Abstract
Physicians and patients have long been aware of skin lesions at the sites of insulin injections, referred to as lipodystrophy that can present as lipoatrophy (LA) or lipohypertrophy (LH). However, the reported prevalence of these different skin lesions varies widely, emphasizing the need for a correct identification method. In this short review we discuss LA and LH and also take into account other skin lesions, such as bruising, as well as different needle injuries, including those associated with the subcutaneous injection of pegvisomant (a drug aimed at counteracting the high levels of growth hormone associated with acromegaly), long-acting exenatide (a glucagon-like peptide-1 receptor agonist), and anti-tumor necrosis factor-alpha biologic agents (used against Crohn’s disease). In these latter cases specific studies are warranted to understand the pathophysiological background and possible prevention. However, the most common lesion is still insulin injection site-related LD, so a strong effort has to be made to avoid the confusion generated by previously misleading classifications which were barely able to reliably distinguish between LA and LH.
Similar content being viewed by others
Avoid common mistakes on your manuscript.
Definition of Lipodystrophy
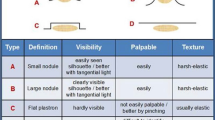
Lipodystrophy (LD), a disorder of adipose tissue, is one of the most common complications of subcutaneous insulin injections and may present as either lipohypertrophy (LH) or lipoatrophy (LA). The latter is defined as a large, often deep, retracted scar on the skin that results from serious damage to subcutaneous fatty tissue [1]. Several features of LA suggest an immunological etiology [2]: (1) it is more frequent in patients with type 1 diabetes, and mostly affects women—who often have other signs of autoimmunity; (2) it is often characterized by the presence of mast cells and eosinophils in biopsy specimens and may be responsive to topical 4% cromolyn sodium preparations (an inhibitor of mast cells); (3) it seems to be the result of a lipolytic reaction to impurities or other components in some insulin preparations, as its prevalence has dropped to only 1–2% with the increasing use of purified insulin [3, 4].
LH is a thickened ‘rubbery’ tissue swelling which is mostly firm but may occasionally present as a soft lesion as well, and thus it is easily missed during a standard medical examination. Although the exact etiology of LH is unclear, several local factors appear to be at play, including both the insulin molecule per se—with its strong growth-promoting properties—and repeated trauma caused by poor injection habits, such as infrequent/missed injection site rotation and/or frequent needle reuse [1]. However, a large body of evidence also lends support to a significant association between LH and many other factors, including female sex, low socioeconomic level, high body mass index, as well as long-standing disease and/or insulin treatment. LH lesions are generally correctly identified during the course of any accurate examination, although in various published series the steps taken to do so were not fully documented [5–7].
This article is based on previously conducted studies, is fully ethics compliant, and does not involve any new studies of human or animal subjects performed by any of the authors. Patients’ consent was also obtained for anonymous picture utilization.
Clinical Consequences of Lipodystrophies
A missed diagnosis of LD may have major clinical consequences. The injection of insulin into parts of the body affected by LD may cause wide glycemic oscillations, including inappropriately high glucose levels and a high rate of unexplained hypoglycemic episodes, both of which are scarcely responsive even large changes in insulin dose [1, 8]. Programs aimed specifically at educating patients with LD on proper injection techniques has proven to be effective in significantly reducing glucose oscillations [9].
Despite LH and LA on occasion being used improperly as synonyms [3], we suggest that the two concepts be kept separate.
