Abstract
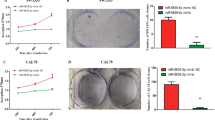
This study is aimed to investigate the role of microRNA-144 (miR-144) in osteosarcoma cell line F5M2 proliferation, apoptosis, invasion, and metastasis. Between 2007 and 2014, 66 cases of osteosarcoma samples in the corresponding adjacent normal tissue samples were selected from surgical resection or biopsy in the Department of Orthopedics, Shengjing Hospital, China Medical University. MiR-144 levels and Ezrin messenger RNA (mRNA) levels in osteosarcoma and the adjacent bone tissues were detected, and clinical and pathological features were analyzed. Exogenous miR-144 was transfected into human osteosarcoma cell lines at two different concentrations (low and high), and the expression levels of miR-144 and Ezrin protein between highly metastatic osteosarcoma cells and lowly metastatic osteosarcoma cells were compared. Real-time polymerase chain reaction (RT-PCR) and Western blot were used for detecting the expression levels of miR-144 or Ezrin protein, respectively. Cell proliferation was measured by methylthiazol tetrazolium (MTT) assay. Cell invasion and migration was evaluated by Transwell assays. Finally, flow cytometry was employed to determine the cell apoptosis. MiR-144 expression in osteosarcoma tissue was significantly lower than that in the surrounding normal bone tissue (P < 0.001), while Ezrin mRNA expression in osteosarcoma tissue was significantly higher than that in the surrounding normal bone tissue (P < 0.001); correlation analysis showed a significant negative correlation between miR-144 and Ezrin mRNA levels (r = 0.982, P < 0.001). MiR-144 and Ezrin mRNA expressions were significantly related with cell metastasis (P < 0.05) but were not related with other clinical factors such as gender, age, tumor location, tumor size, Enneking staging, and Dahlin’s histological classification. The results of RT-PCR showed that the expression level of miR-144 in osteosarcoma cells increased after transfected with exogenous miR-144 mimics, and this increase positively correlated with the transfection concentration of miR-144 mimics. Furthermore, Western blotting revealed a significant and dose-dependent decrease in Ezrin protein levels in F5M2 cells transfected with miR-144. MTT and Transwell assays showed that the invasion and metastasis of F5M2 cells was significantly decreased following exogenous overexpression of miR-144. Our study supports the view that the miR-144 may regulate Ezrin protein expression by inhibiting the invasion and metastasis of osteosarcoma cells.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Yuan D, Liu B, Liu K, Zhu G, Dai Z, Xie Y. Overexpression of fibroblast activation protein and its clinical implications in patients with osteosarcoma. J Surg Oncol. 2013;108(3):157–62.
Sabatier R, Bouvier C, de Pinieux G, Sarran A, Brenot-Rossi I, Pedeutour F, et al. Low-grade extraskeletal osteosarcoma of the chest wall: case report and review of literature. BMC Cancer. 2010;10:645.
Wang Z, Cai H, Lin L, Tang M, Cai H. Upregulated expression of microRNA-214 is linked to tumor progression and adverse prognosis in pediatric osteosarcoma. Pediatr Blood Cancer. 2014;61(2):206–10.
Mu Y, Zhang H, Che L, Li K. Clinical significance of microRNA-183/Ezrin axis in judging the prognosis of patients with osteosarcoma. Med Oncol. 2014;31(2):821.
Jiang C, Chen H, Shao L, Dong Y. GRM4 gene polymorphism is associated with susceptibility and prognosis of osteosarcoma in a Chinese Han population. Med Oncol. 2014;31(7):50.
Ottaviani G, Jaffe N. The etiology of osteosarcoma. Cancer Treat Res. 2009;152:15–32.
Kourti M, Sidi V, Papakonstantinou E. Osteosarcoma in an adolescent previously treated for Hodgkin’s disease. Hippokratia. 2014;18(1):96.
Ottaviani G, Jaffe N. The epidemiology of osteosarcoma. Cancer Treat Res. 2009;152:3–13.
Duan Z, Choy E, Harmon D, Liu X, Susa M, Mankin H, et al. MicroRNA-199a-3p is downregulated in human osteosarcoma and regulates cell proliferation and migration. Mol Cancer Ther. 2011;10(8):1337–45.
