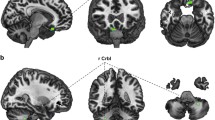
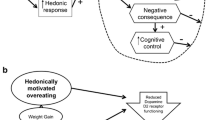
Abstract
The most common cause for obesity is a positive energy balance, i.e. more energy is being consumed than is expended. The rise in obesity rates cannot be explained on the basis of our obesogenic environment alone, because large interindividual differences in weight status exist between people. Therefore, the cause is most probably to be found in an interaction between individual behaviour and our changed environment. This warrants the investigation of the brain’s role in the development and maintenance of obesity that indeed has become a growing field in the neurosciences. This article will give an overview about the findings in neuroimaging associated with human obesity. Further, this article will elucidate the relationship between common genetic variation, eating behaviour and brain structure in the context of obesity. Finally, important open questions in the field will be summarised.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Hare TA, Camerer CF, Rangel A (2009) Self-control in decision-making involves modulation of the vmPFC valuation system. Science 324(5927):646–648
Horstmann A, Busse F, Mathar D et al (2011) Obesity-related differences between women and men in brain structure and goal-directed behavior. Front Hum Neurosci 5. doi:10.3389/fnhum.2011.00058
Horstmann A, Kovacs P, Kabisch S et al (2013) Common genetic variation near MC4R has a sex-specific impact on human brain structure and eating behavior. (F. J. Esteban, Ed.) PLoS One 8(9):e74362
Kenny PJ (2011) Reward mechanisms in obesity: new insights and future directions. Neuron 69(4):664–679
Kullmann S, Heni M, Veit R et al (2012) The obese brain: association of body mass index and insulin sensitivity with resting state network functional connectivity. Hum Brain Mapp 33(5):1052–1061
Mueller K, Anwander A, Möller HE et al (2011) Sex-dependent influences of obesity on cerebral white matter investigated by diffusion-tensor imaging. PLoS One 1–30
Speliotes EK, Willer CJ, Berndt SI et al (2010) Association analyses of 249,796 individuals reveal 18 new loci associated with body mass index. Nat Genet 42(11):937–948
Stanek KM, Grieve SM, Brickman AM et al (2011) Obesity is associated with reduced white matter integrity in otherwise healthy adults. Obesity (Silver Spring) 19(3):500–504
Stice E, Yokum, S, Blum K, Bohon C (2010) Weight gain is associated with reduced striatal response to palatable food. J Neurosci 30(39):13105–13109
Willer CJ, Speliotes EK, Loos RJF et al (2009) Six new loci associated with body mass index highlight a neuronal influence on body weight regulation. Nat Genet 41(1):25–34
Acknowledgments
This work of was supported by the IFB Adiposity Diseases, Federal Ministry of Education and Research (BMBF), Germany, FKZ: 01E01001 (http://www.bmbf.de) and the German Research Foundation (DFG) (http://www.dfg.de), within the framework of the CRC 1052 ‘Obesity Mechanisms’, projects A1 and A5.
Compliance with ethical guidelines
Conflict of interest. A. Horstmann and A. Villringer state that there are no conflicts of interest.
The accompanying manuscript does not include studies on humans or animals.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Horstmann, A., Villringer, A. The brain’s role in human obesity. e-Neuroforum 4, 79–84 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13295-013-0048-y
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13295-013-0048-y