Most studies suggest that insulin absorption at areas affected by LH may be both delayed and erratic, leading to the need for ever increasing doses of insulin and worsening metabolic control [10–14]. This in turn causes unacceptable glucose oscillations due to a high rate of serious hypoglycemic episodes followed by rebound glucose spikes whenever patients suddenly switch from affected injection sites to normal ones. Under these conditions, the economic burden of the disease increases for both patients and the healthcare system. Therefore, it is crucial that as many areas affected by LH as possible are systematically identified in order to educate patients on good insulin injection habits. The reported prevalence of LH in patients receiving insulin injections varies widely in published studies [6], possibly due to the lack of a well-structured diagnostic flow-chart despite the world-wide availability of suitable ultrasound and radiological methods [1, 15–24]. We recently published a methodological paper on a palpation technique that enables the clinician to identify skin lipohypertrophic lesions in diabetic patients receiving insulin [6]. We therefore propose that diabetes teams be formed at medical institutions which would systematically follow that simple procedure we describe for the diagnosis of LH at all insulin injection sites and then implement and hopefully progressively refine this procedure in large-scale studies. In particular, unexplained variations in glucose levels and/or unexplained hypoglycemic episodes may alert healthcare providers to look for LH in diabetic patients receiving insulin injections.
Bruising
Another original aspect of insulin injection-related skin lesions is bruising at the level of the injection site, as shown in Fig. 1. Bruising is mentioned in several published studies on insulin injections [25–28]. It is a problematic side-effect of insulin injections which disturbs diabetic patients due to the resulting blemishes, for which there are as yet no solutions. Unfortunately, in terms of both patient and healthcare provider perspectives, injection-related problems negatively affect the overall number of shots diabetic patients are willing to take [28]. In fact, in some studies one-half of the patients reported mentioning injection-related problems to their healthcare providers who were unable to resolve the associated pain and bruising [28, 29].
In a series of 780 insulin-treated adults with type 2 (n = 556) or type 1 (n = 223) diabetes mellitus on a multiple daily injection regimen (4 shots/day), we identified 46.2% of patients had areas affected by LH, with a mean lesion diameter of 4.8 + 3.1 cm, but LA was quite uncommon (3.2%) (unpublished data). In this same series, 33.2% of patients showed bruising, either associated with LH (n = 178, 53.9%) or isolated (n = 156, 46.6%), independent of the use of antiplatelet and/or anticlotting drugs (unpublished data).
It is important to note that injection site-related adverse events, such as pain, redness, bruising, and bleeding, are significant barriers to patient adherence to treatment regimens involving multiple daily injections. This is especially important when physicians and/or healthcare providers are not sufficiently experienced or possess insufficient knowledge to provide assistance [28–30] or when the doctor–patient relationship is unsatisfactory [29].
To fill this gap, during the last few years an interesting exchange of experiences has developed among patients through various networks, beginning with the American Diabetes Association Community [31]. Such forums have enabled diabetic patients themselves to propose several interesting solutions, including a sufficiently long injection time, very thin and short needles, and a careful injection site rotation technique. However, specific investigations are still warranted to assess reasons behind such complications associated with the injection site and to identify scientifically sound solutions aimed at improving patient adherence to insulin therapy.
Other, Genetic or Acquired Lipodystrophies, Including Those Associated to Human Immunodeficiency Virus
After taking into consideration all of the concepts mentioned in the preceding sections, it should be noted that LD does not represent only a single complication of insulin treatment—rather, a number of different clinical pictures, all falling under the name ‘LD’, have also been reported to be associated with skin lesions. These are heterogeneous, genetic, or acquired disorders of skin fat. It is well known that exogenous proteins may induce local inflammatory reactions and that the injection of different medications may cause local adverse events.
The most prevalent subtype of acquired non-insulin treatment-related LD occurs in human immunodeficiency virus-infected patients on long-lasting protease inhibitor-containing, highly active antiretroviral therapy. This type of LD likely results from lipid and/or glucose metabolic disorders, with the latter ranging from fasting hyperglycemia to insulin resistance/hyperinsulinemia [32, 33].
Pegvisomant
Another reversible LD association reported to date is the one between LH and pegvisomant injections in patients with acromegaly. Several cases of this association have been published [34] and, interestingly enough, LH was reported to have regressed in all patients when the medication was discontinued or a regular injection site rotation technique was implemented according to a structured educational program [35].
