Abstract
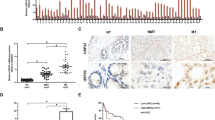
The paper was aimed to detect the expression of Skp2, p27kip1 (p27), and p-p27 (Thr187) in patients with cholangiocarcinoma (CCA). Western blot and immunohistochemistry were used to analyze the expression and subcellular localization of p27, Skp2, and p-p27 (Thr187) in tissue specimens of 53 patients with CCA and 10 with chronic proliferative cholangitis (CPC). Besides, the relationships of p27, Skp2, and p-p27 (Thr187) with clinicopathologic findings were examined, followed by analysis of the relationships of p27 expression with p-p27 (Thr187) and Skp2 in CCA tissue. The expression of p27 was lower in CCA than CPC tissue, and the expression of Skp2 and p-p27 (Thr187) was higher in CCA than CPC tissue (P < 0.05). The positive p27 and Skp2 proteins were mainly expressed in nucleus and cytoplasm of CCA, and p-p27 (Thr187) was only observed in nucleus. The expression of p27, Skp2, and p-p27 (Thr187) was closely associated with tumor grade and TNM stage (P < 0.05). A significantly negative correlation between the expression of p27 and Skp2 (r = −0.480, P < 0.05) and between the expression of p27 and p-p27 (Thr187) (r = −0.387, P < 0.05) was observed. Skp2-dependent proteasomal degradation of p27 plays role in the malignant transformation of CCA. Besides, the expression of p27, Skp2, and p-p27 (Thr187) may serve as markers for the progression of CCA.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Demols A, Marechal R, Deviere J, Van Laethem JL. The multidisciplinary management of gastrointestinal cancer. Biliary tract cancers: from pathogenesis to endoscopic treatment. Best Pract Res Clin Gastroenterol. 2007;21:1015–29.
Friman S. Cholangiocarcinoma—current treatment options. Scand J Surg. 2011;100:30–4.
Mosconi S, Beretta GD, Labianca R, Zampino MG, Gatta G, Heinemann V. Cholangiocarcinoma. Crit Rev Oncol Hematol. 2009;69:259–70.
Shen D-Y, Zhan Y-H, Wang Q-M, Rui G, Zhang Z-M. Oncogenic potential of cyclin kinase subunit-2 in cholangiocarcinoma. Liver Int. 2013;33:137–48.
Jarnagin WR, Klimstra DS, Hezel M, Gonen M, Fong Y, Roggin K, et al. Differential cell cycle-regulatory protein expression in biliary tract adenocarcinoma: correlation with anatomic site, pathologic variables, and clinical outcome. J Clin Oncol. 2006;24:1152–60.
Tsvetkov LM, Yeh KH, Lee SJ, Sun H, Zhang H. p27(Kip1) ubiquitination and degradation is regulated by the SCF(Skp2) complex through phosphorylated Thr187 in p27. Curr Biol. 1999;9:661–4.
Lloyd RV, Erickson LA, Jin L, Kulig E, Qian X, Cheville JC, et al. p27kip1: a multifunctional cyclin-dependent kinase inhibitor with prognostic significance in human cancers. Am J Pathol. 1999;154:313–23.
Hashimoto N, Yachida S, Okano K, Wakabayashi H, Imaida K, Kurokohchi K, et al. Immunohistochemically detected expression of p27(Kip1) and Skp2 predicts survival in patients with intrahepatic cholangiocarcinomas. Ann Surg Oncol. 2009;16:395–403.
Li SH, Li CF, Sung MT, Eng HL, Hsiung CY, Huang WW, et al. Skp2 is an independent prognosticator of gallbladder carcinoma among p27(Kip1)-interacting cell cycle regulators: an immunohistochemical study of 62 cases by tissue microarray. Mod Pathol. 2007;20:497–507.
