Abstract
Introduction
Hyperglycemia plays an important role in the pathogenesis of diabetic complications, as it increases protein glycation, as well as the progressive accumulation of advanced glycation end products (AGEs), which are complex structures that produce fluorescence. The glycation reaction raises the levels of protein carbonyl, N ε-(carboxymethyl)lysine (CML), and fructosamine and decreases the level of thiol groups.
Methods
In the present study, the antiglycation activity was determined by fluorescence intensity using the bovine serum albumin (BSA)/glucose, CML method, and the level of fructosamine. The oxidation of proteins was determined by the carbonyl protein content and thiol groups.
Results
The results show that the hexane extract of Acca sellowiana (FOH) at different concentrations (0.30–5 mg/ml) significantly inhibited the formation of AGEs in the BSA/glucose model during the 4 weeks of the study. FOH reduced the levels of fructosamine and CML. Our results showed a significant effect of FOH in the prevention of oxidative damage of proteins, as well as an effect on the oxidation of thiol groups and carbonyl proteins.
Conclusion
The present study indicates that FOH is effective in inhibiting the glycation of proteins in vitro, so it can prevent or ameliorate the chronic conditions of diabetes associated with the formation of AGEs.
Similar content being viewed by others
Avoid common mistakes on your manuscript.
Introduction
Advanced glycation end products (AGEs) are a heterogeneous group of molecules that are produced in vivo by glycation and oxidation [1]. The formation of AGEs starts from a series of complex reactions between the carbonyl of a reducing sugar or aldehyde and the free amino group of a protein, resulting in the reversible formation of Schiff bases. Molecular rearrangements then form covalently bound Amadori products, which induce further oxidation resulting in dicarbonyl compounds, forming fluorescent cross-links (e.g., pentosidine) in addition to non-fluorescent compounds (e.g., N ε-(carboxymethyl)lysine, CML), referred to as AGEs [2, 3]. The glycation reaction occurs slowly under physiological conditions, but when insulin resistance is present with hyperglycemia and lipid peroxidation, it notably increases the formation of AGEs, helping the development of several chronic diseases such as diabetes mellitus, renal failure, atherosclerosis, Alzheimer’s, as well as gastrointestinal disorders such as fatty liver and cirrhosis of the liver [1]. It is believed that the formation of AGEs over a prolonged time in vivo especially affects long-lived proteins such as hemoglobin, alkaline phosphatase, lysozyme, collagen, or elastin. The glycation reaction alters the structure of the proteins, which makes them more resistant to degradation processes, resulting in the accumulation of AGEs in cells and body tissues. It has been shown that AGEs can be found in numerous types of tissues, such as the retina, glomeruli, and aorta, regardless of the type of diabetes. It is thought that the accumulation of AGEs in diabetes is directly related to hyperglycemia levels, although it is suggested the formation of AGEs may be determined by modifications in the metabolism of glucose intermediates regardless of the concentrations of glucose [4].
Acca sellowiana is a thorny shrub which is native to South America and is cultivated in different subtropical areas because of its edible fruit [5]. It belongs to the Myrtaceae family and is also known as the pineapple guava (Fig. 1) [6]. This species has different pharmacological activities such as antimicrobial [7], anticancer [8], anti-inflammatory [9], and antioxidant [10] among others. However, to date its ability to inhibit the in vitro glycation reaction has not been reported. The present investigation therefore determined the potential of Acca sellowiana to inhibit the formation of AGEs. Specifically, the purpose of this study was to determine if the hexane extract of Acca sellowiana fruit could inhibit the non-enzymatic protein glycation reaction in vitro and thus provide an alternative of natural origin that helps reduce some of the complications associated with diabetes.
Methods
Collection of Fruit
The fresh Acca sellowiana fruit was collected in the State of Mexico, in Mayo 2016. A voucher specimen (No. 2675) was deposited in the Herbarium of the Universidad Autonoma Metropolitana for further reference.
Preparation of Extract
One hundred grams of fruits was dried and powdered in a mechanical grinder. Powdered material was extracted with 500 ml of hexane using a Soxhlet apparatus. The extract (FOH) was filtered and concentrated by rotary vacuum evaporator for complete removal of solvent.
In Vitro Glycation of Bovine Serum Albumin
The glycosylation of BSA was carried out in accordance with a literature method [11] with some modifications. FOH dissolved in DMSO (0.30–5 mg/ml) was incubated in 10 mg/ml BSA with 1.1 M glucose in 0.1 M phosphate buffer at pH 7.4 containing 0.2% sodium azide at 37 °C for 1, 2, 3, and 4 weeks. The formation of glycated BSA was determined at an excitation wavelength of 355 nm and emission of 460 nm (GENios, TECAN). Aminoguanidine (AG) was used as a positive control.