Exenatide Long-Acting Once-Weekly Formulation
Another type of palpable, yet often invisible subcutaneous nodule is the one occurring following subcutaneous shots of long-acting, once-weekly formulation of exenatide (EQW), a glucagon-like peptide-1 receptor agonist (GLP-1 RA) [36]. This adverse event was reported in registration studies, together with other injection site-related adverse events [37], among which itching was the most common, although its rate appeared to wane over time, from 11.0% between weeks 4 and 6 to 4.6% between weeks 28 and 30 [38]. An informal communication from the DURATION-1 study staff indicated that nodules were generally 0.5–0.75 cm in diameter, and their incidence seemed to decline over time and slowly vanished, even in patients with several earlier similar episodes [37–39]. As EQW uses a PLG [poly(d,l-lactide-co-glycolide)] microsphere technology, LH lesions were thought to be the result of a typical foreign body local reaction [39], implying the migration of polymorphonuclear leukocytes, monocytes/macrophages, and lymphocytes [40].
Despite these reports, no published studies are available on any injection site-related adverse effects involving EQW. Neither is information available on any possible skin reaction-driven changes in EQW pharmacokinetics and pharmacodynamics or on any related potential clinical consequences. In addition, no reports are available in the literature on any injection-related skin lesions associated to other daily or weekly GLP-1 RA formulation.
Anti-Tumor Necrosis Factor
The anti-tumor necrosis factor (anti-TNF) biologic agents used against Crohn’s disease have been associated with a number of injection site reactions, including redness, itching, bruising, pain, or swelling [41]. These have been commonly observed with subcutaneous protein injections even in the combined safety trial [42–44]. However, once again no published reports are available on anti-TNF-related lipodystrophic injuries similar to those due to insulin injections, and therefore specific studies are warranted in this area also.
Conclusions and Methodological Considerations
All of these different types of skin lesions can be confounding, especially when no clear-cut differentiation can be made between well-defined lesions with different morphology and pathogenesis, such as insulin-related LH and LA. Specifically, LH and LA are still occasionally confused [9], even though the latter is a scarring lesion and is therefore quite different from LH in terms of both morphology (see Fig. 2) and pathogenesis. Indeed, while confusing these two lesion types may have been justified back in 2002, when a letter to the editor published in Diabetes Care proposed a three-stage classification for insulin-related LD despite little being admittedly known about the nature and causes of described phenomena [3, 7, 23]. However, given the state of current scientific knowledge, no confusion should be made between lesions having so different an appearance and metabolic consequences.
In conclusion, even today little information is available on possible clinical consequences of local injection-related side-effects of subcutaneous medications against diabetes (exenatide and other GLP-1-RA), acromegaly (pegvisomant), or Crohn’s disease (anti-TNF).
Based on evidence showing that insulin shots are the most frequent factors associated to skin lesions, we suggest that precautions recommended for insulin injections may be adopted for all other subcutaneously injected drugs as well. In particular, local damage may be minimized through the use of very short and thin needles and a careful injection site rotation method [45]. However, dedicated studies are needed to support this hypothesis.
Conversely, no cases of LA associated with subcutaneous use of drugs other than insulin have been reported to date. LA lesions are even quite rare in insulin-treated patients, since the most numerous patient series described in the literature adds up to 24 subjects [4]. LA has been suggested to be related to the use of animal insulins [46], and the prevalence of LA lesions has been noted to have declined considerably following the introduction of new insulin analogs on the market, although some cases of LA have also been reported to be associated with the latter as well.
Given the state of current knowledge, any confusion between LA and LH is no longer justified from a clinical perspective, as insulin has a much higher chance to penetrate into the subcutaneous muscle tissue when injected into areas affected by LA, thus eventually causing more severe hypoglycemic events and at a much higher frequency than that observed with LH.
Prevention of wide glycemic variations and the risk of hypoglycemia is primarily based on patient education with respect to the need for regular injection site rotation and avoidance of areas affected by LA or LH. In fact, we suggest that patients be educated so as to be able to identify LA and LH themselves in order to avoid damaged areas as much as possible [3, 23].
