Summary
Purpose
The cell cycle is controlled by cyclin-dependent kinases and one of the key players is the cyclin-dependent kinase inhibitor p27. The F-box protein Skp2 is a regulator of G1-S transition and promotes specifically the ubiquitin-mediated proteolysis of p27 via the proteasome pathway. In breast carcinomas, overexpression of Skp2 has been implicated in cell transformation and oncogenesis, but no data are available on the association of Skp2 and p27. The purpose was to evaluate the prevalence of Skp2 and p27 expression and determine whether a combined index has prognostic power in breast carcinomas.
Experimental design
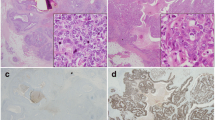
Three hundred and thirty-eight breast cancer specimens were analyzed for Skp2 and p27 expression by immunohistochemistry. Results were compared with classical histopathological criteria as well as other prognostic markers (ER, PR, HER2, p53, Ki-67) and correlated with the clinical outcome.
Results
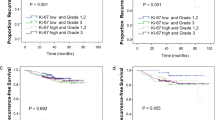
Thirty-four percent of breast cancers analyzed showed both a high expression for Skp2 and a low expression for p27. In univariate Kaplan–Meier analysis, this combination was found to be significantly associated with a worse clinical course (p<0.0001). Including staging, grading and the other tested marker, the Skp2/p27 index proved to be of prognostic relevance in multivariate analysis.
Conclusions
The combined assessment of Skp2 and p27 identifies aggressive breast cancer. In long-term follow-up, high Skp2 and low p27 indicate an unfavorable course. Beyond the prognostic importance of the Skp2/p27 index, it could serve as a predictive marker for new molecular targeted therapies aiming at Skp2.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Singletary SE, Allred C, Ashley P, Bassett LW, Berry D, Bland KI, Borgen PI, Clark GM, Edge SB, Hayes DF, Hughes LL, Hutter RV, Morrow M, Page DL, Recht A, Theriault RL, Thor A, Weaver DL, Wieand HS, Greene FL., Staging system for breast cancer: revisions for the 6th edition of the AJCC Cancer Staging Manual Surg Clin North Am 83: 803–819, 2003
Bast RC Jr, Ravdin P, Hayes DF, Bates S, Fritsche H Jr, Jessup JM, Kemeny N, Locker GY, Mennel RG, Somerfield MR, 2000 Update of recommendations for the use of tumor markers in breast and colorectal cancer: clinical practice guidelines of the American society of clinical oncology J Clin Oncol 19: 1865–1878, 2001
Bryant J, Fisher B, Gunduz N, Costantino JP, Emir B, S-phase fraction combined with other patient and tumor characteristics for the prognosis of node-negative, estrogen-receptor-positive breast cancer Breast Cancer Res Treat 51: 239–253, 1998
Henderson IC, Patek AJ, The relationship between prognostic and predictive factors in the management of breast cancer Breast Cancer Res Treat 52: 261–288, 1998
Paik S, Shak S, Tang G, Kim C, Baker J, Cronin M, Baehner FL, Walker MG, Watson D, Park T, Hiller W, Fisher ER, Wickerham DL, Bryant J, Wolmark N, A multigene assay to predict recurrence of tamoxifen-treated, node-negative breast cancer N Engl J Med 351: 2817–2826, 2004
Eifel P, Axelson JA, Costa J, Crowley J, Curran WJ Jr, Deshler A, Fulton S, Hendricks CB, Kemeny M, Kornblith AB, Louis TA, Markman M, Mayer R, Roter D, National Institutes of Health Consensus Development Conference Statement: adjuvant therapy for breast cancer, November 1–3, 2000 J Natl Cancer Inst 93: 979–989, 2001
Clinical practice guidelines for the use of tumor markers in breast and colorectal cancer. Adopted on May 17, 1996 by the American Society of Clinical Oncology. J Clin Oncol 14: 2843–2877, 1996
Keyomarsi K, Tucker SL, Buchholz TA, Callister M, Ding Y, Hortobagyi GN, Bedrosian I, Knickerbocker C, Toyofuku W, Lowe M, Herliczek TW, Bacus SS, Cyclin E and survival in patients with breast cancer N Engl J Med 347: 1566–1575, 2002
Bloom J, Pagano M, Deregulated degradation of the CDK inhibitor p27 and malignant transformation Semin Cancer Biol 13: 41–47, 2003
Katayose Y, Kim M, Rakkar AN, Li Z, Cowan KH, Seth P, Promoting apoptosis: a novel activity associated with the cyclin-dependent kinase inhibitor p27 Cancer Res 57: 5441–5445, 1997
Levkau B, Koyama H, Raines EW, Clurman BE, Herren B, Orth K, Roberts JM, Ross R, Cleavage of p21Cip1/Waf1 and p27Kip1 mediates apoptosis in endothelial cells through activation of Cdk2: role of a caspase cascade Mol Cell 1: 553–563, 1998
St Croix B, Florenes VA, Rak JW, Flanagan M, Bhattacharya N, Slingerland JM, Kerbel RS, Impact of the cyclin-dependent kinase inhibitor p27Kip1 on resistance of tumor cells to anticancer agents Nat Med 2: 1204–1210, 1996