Kobayashi E, Hornicek FJ, Duan Z. MicroRNA involvement in osteosarcoma. Sarcoma. 2012;2012:359739.
Fujii T, Yajima R, Hirakata T, Miyamoto T, Fujisawa T, Tsutsumi S, et al. Impact of the prognostic value of vascular invasion, but not lymphatic invasion, of the primary tumor in patients with breast cancer. Anticancer Res. 2014;34(3):1255–9.
Toledo SR, Oliveira ID, Okamoto OK, Zago MA, de Seixas Alves MT, Filho RJ, et al. Bone deposition, bone resorption, and osteosarcoma. J Orthop Res: Off Publ Orthop Res Soc. 2010;28(9):1142–8.
Lee JS, DuBois SG, Boscardin WJ, Wustrack RL, Goldsby RE. Secondary malignant neoplasms among children, adolescents, and young adults with osteosarcoma. Cancer. 2014;120(24):3987–93.
An J, Choi KP, Wells CA, Chen YP. Identifying co-regulating microRNA groups. J Bioinforma Comput Biol. 2010;8(1):99–115.
He C, Xiong J, Xu X, Lu W, Liu L, Xiao D, et al. Functional elucidation of MiR-34 in osteosarcoma cells and primary tumor samples. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2009;388(1):35–40.
Du TT, Fu YF, Dong M, Wang L, Fan HB, Chen Y, et al. Experimental validation and complexity of miRNA-mRNA target interaction during zebrafish primitive erythropoiesis. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2009;381(4):688–93.
Creighton CJ, Fountain MD, Yu Z, Nagaraja AK, Zhu H, Khan M, et al. Molecular profiling uncovers a p53-associated role for microRNA-31 in inhibiting the proliferation of serous ovarian carcinomas and other cancers. Cancer Res. 2010;70(5):1906–15.
Drusco A, Nuovo GJ, Zanesi N, Di Leva G, Pichiorri F, Volinia S, et al. MicroRNA profiles discriminate among colon cancer metastasis. PLoS One. 2014;9(6):e96670.
Guan H, Liang W, Xie Z, Li H, Liu J, Liu L, et al. Down-regulation of miR-144 promotes thyroid cancer cell invasion by targeting ZEB1 and ZEB2. Endocrine. 2014 Jun;27.
Zha W, Cao L, Shen Y, Huang M. Roles of Mir-144-ZFX pathway in growth regulation of non-small-cell lung cancer. PLoS One. 2013;8(9):e74175.
Kalimutho M, Del Vecchio BG, Di Cecilia S, Sileri P, Cretella M, Pallone F, et al. Differential expression of miR-144* as a novel fecal-based diagnostic marker for colorectal cancer. J Gastroenterol. 2011;46(12):1391–402.
Liu Y, Wang X, Jiang J, Cao Z, Yang B, Cheng X. Modulation of T cell cytokine production by miR-144* with elevated expression in patients with pulmonary tuberculosis. Mol Immunol. 2011;48(9–10):1084–90.
Andersson G, Wennersten C, Gaber A, Boman K, Nodin B, Uhlen M, et al. Reduced expression of ezrin in urothelial bladder cancer signifies more advanced tumours and an impaired survival: validatory study of two independent patient cohorts. BMC Urol. 2014;14:36.
Athanasopoulou A, Aroukatos P, Nakas D, Repanti M, Papadaki H, Bravou V. Decreased ezrin and paxillin expression in human urothelial bladder tumors correlate with tumor progression. Urol Oncol. 2013;31(6):836–42.
Ren L, Khanna C. Role of ezrin in osteosarcoma metastasis. Adv Exp Med Biol. 2014;804:181–201.
Zhao M, Huang J, Gui K, Xiong M, Cai G, Xu J, et al. The downregulation of mir-144 is associated with the growth and invasion of osteosarcoma cells through the regulation of TAGLN expression. Int J Mol Med. 2014;34(6):1565–72.
Enneking WF. A system of staging musculoskeletal neoplasms. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 1986;204:9–24.
Zhang C, Yao C, Li H, Wang G, He X. Serum levels of microRNA-133b and microRNA-206 expression predict prognosis in patients with osteosarcoma. Int J Clin Exp Pathol. 2014;7(7):4194–203.