References
Blanco M, Hernández MT, Strauss KW, Amaya M. Prevalence and risk factors of lipohypertrophy in insulin-injecting patients with diabetes. Diabetes Metab. 2013;39:445–53.
Holstein A, Stege H, Kovacs P. Lipoatrophy associated with the use of insulin analogues: a new case associated with the use of insulin glargine and review of the literature. Expert Opin Drug Saf. 2010;9:225–31.
Lopez X, Castells M, Ricker A, Velazquez EF, Mun E, Goldfine AB. Human insulin analog–induced lipoatrophy. Diabetes Care. 2008;31:442–4.
Phua EJ, Lopez X, Ramus J, Goldfine AB. Cromolyn sodium for insulin-induced lipoatrophy: old drug, new use. Diabetes Care. 2013;36:e204–5.
Al Ajlouni M, Abujbara M, Batieha A, Ajlouni K. Prevalence of lipohypertrophy and associated risk factors in insulin-treated patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus. Int J Endocrinol Metab. 2015;13:e20776.
Gentile S, Guarino G, Guida P, Strollo F, On behalf of the AMD-OSDI Italian Injection Technique Study Group. A suitable palpation technique allows to identify skin lipohypertrophic lesions in insulin-treated people with diabetes. SpringerPlus. 2016;5:563. doi:10.1186/s40064-016-1978-y.
Gentile S, Strollo F, Guarino G, Giancaterini A, Ames PRJ, et al. Factors hindering correct identification of unapparent lipohypertrophy. J Diabetes Metab Disord Control. 2016;3:00065. doi:10.15406/jdmdc.2016.03.00065.
Perciun R. Ultrasonographic aspect of subcutaneous tissue dystrophies as a result of insulin injections. Med Ultrason. 2010;12:104–9.
Al-Hayek AA, Robert AA, Braham RB, Al-Dawish MA. Frequency of lipohypertrophy and associated risk factors in young patients with type 1 diabetes: a cross-sectional study. Diabetes Ther. 2016. doi:10.1007/s13300-016-0161-3.
Gentile S, Agrusta M, Guarino G, Carbone L, Cavallaro V, et al. Metabolic consequence of incorrect insulin administration techniques in aging subjects with diabetes. Acta Diabetol. 2011;48:121–5.
Young RJ, Hannan WJ, Frier BM, Steel JM, Duncan LJ. Diabetic lipohypertrophy delays insulin absorption. Diabetes Care. 1984;7:479–80.
Frid A, Linden B. Computed tomography of injection sites in patients with diabetes mellitus. Injection and absorption of insulin. Stockholm 1992: Thesis.
Chowdhury TA, Escudier V. Poor glycaemic control caused by insulin induced lipohypertrophy. Br Med J. 2003;327:383–4.
Johansson UB, Amsberg S, Hannerz L, Wredling R, Adamson U, Arnqvist HJ, Lins PE. Impaired absorption of insulin aspart? From lipohypertrophic injection sites. Diabetes Care. 2005;28:2025–7.
Grassi G, Scuntero P, Trepiccioni R, Marubbi F, Strauss K. Optimizing insulin injection technique and its effect on blood glucose control. J Clin Translat Endocrinol. 2014;1:145–50.
Vardar B, Kizilci S. Incidence of lipohypertrophy in diabetic patients and a study of influencing factors. Diabetes Res Clin Pract. 2007;77:231–6.
Seyoum B, Abdulkadir J. Systematic inspection of insulin injection sites for local complications related to incorrect injection technique. Trop Dr. 1996;26:159–61.
Hauner H, Stockamp B, Haastert B. Prevalence of lipohypertrophy in insulin-treated diabetic patients and predisposing factors. Exp Clin Endocrinol Diabetes. 1996;104:106–10.
