomics and Health. Geneva: World Health Organization; 2001. Available from: http://apps.who.int/iris/bitstream/10665/42435/1/924154550X.pdf.
Evans M, Chubb B, Gundgaard J. Cost-effectiveness of insulin degludec versus insulin glargine in adults with type 1 and type 2 diabetes mellitus. Diabetes Ther. 2017;8:275–91.
Food and Drug Administration. Guidance for Industry. Diabetes mellitus: developing drugs and therapeutic biologics for treatment and prevention—Draft Guidance. February 2008. Available at: http://www.fda.gov/downloads/Drugs/GuidanceComplianceRegulatoryInformation/Guidances/ucm071624.pdf.
Marseille E, Larson B, Kazi DS, et al. Thresholds for the cost-effectiveness of interventions: alternative approaches. Bull World Health Organ. 2015;93:118–24.
Heller SR, Frier BM, Herslov ML, et al. Severe hypoglycaemia in adults with insulin-treated diabetes: impact on healthcare resources. Diabet Med. 2016;33:471–7.
Sanofi-Aventis. Lantus (insulin glargine): Structure titration to target fasting glucose. Available at: http://www.lantus.com/hcp/dosing-titration/titration-guide.aspx.
Davies M, Storms F, Shutler S, et al. Improvement of glycemic control in subjects with poorly controlled type 2 diabetes: comparison of two treatment algorithms using insulin glargine. Diabetes Care. 2005;28:1282–8.
Endocrinologic and Metabolic Drug Advisory Committee. Insulin degludec and insulin degludec/insulin aspart treatment to improve glycemic control in patients with diabetes mellitus: NDAs 203314 and 203313 briefing document. 2012. Available at http://www.fda.gov/downloads/AdvisoryCommittees/CommitteesMeetingMaterials/Drugs/EndocrinologicandMetabolicDrugsAdvisoryCommittee/UCM327017.pdf. Accessed June 2014.
Ostenson CG, Geelhoed-Duijvestijn P, Lahtela J, et al. Self-reported non-severe hypoglycaemic events in Europe. Diabet Med. 2014;31:92–101.
Donnelly LA, Morris AD, Frier BM, et al. Frequency and predictors of hypoglycaemia in type 1 and insulin-treated type 2 diabetes: a population-based study. Diabet Med. 2005;22:749–55.
Henderson JN, Allen KV, Deary IJ, et al. Hypoglycaemia in insulin-treated type 2 diabetes: frequency, symptoms and impaired awareness. Diabet Med. 2003;20:1016–21.
Akram K, Pedersen-Bjergaard U, Borch-Johnsen K, et al. Frequency and risk factors of severe hypoglycemia in insulin-treated type 2 diabetes: a literature survey. J Diabetes Complicat. 2006;20:402–8.
Gold AE, MacLeod KM, Frier BM. Frequency of severe hypoglycemia in patients with type I diabetes with impaired awareness of hypoglycemia. Diabetes Care. 1994;17:697–703.
Smith CB, Choudhary P, Pernet A, et al. Hypoglycemia unawareness is associated with reduced adherence to therapeutic decisions in patients with type 1 diabetes: evidence from a clinical audit. Diabetes Care. 2009;32:1196–8.
Heller SR. Hypoglycaemia: its pathophysiology in insulin treated diabetes and hypoglycaemia unawareness. Br J Diabetes Vasc Dis. 2011;11:6–9.
Evans M, Khunti K, Mamdani M, et al. Health-related quality of life associated with daytime and nocturnal hypoglycaemic events: a time trade-off survey in five countries. Health Qual Life Outcomes. 2013;11:90.
Boye KS, Matza LS, Walter KN, et al. Utilities and disutilities for attributes of injectable treatments for type 2 diabetes. Eur J Health Econ. 2011;12:219–30.
Brod M, Christensen T, Thomsen TL, et al. The impact of non-severe hypoglycemic events on work productivity and diabetes management. Value Health. 2011;14:665–71.
Evans M, Jensen HH, Bogelund M, et al. Flexible insulin dosing improves health-related quality-of-life (HRQoL): a time trade-off survey. J Med Econ. 2013;16:1357–65.
Ericsson A, Pollock RF, Hunt B, et al. Evaluation of the cost-utility of insulin degludec vs insulin glargine in Sweden. J Med Econ. 2013;16:1442–52.
Meneghini L, Miranda-Palma B. Insulin degludec: a novel ultra-long-acting basal insulin for use in type 1 and type 2 diabetes. Expert Rev Endocrinol Metab. 2012;7:9–14.
Food and Drug Administration. Endocrinologic and Metabolic Drug Advisory Committee. Insulin degludec and insulin degludec/insulin aspart treatment to improve glycemic control in patients with diabetes mellitus: NDAs 203314 and 203313 briefing document. Available at: http://www.fda.gov/downloads/AdvisoryCommittees/CommitteesMeetingMaterials/Drugs/EndocrinologicandMetabolicDrugsAdvisoryCommittee/UCM327017.pdf (last accessed 13 Feb 2014). 2012.
Philis-Tsimikas A, Brod M, Niemeyer M, et al. Insulin degludec once-daily in type 2 diabetes: simple or step-wise titration (BEGIN: once simple use). Adv Ther. 2013;30:607–22.