Han K, Zhao T, Chen X, Bian N, Yang T, Ma Q, et al. MicroRNA-194 suppresses osteosarcoma cell proliferation and metastasis in vitro and in vivo by targeting CDH2 and IGF1R. Int J Oncol. 2014;45(4):1437–49.
Zhou X, Wei M, Wang W. MicroRNA-340 suppresses osteosarcoma tumor growth and metastasis by directly targeting ROCK1. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2013;437(4):653–8.
Yan K, Gao J, Yang T, Ma Q, Qiu X, Fan Q, et al. MicroRNA-34a inhibits the proliferation and metastasis of osteosarcoma cells both in vitro and in vivo. PLoS One. 2012;7(3):e33778.
Botter SM, Neri D, Fuchs B. Recent advances in osteosarcoma. Curr Opin Pharmacol. 2014;16:15–23.
Won KY, Kim YW, Kim HS, Lee SK, Jung WW, Park YK. MicroRNA-199b-5p is involved in the Notch signaling pathway in osteosarcoma. Hum Pathol. 2013;44(8):1648–55.
Song B, Wang Y, Titmus MA, Botchkina G, Formentini A, Kornmann M, et al. Molecular mechanism of chemoresistance by mir-215 in osteosarcoma and colon cancer cells. Mol Cancer. 2010;9:96.
Ziyan W, Shuhua Y, Xiufang W, Xiaoyun L. MicroRNA-21 is involved in osteosarcoma cell invasion and migration. Med Oncol. 2011;28(4):1469–74.
Zhao H, Guo M, Zhao G, Ma Q, Ma B, Qiu X, et al. MiR-183 inhibits the metastasis of osteosarcoma via downregulation of the expression of Ezrin in F5M2 cells. Int J Mol Med. 2012;30(5):1013–20.
Zhang J, Zuo J, Lei M, Wu S, Zang X, Zhang C. Ezrin promotes invasion and migration of the MG63 osteosarcoma cell. Chin Med J. 2014;127(10):1954–9.
Zhu J, Feng Y, Ke Z, Yang Z, Zhou J, Huang X, et al. Down-regulation of miR-183 promotes migration and invasion of osteosarcoma by targeting Ezrin. Am J Pathol. 2012;180(6):2440–51.
Bulut G, Hong SH, Chen K, Beauchamp EM, Rahim S, Kosturko GW, et al. Small molecule inhibitors of ezrin inhibit the invasive phenotype of osteosarcoma cells. Oncogene. 2012;31(3):269–81.
Rodriguez-Pinilla SM, Sanchez ME, Rodriguez J, Garcia JF, Sanchez-Espiridion B, Lamana LF, et al. Loss of TCR-beta F1 and/or EZRIN expression is associated with unfavorable prognosis in nodal peripheral T-cell lymphomas. Blood Cancer J. 2013;3:e111.
Wang JW, Peng SY, Li JT, Wang Y, Zhang ZP, Cheng Y, et al. Identification of metastasis-associated proteins involved in gallbladder carcinoma metastasis by proteomic analysis and functional exploration of chloride intracellular channel 1. Cancer Lett. 2009;281(1):71–81.
Ferrari S, Zanella L, Alberghini M, Palmerini E, Staals E, Bacchini P. Prognostic significance of immunohistochemical expression of ezrin in non-metastatic high-grade osteosarcoma. Pediatr Blood Cancer. 2008;50(4):752–6.
Lam EK, Wang X, Shin VY, Zhang S, Morrison H, Sun J, et al. A microRNA contribution to aberrant Ras activation in gastric cancer. Am J Transl Res. 2011;3(2):209–18.
Acknowledgments
We would like to acknowledge the reviewers for their helpful comments on this paper.
Conflicts of interest
None
Authors’ contributions
SQ Cui designed, conceived, and supervised the study; performed the examination and the analysis; interpreted the results; and revised the paper. H Wang conceived and supervised the study, performed the statistical analysis, interpreted the results, and drafted the paper. All authors read and approved the final paper.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Cui, SQ., Wang, H. MicroRNA-144 inhibits the proliferation, apoptosis, invasion, and migration of osteosarcoma cell line F5M2. Tumor Biol. 36, 6949–6958 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13277-015-3396-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13277-015-3396-0