Determination of Fructosamine
After 1, 2, 3, and 4 weeks of incubation, the fructosamine concentration of the Amadori product was determined, which was measured by the nitroblue tetrazolium (NBT) assay [11]. For this purpose, 10 μl of glycated BSA was incubated with 90 μl of 0.5 mM NBT in 0.1 M carbonate buffer at pH 10.4 at 37 °C. After 10–15 min the absorbance was read at 530 nm (6405, JENWAY). The fructosamine concentration was calculated by comparing it with 1-deoxy-1-morpholinofructose (1-DMF), which was used as the standard.
Determination of Protein Carbonyl Content
After 1, 2, 3, and 4 weeks of incubation, the content of the carbonyl group in glycosylated BSA was determined by a literature method [11] with some modifications; the carbonyl content was a marker of oxidative protein damage. To 200 μl of glycated samples, 800 μl of 10 mM 2,4-dinitrophenylhydrazine (DNPH) in 2.5 M HCl was added. Samples were allowed to incubate in the dark for 1 h. The proteins were precipitated using 1 ml of trichloroacetic acid (TCA) at 20% (w/v), leaving the samples on ice for 5 min, then centrifuging at 10,000g for 10 min at 4 °C. The supernatant was washed three times using 500 μl of an ethanol/ethyl acetate mixture (1:1) and the protein supernatant was then dissolved in 500 μl of 6 M guanidine hydrochloride. The absorbance was read at 370 nm (6405, JENWAY). The carbonyl group concentration of the samples was calculated using the absorption coefficient (ɛ = 22,000 M−1 cm−1). The results were expressed as nanomoles of carbonyl per milligram of protein.
Thiol Group Estimation
After 1, 2, 3, and 4 weeks of incubation the free thiol groups were determined in glycated BSA using a literature method [11] with some modifications. Thus 70 μl of sample was incubated with 130 μl of 5 mM 5,5′-dithiobis(2-nitrobenzoic acid) (DTNB) in 0.1 M PBS, pH 7.4 at 25 °C for 15 min. The absorbance of the samples was then read at 412 nm (6405, JENWAY), and the free thiol concentration was calculated using a standard l-cysteine curve. The results were expressed as nmoles per milligram of protein.
Determination of CML
At the end of the 4-week incubation, CML, a major antigenic AGE structure, was determined by using an enzyme-linked immunosorbant assay (ELISA) kit. The concentration of CML was calculated by using the standard CML-BSA curve from the assay kit.
Statistical Analysis
The results were expressed as the mean ± standard error of the mean (SEM) (n = 3). The statistical significance of the results was evaluated by using one-way ANOVA. The least significant difference (LSD) test was used for mean comparisons, and P < 0.05 was considered to be statistically significant.
Compliance with Ethics Guidelines
This article does not contain any new studies with human or animal subjects performed by any of the authors.
Results
In Vitro Glycation of Bovine Serum Albumin
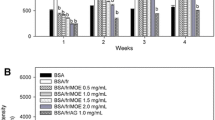
Figure 2 shows the fluorescence intensity as a consequence of AGEs formation of different BSA/glucose solutions at different time intervals (1–4 weeks). When BSA/glucose was incubated the fluorescence increased significantly over the 4 weeks of the experiment. By adding different concentrations of FOH to the BSA/glucose media, the fluorescence intensity significantly decreased in a concentration-dependent manner over the duration of the study compared to media containing only BSA/glucose. At the end of the experiment, a concentration of FOH of 5 mg/ml resulted in a decrease in fluorescence intensity of 65.68%, compared to the BSA/glucose/AG (5 mg/ml) system which was 67.32%.
Effects of FOH extract on formation of fluorescent advanced glycation end products (AGEs) in BSA incubated with glucose. Each value represents the mean ± SE (n = 3). a p < 0.05 when compared to BSA/glucose at week 1; b p < 0.05 when compared to BSA/glucose at week 2; c p < 0.05 when compared to BSA/glucose at week 3; d p < 0.05 when compared to BSA/glucose at week 4
Determination of Fructosamine
The effects of FOH on the level of fructosamine in the BSA/glucose system are shown in Table 1. The amount of fructosamine increased significantly during the 4 weeks of the experiment. When FOH was added at different concentrations to the BSA/glucose system, it significantly inhibited the formation of fructosamine for the duration of the experiment. At the end of the experiment and at a FOH concentration of 5 mg/ml, the fructosamine level was 68.31 nM, whereas AG (5 mg/ml) had a fructosamine level of 67.10 nM.