McNally PG, Jowett NI, Kurinczuk JJ, Peck RW, Hearnshaw JR. Lipohypertrophy and lipoatrophy complicating treatment with highly purified bovine and porcine insulin. Postgrad Med J. 1988;64:850–3.
Partanen T, Rissanen A. Insulin injection practices. Pract Diabetes Int. 2000;17:252–4.
Raile K, Noelle V, Schawarz HP. Insulin antibodies are associated with lipoatrophy but also with lipohypertrophy in children and adolescents with type 1 diabetes. Exp Clin Endocrinol Diabetes. 2001;109:393–6.
Teft G. Lipohypertrophy: patient awareness and implications for practice. January–February/2002. http://www.findsarticle.com. Accessed 7 May 2016.
Kordonouri O, Lauterborn R, Deıss D. Lipohypertrophy in young patients with type 1 diabetes. Diabetes Care. 2002;25:634.
Hajheydari Z, Kashi Z, Akha O, Akbarzadeh S. Frequency of lipodystrophy induced by recombinant human insulin. Eur Rev Med Pharmacol Sci. 2011;15:1196–201.
Annersten M, Willman A. Performing subcutaneous injections: a literature review. Worldviews Evid Based Nurs. 2005;2:122–30.
Kreugel G, Beijer HJM, Kerstens MN, Ter Maaten JC, Sluiter WJ, Boot BS. Influence of needle size on metabolic control and patient acceptance. Eur Diabetes Nursing. 2007;4:51–5.
Strauss K, De Gols H, Hannet I, Partanen TM, Frid A. A pan-European epidemiologic study of insulin injection technique in patients with diabetes. Pract Diabetes Int. 2002;19:71–6.
Rubin RR, Peyrot M, Kruger DF, Travis LB. Barriers to insulin injection therapy: patient and health care provider perspectives. Diabetes Educ. 2009;35:1014–22.
De Coninck C, Frid A, Gaspar R, Hicks D, Hirsch L, Kreugel G, Liersch J, Letondeur C, Sauvanet JP, Tubiana N, Strauss K. Results and analysis of the 2008–2009 insulin injection technique questionnaire survey. J Diabetes. 2010;2:168–79.
Peyrot M, Rubin RR, Kruger DF, Travis LB. Correlates of insulin injection omission. Diabetes Care. 2010;33:240–5.
American Diabetes Association Community. Available at: http://community.diabetes.org/t5/Adults-Living-with-Type-2/Bruising-at-Injection-Sites/td-p/226433. Accessed 7 May 2016.
Kumar NS, Shashibhushan J, Malappa, Venugopal K, Vishwanatha H, et al. Lipodystrophy in human immunodeficiency virus (HIV) patients on highly active antiretroviral therapy (HAART). J Clin Diagn Res. 2015;9:OC05–8.
Leung VL, Glesby MJ. Pathogenesis and treatment of HIV lipohypertrophy. Curr Opin Infect Dis. 2011;24:43–9.
Bonert VS, Kennedy L, Petersenn S, Barkan A, Carmichael J, et al. Lipodystrophy in patients with acromegaly receiving pegvisomant. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2008;93:3515–8.
Marazuela M, Daudén E, Ocón E, Moure D, Nattero L. Pegvisomant-induced lipohypertrophy: report of a case with histopathology. Ann Intern Med. 2007;147:741–3.
Buse JB, Drucker DJ, Taylor KL, Kim T, Walsh B, DURATION-1 Study Group, et al. DURATION-1: exenatide once weekly produces sustained glycemic control and weight loss over 52 weeks. Diabetes Care. 2010;33:1255–61.
DeYoung MB, MacConell L, Sarin V, Trautmann M, Herbert P. Encapsulation of exenatide in poly-(d, l-lactide-co-glycolide) microspheres produced an investigational long-acting once-weekly formulation for type 2 diabetes. Diabetes Technol Ther. 2011;13:1145–54.