Freemantle N, Meneghini L, Christensen T, et al. Insulin degludec improves health-related quality of life (SF-36®) compared with insulin glargine in people with type 2 diabetes starting on basal insulin: a meta-analysis of phase 3a trials. Diabet Med. 2013;30:226–32.
Graveling AJ, Frier BM. Hypoglycaemia: an overview. Prim Care Diabetes. 2009;3:131–9.
Cryer P. Hypoglycemia in diabetes. In: Holt RIG, Cockram CS, Flyvbjerg A, et al., editors. Textbook of diabetes. Hoboken: Blackwell Publishing; 2010.
Khunti K, Alsifri S, Aronson R, et al. Rates and predictors of hypoglycaemia in 27 585 people from 24 countries with insulin-treated type 1 and type 2 diabetes: the global HAT study. Diabetes Obes Metab. 2016;18:907–15.
Khunti K, Alsifri S, Aronson R, et al. Impact of hypoglycaemia on patient-reported outcomes from a global, 24-country study of 27,585 people with type 1 and insulin-treated type 2 diabetes. Diabetes Res Clin Pract. 2017;130:121–9.
Cryer PE. Hypoglycaemia: the limiting factor in the glycaemic management of type I and type II diabetes. Diabetologia. 2002;45:937–48.
Meneghini L. Why and how to use insulin therapy earlier in the management of type 2 diabetes. South Med J. 2007;100:164–74.
Diabetes UK. Facts and stats 2016. Available at: https://www.diabetes.org.uk/Documents/Position%20statements/DiabetesUK_Facts_Stats_Oct16.pdf.
Inzucchi SE, Bergenstal RM, Buse JB, et al. Management of hyperglycemia in type 2 diabetes, 2015: a patient-centered approach: update to a position statement of the American diabetes association and the European association for the study of diabetes. Diabetes Care. 2015;38:140–9.
Lane W, Bailey TS, Gerety G, et al. Effect of insulin degludec vs insulin glargine U100 on hypoglycemia in patients with type 1 diabetes: the SWITCH 1 randomized clinical trial. JAMA. 2017;318:33–44.
Wysham C, Bhargava A, Chaykin L, et al. Effect of insulin degludec vs insulin glargine U100 on hypoglycemia in patients with type 2 diabetes: the SWITCH 2 randomized clinical trial. JAMA. 2017;318:45–56.
Evans M, Wolden M, Gundgaard J, et al. Cost-effectiveness of insulin degludec compared with insulin glargine for patients with type 2 diabetes treated with basal insulin—from the UK health care cost perspective. Diabetes Obes Metab. 2014;16:366–75.
Evans M, Wolden M, Gundgaard J, et al. Cost-effectiveness of insulin degludec compared with insulin glargine in a basal-bolus regimen in patients with type 1 diabetes mellitus in the UK. J Med Econ. 2015;18:56–68.
Pollock RF, Tikkanen CK. A short-term cost-utility analysis of insulin degludec versus insulin glargine U100 in patients with type 1 or type 2 diabetes in Denmark. J Med Econ. 2017;20:213–20.
Acknowledgements
Funding
The study and article processing charges were funded by Novo Nordisk. All authors had full access to all of the data in this study and take complete responsibility for the integrity of the data and accuracy of the data analysis.
Medical Writing and Editorial Assistance
The authors acknowledge writing and editorial support from Carrie Fidler of DRG Abacus (sponsored by Novo Nordisk).
Authorship
All named authors meet the International Committee of Medical Journal Editors (ICMJE) criteria for authorship for this manuscript, take responsibility for the integrity of the work as a whole and have given final approval for the version to be published.
Authorship Contributions
All authors contributed to study design, data collection and analysis, and interpretation of results, as well as to the writing and final approval of this manuscript.
Disclosures
Nebojša Lalić has nothing to disclose. Monika Russel-Szymczyk is an employee of Novo Nordisk. Marina Culic is an employee of Novo Nordisk. Christian Klyver Tikkanen is an employee of Novo Nordisk. Barrie Chubb is an employee of Novo Nordisk.
Compliance with Ethics Guidelines
This article does not contain any studies with human participants or animals performed by any of the authors.
Data Availability
All data generated or analysed during this study are included in this published article/as supplementary information files.
Open Access
This article is distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc/4.0/), which permits any noncommercial use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided you give appropriate credit to the original author(s) and the source, provide a link to the Creative Commons license, and indicate if changes were made.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Enhanced digital features
To view enhanced digital features for this article go to https://doi.org/10.6084/m9.figshare.6106889.
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
This article is published under an open access license. Please check the 'Copyright Information' section either on this page or in the PDF for details of this license and what re-use is permitted. If your intended use exceeds what is permitted by the license or if you are unable to locate the licence and re-use information, please contact the Rights and Permissions team.
About this article
Cite this article
Lalić, N., Russel-Szymczyk, M., Culic, M. et al. Cost-Effectiveness of Insulin Degludec Versus Insulin Glargine U100 in Patients with Type 1 and Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus in Serbia. Diabetes Ther 9, 1201–1216 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13300-018-0426-0
Received:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13300-018-0426-0