Effect of FOH on Protein Oxidation
The content of carbonyl and thiol groups was measured to evaluate protein oxidation, which occurs during the protein glycation process. In Table 2, the carbonyl group content in the BSA/glucose system increased significantly over the experimentation period (1–4 weeks). In contrast, the BSA/glucose/FOH system significantly decreased the carbonyl group content throughout the experiment. At week 4 using the BSA/glucose/FOH system at a concentration of 5 mg/ml, a value of 67.14 nmol/mg protein was obtained, compared to the glycated BSA which had a value of 80.29 nmol/mg protein, while AG (5 mg/ml) showed a value of 64.87 nmol/mg protein.
Effect of FOH on Thiol Groups
The effect of FOH on the oxidation of thiol groups is shown in Table 3. When the BSA/glucose system was used, thiol groups decreased during the experimental period; when the BSA/glucose/FOH system (5 mg/ml) was used, a significant increase was observed in thiol groups showing 56.54 mmol/mg protein at week 4 compared to glycated BSA, which presented a value of 52.57 nmol/mg protein, whereas AG (5 mg/ml) at week 4 had 56.87 nmol/mg protein.
Effect of FOH on Levels of CML
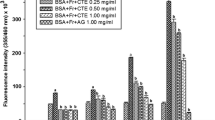
CML is a biomarker that has been used to determine non-fluorescent AGEs. The BSA/glucose/FOH system at a concentration of 0.30 mg/ml and 5 mg/ml showed a significant concentration-dependent decrease in the formation of SMC of 28.89% and 67.77%, respectively, whereas AG at a concentration of 5 mg/ml reduced the formation of CML by 74.22%, as compared to glycated BSA (Fig. 3).
Discussion
The non-enzymatic reaction of proteins leads to heterogeneous and toxic AGEs. The intermediate products in the formation of AGEs may originate from free sugar or via condensation products [12]. The BSA/glucose assay is a useful tool to determine the effect of FOH on non-enzymatic glycation and in our study it indicated that the hexane extract of the Acca sellowiana fruit can inhibit the formation of AGEs, which are related to the pathogenic processes of diabetes complications.
In the early stages of glycation, Schiff bases are formed, which are converted into Amadori products such as fructosamine [13], which is a measure of non-enzymatic protein glycation used clinically as an indicator for short-term blood sugar levels in people with diabetes; fructosamine formation increases the complications of diabetes such as nephropathy, neuropathy, and retinopathy [14]. FOH extract decreased the formation of fructosamine, which is a therapeutic way to reduce the vascular complications of diabetes.
The glycation reaction is one of the main non-enzymatic pathways which contributes to protein damage, autoxidation of sugars, and oxidative degradation of Amadori products. These reactions modify proteins through reactive oxygen species. The oxidation of the proteins is accompanied by the formation of carbonylic protein and the loss of protein thiols, which are commonly used as protein oxidation indexes [13].
In this study, it was observed that FOH, depending on the dose, reduces oxidative damage, decreases the formation of reactive oxygen species, and protects protein thiols from oxidation. This suggests that the hexane extract of the Acca sellowiana fruit decreases oxidative stress and may be useful in preventing oxidative damage to the protein, which is attributed to the glycation reaction.
One of the best chemically characterized AGEs in humans is CML [15], which is formed by oxidative degradation mediated by hydroxyl radicals [16] of Amadori products and during the metal-catalyzed oxidation of polyunsaturated fatty acids in the presence of protein [17]. In the blood vessels of the retina of people with type 2 diabetes, CML has been found along with other AGEs; in addition, high levels of CML have been reported in peripheral nerves in patients with diabetes, which brings with it microangiopathy and neuropathy [15]. Our results show that FOH inhibits the formation of CML, suggesting that FOH can prevent the complications of diabetes associated with AGEs.
Conclusion
The hexane extract of the Acca sellowiana fruit was effective in inhibiting protein glycation, as well as protein oxidation. Its antiglycation effect may have been due to its ability to react with dicarbonyl intermediates, which is the main mechanism to inhibit the formation of AGEs. These results suggest that FOH can prevent damage caused by AGEs in people with diabetes. However, the mechanism by which FOH inhibits the glycation reaction has not yet been determined, so investigation of its major bioactive constituents is still ongoing.
References
Santos J, Valentim I, de Araújo O, et al. Development of nonalcoholic hepatopathy: contributions of oxidative stress and advanced glycation end products. Int J Mol Sci. 2013;14:19846–66.