Grimm M, Han J, Weaver C, Griffin P, Schulteis CT, et al. Efficacy, safety, and tolerability of exenatide once weekly in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus: an integrated analysis of the DURATION trials. Postgrad Med. 2013;125:47–57.
Anderson JM, Rodriguez A, Chang DT. Foreign body reaction to biomaterials. Semin Immunol. 2008;20:86–100.
Anderson JM, Shive MS. Biodegradation and biocompatibility of PLA and PLGA microspheres. Adv Drug Deliv Rev. 1997;28:5–24.
Moustou AE, Matekovits A, Dessinioti C, Antoniou C, Sfikakis PP, Stratigos AJ. Cutaneous side effects of anti-tumor necrosis factor biologic therapy: a clinical review. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2009;61:486–504.
Sandborn WJ, Rutgeerts P, Enns R, Hanauer SB, Colombel JF, et al. Adalimumab induction therapy for Crohn disease previously treated with infliximab: a randomized trial. Ann Intern Med. 2007;146:829–38.
Colombel JF, Sandborn WJ, Rutgeerts P, Enns R, Hanauer SB, et al. Adalimumab for maintenance of clinical response and remission in patients with Crohn’s disease: the CHARM trial. Gastroenterology. 2007;132:52–65.
Van Assche G, Vermeire S, Rutgeerts P. Adalimumab in Crohn’s disease. Biol Targets Ther. 2007;1:355–65.
Frid A, Hirsch L, Gaspar R, Hicks D, Kreugel G, Liersch J, et al. New injection recommendations for patients with diabetes. Diabetes Metab. 2010;36:S3–18.
Reeves WG, Allen BR, Tattersall RB. Insulin-induced lipoatrophy: evidence for an immune pathogenesis. BMJ. 1980;280:1500–3.
Acknowledgments
This paper was not funded by any external support. No funding or sponsorship was received for this study or publication of this article. The article was realized with the fundamental contribution of the members of the AMD-OSDI Injection Technique Study Group, the members of which revised the manuscript. All named authors meet the International Committee of Medical Journal Editors (ICMJE) criteria for authorship for this manuscript, take responsibility for the integrity of the work as a whole, and have given final approval for the version to be published.
Members of the Study Group Coordinator: S Gentile. Collaborators: A Botta, L Cucco, N De Rosa, S De Riu, G Garrapa, L Gentile, G Grassi, C Lalli, G Lo Grasso, TM Marcone, M Sudano, P Tatti, L Tonutti, R Chiandetti.
Disclosures
Sandro Gentile, Felice Strollo, and Antonio Ceriello declare that they have no confict of interests to disclose.
Compliance with Ethics Guidelines
This article is based on previously conducted studies and is fully ethics compliant. It does not involve any new studies of human or animal subjects performed by any of the authors. Consent was obtained from the patients whose pictures appear in the article under a guarantee of anonymity.
Open Access
This article is distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc/4.0/), which permits any noncommercial use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided you give appropriate credit to the original author(s) and the source, provide a link to the Creative Commons license, and indicate if changes were made.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Consortia
Corresponding author
Additional information
Enhanced content
To view enhanced content for this article go to http://www.medengine.com/Redeem/13E4F0605E44F239.
AMD is the Italian acronym for the Association of Diabetes Specialists and OSDI is the Italian acronym for Diabetes Care Health Professionals.
Rights and permissions
Open Access This article is distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0), which permits use, duplication, adaptation, distribution, and reproduction in any medium or format, as long as you give appropriate credit to the original author(s) and the source, provide a link to the Creative Commons license, and indicate if changes were made.
About this article
Cite this article
Gentile, S., Strollo, F., Ceriello, A. et al. Lipodystrophy in Insulin-Treated Subjects and Other Injection-Site Skin Reactions: Are We Sure Everything is Clear?. Diabetes Ther 7, 401–409 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13300-016-0187-6
Received:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13300-016-0187-6