Taguchi K, Aishima S, Asayama Y, Kajiyama K, Kinukawa N, Shimada M, et al. The role of p27kip1 protein expression on the biological behavior of intrahepatic cholangiocarcinoma. Hepatology. 2001;33:1118–23.
Jang JY, Kim SW, Park DJ, Ahn YJ, Yoon YS, Choi MG, et al. Actual long-term outcome of extrahepatic bile duct cancer after surgical resection. Ann Surg. 2005;241:77–84.
Ganeshan D. Extrahepatic biliary cancer: new staging classification. World J Radiol. 2012;4:345.
Shapira MA, Ben-Izhak O, Linn S, Futerman B, Minkov I, Hershko DD. The prognostic impact of the ubiquitin ligase subunits Skp2 and Cks1 in colorectal carcinoma. Cancer. 2005;103:1336–46.
Shapira MA, Ben-Izhak O, Slotky M, Goldin O, Lahav-Baratz S, Hershko DD. Expression of the ubiquitin ligase subunit cyclin kinase subunit 1 and its relationship to s-phase kinase protein 2 and p27Kip1 in prostate cancer. J Urol. 2006;176:2285–9.
Traub F, Mengel M, Lück HJ, Kreipe HH, Von Wasielewski R. Prognostic impact of Skp2 and p27 in human breast cancer. Breast Cancer Res Treat. 2006;99:185–91.
Pavlides SC, Huang KT, Reid DA, Wu L, Blank SV, Mittal K, et al. Inhibitors of SCF-Skp2/Cks1 E3 ligase block estrogen-induced growth stimulation and degradation of nuclear p27kip1: therapeutic potential for endometrial cancer. Endocrinology. 2013.
Wen S, So Y, Singh K, Slingerland JM, Resnick MB, Zhang S, et al. Promotion of cytoplasmic mislocalization of p27 by Helicobacter pylori in gastric cancer. Oncogene. 2012;31:1771–80.
Liu Z, Fu Q, Lv J, Wang F, Ding K. Prognostic implication of p27Kip1, Skp2 and Cks1 expression in renal cell carcinoma: a tissue microarray study. J Exp Clin Cancer Res. 2008;27:1–8.
Carracedo DG, Astudillo A, Rodrigo JP, Suarez C, Gonzalez MV. Skp2, p27kip1 and EGFR assessment in head and neck squamous cell carcinoma: prognostic implications. Oncol Rep. 2008;20:589–95.
Zhang JJ, Zhao GQ, Lin H, Yang X, Lin J. The expression and meaning of Skp2, p27, PTEN proteins in non-Hodgkin B-cell lymphoma of ocular adnexa. Zhonghua Yan Ke Za Zhi. 2012;48:1107–12.
Seki R, Ohshima K, Okamura T. Prognostic significance of Skp2 and p27(kip) in diffuse large B cell lymphoma. Rinsho Ketsueki. 2010;51:1741–7.
Chen Q, Xie W, Kuhn DJ, Voorhees PM, Lopez-Girona A, Mendy D, et al. Targeting the p27 E3 ligase SCF(Skp2) results in p27- and Skp2-mediated cell-cycle arrest and activation of autophagy. Blood. 2008;111:4690–9.
Miranda-Carboni GA, Krum SA, Yee K, Nava M, Deng QE, Pervin S, et al. A functional link between Wnt signaling and SKP2-independent p27 turnover in mammary tumors. Genes Dev. 2008;22:3121–34.
Kotoshiba S, Gopinathan L, Pfeiffenberger E, Rahim A, Vardy LA, Nakayama K, et al. p27 is regulated independently of Skp2 in the absence of Cdk2. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1843;2014:436–45.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Luo, J., Zhou, Y., Wang, B. et al. Immunohistochemically detected expression of Skp2, p27kip1, and p-p27 (Thr187) in patients with cholangiocarcinoma. Tumor Biol. 36, 5119–5125 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13277-015-3164-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13277-015-3164-1