Ott C, Jacobs K, Haucke E, et al. Role of advanced glycation end products in cellular signaling. Redox Biol. 2014;2:411–29.
Jariyapamornkoon N, Yibchok-anun S, Adisakwattana S. Inhibition of advanced glycation end products by red grape skin extract and its antioxidant activity. BMC Complement Altern Med. 2013;13:171.
Rask-Madsen C, King GL. Vascular complications of diabetes: mechanisms of injury and protective factors. Cell Metab. 2013;17:20–33.
Lapčík O, Klejdus B, Kokoška L, et al. Identification of isoflavones in Acca sellowiana and two Psidium species (Myrtaceae). Biochem Syst Ecol. 2005;33:983–92.
Weston RJ. Bioactive products from fruit of the feijoa (Feijoa sellowiana, Myrtaceae): a review. Food Chem. 2010;121:923–6.
Motohashi N, Kawase M, Shirataki Y, et al. Biological activity of feijoa peel extracts. Anticancer Res. 2000;20:4323–30.
Bontempo P, Mita L, Miceli M, et al. Feijoa sellowiana derived natural flavone exerts anti-cancer action displaying HDAC inhibitory activities. Int J Biochem Cell Biol. 2007;39:1902–14.
Rossi A, Rigano D, Pergola C, et al. Inhibition of inducible nitric oxide synthase expression by an acetonic extract from Feijoa sellowiana Berg. fruits. J Agric Food Chem. 2007;55:5053–61.
Turco F, Palumbo I, Andreozzi P, et al. Acetonic extract from the Feijoa sellowiana Berg. fruit exerts antioxidant properties and modulates disaccharidases activities in human intestinal epithelial cells. Phytother Res. 2016;1315:1308–15.
Adisakwattana S, Sompong W, Meeprom A, et al. Cinnamic acid and its derivatives inhibit fructose-mediated protein glycation. Int J Mol Sci. 2012;13:1778–89.
Booth AA, Khalifah RG, Todd P, et al. In vitro kinetic studies of formation of antigenic advanced glycation end products (AGEs). Novel inhibition of post-Amadori glycation pathways. J Biol Chem. 1997;28:5430–7.
Ardestani A, Yazdanparast R. Cyperus rotundus suppresses AGE formation and protein oxidation in a model of fructose-mediated protein glycoxidation. Int J Biol Macromol. 2007;41:572–8.
Shield JPH, Poyser K, Hunt L, et al. Fructosamine and glycated haemoglobin in the assessment of long term glycaemic control in diabetes. Arch Dis Child. 1994;71:443–5.
Goh S-Y, Cooper ME. The role of advanced glycation end products in progression and complications of diabetes. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2008;93:1143–52.
Rahbar S, Figarola JL. Novel inhibitors of advanced glycation endproducts. Arch Biochem Biophys. 2003;419:63–79.
Ahmed N. Advanced glycation endproducts–role in pathology of diabetic complications. Diabetes Res Clin Pract. 2005;67:3–21.
Acknowledgements
No funding or sponsorship was received for this study or the publication of this article. Article processing charges were funded by the authors. All named authors meet the International Committee of Medical Journal Editors (ICMJE) criteria for authorship for this manuscript, take responsibility for the integrity of the work as a whole, and have given final approval for the version to be published.
Disclosures
Alethia Muñiz, Abraham H. Garcia, Rosa M. Gutiérrez, Efren V. Garcia Baez, and Daphne E. González have nothing to disclose.
Compliance with Ethics Guidelines
This article does not contain any new studies with human or animal subjects performed by any of the authors.
Data Availability
All data generated or analyzed during this study are included in this published article.
Open Access
This article is distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc/4.0/), which permits any noncommercial use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided you give appropriate credit to the original author(s) and the source, provide a link to the Creative Commons license, and indicate if changes were made.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Enhanced content
To view enhanced content for this article go to http://www.medengine.com/Redeem/FFCCF060741441B0.
Rights and permissions
Open Access This article is distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0), which permits use, duplication, adaptation, distribution, and reproduction in any medium or format, as long as you give appropriate credit to the original author(s) and the source, provide a link to the Creative Commons license, and indicate if changes were made.
About this article
Cite this article
Muñiz, A., Garcia, A.H., Pérez, R.M. et al. In Vitro Inhibitory Activity of Acca sellowiana Fruit Extract on End Products of Advanced Glycation. Diabetes Ther 9, 67–74 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13300-017-0335-7
Received:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13300-017-0335-7