Pagano M, Tam SW, Theodoras AM, Beer-Romero P, Del Sal G, Chau V, Yew PR, Draetta GF, Rolfe M, Role of the ubiquitin–proteasome pathway in regulating abundance of the cyclin-dependent kinase inhibitor p27 Science 269: 682–685, 1995
Loda M, Cukor B, Tam SW, Lavin P, Fiorentino M, Draetta GF, Jessup JM, Pagano M, Increased proteasome-dependent degradation of the cyclin-dependent kinase inhibitor p27 in aggressive colorectal carcinomas Nat Med 3: 231–234, 1997
Kossatz U, Dietrich N, Zender L, Buer J, Manns MP, Malek NP, Skp2-dependent degradation of p27kip1 is essential for cell cycle progression Genes Dev 18: 2602–2607, 2004
Fang S, Lorick KL, Jensen JP, Weissman AM, RING finger ubiquitin protein ligases: implications for tumorigenesis, metastasis and for molecular targets in cancer Semin Cancer Biol 13: 5–14, 2003
Ciechanover A, Protein degradation in tumor development. Introduction and overview Semin Cancer Biol 13: 1–4, 2003
Arteaga CL, Cdk inhibitor p27Kip1 and hormone dependence in breast cancer Clin Cancer Res 10: 368S–371S, 2004
Mengel M, Kreipe HH, von Wasielewski R, Rapid and large-scale transition of new tumor biomarkers to clinical biopsy material by innovative tissue microarray systems Appl Immunohistochem Mol Morphol 11: 261–268, 2003
Nocito A, Kononen J, Kallioniemi OP, Sauter G, Tissue microarrays (TMAs) for high-throughput molecular pathology research Int J Cancer 94: 1–5, 2001
Nocito A, Bubendorf L, Tinner EM, Suess K, Wagner U, Forster T, Kononen J, Fijan A, Bruderer J, Schmid U, Ackermann D, Maurer R, Alund G, Knonagel H, Rist M, Anabitarte M, Hering F, Hardmeier T, Schoenenberger AJ, Flury R, Jager P, Fehr JL, Schraml P, Moch H, Mihatsch MJ, Gasser T, Sauter G, Microarrays of bladder cancer tissue are highly representative of proliferation index and histological grade J Pathol 194: 349–357, 2001
Remmele W, Stegner HE, Recommendation for uniform definition of an immunoreactive score (IRS) for immunohistochemical estrogen receptor detection (ER-ICA) in breast cancer tissue Pathologe 8: 138–140, 1987
Catzavelos C, Tsao MS, DeBoer G, Bhattacharya N, Shepherd FA, Slingerland JM, Reduced expression of the cell cycle inhibitor p27Kip1 in non-small cell lung carcinoma: a prognostic factor independent of Ras Cancer Res 59: 684–688, 1999
Lloyd RV, Erickson LA, Jin L, Kulig E, Qian X, Cheville JC, Scheithauer BW, p27kip1: a multifunctional cyclin-dependent kinase inhibitor with prognostic significance in human cancers Am J Pathol 154: 313–323, 1999
Guo Y, Sklar GN, Borkowski A, Kyprianou N, Loss of the cyclin-dependent kinase inhibitor p27(Kip1) protein in human prostate cancer correlates with tumor grade Clin Cancer Res 3: 2269–2274, 1997
Tsihlias J, Kapusta LR, DeBoer G, Morava-Protzner I, Zbieranowski I, Bhattacharya N, Catzavelos GC, Klotz LH, Slingerland JM, Loss of cyclin-dependent kinase inhibitor p27Kip1 is a novel prognostic factor in localized human prostate adenocarcinoma Cancer Res 58: 542–548, 1998
Barbareschi M, van Tinteren H, Mauri FA, Veronese S, Peterse H, Maisonneuve P, Caffo O, Scaioli M, Doglioni C, Galligioni E, Dalla Palma P, Michalides R, p27(kip1) expression in breast carcinomas: an immunohistochemical study on 512 patients with long-term follow-up Int J Cancer 89: 236–241, 2000
Volpi A, De Paola F, Nanni O, Granato AM, Bajorko P, Becciolini A, Scarpi E, Riccobon A, Balzi M, Amadori D, Prognostic significance of biologic markers in node-negative breast cancer patients: a prospective study Breast Cancer Res Treat 63: 181–192, 2000
Cariou S, Donovan JC, Flanagan WM, Milic A, Bhattacharya N, Slingerland JM, Down-regulation of p21WAF1/CIP1 or p27Kip1 abrogates antiestrogen-mediated cell cycle arrest in human breast cancer cells Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 97: 9042–9046, 2000
Signoretti S, Di Marcotullio L, Richardson A, Ramaswamy S, Isaac B, Rue M, Monti F, Loda M, Pagano M, Oncogenic role of the ubiquitin ligase subunit Skp2 in human breast cancer J Clin Invest 110: 633–641, 2002
Foster JS, Fernando RI, Ishida N, Nakayama KI, Wimalasena J, Estrogens down-regulate p27Kip1 in breast cancer cells through Skp2 and through nuclear export mediated by the ERK pathway J Biol Chem 278: 41355–41366, 2003
Sanada T, Yokoi S, Arii S, Yasui K, Imoto I, Inazawa J, Skp2 overexpression is a p27Kip1-independent predictor of poor prognosis in patients with biliary tract cancers Cancer Sci 95: 969–976, 2004
Knowles LM, Axelrod F, Browne CD, Smith JW, A fatty acid synthase blockade induces tumor cell-cycle arrest by down-regulating Skp2 J Biol Chem 279: 30540–30545, 2004
Orlowski RZ, Dees EC, The role of the ubiquitination–proteasome pathway in breast cancer: applying drugs that affect the ubiquitin-proteasome pathway to the therapy of breast cancer Breast Cancer Res 5: 1–7, 2003
Boccadoro M, Morgan G, Cavenagh J, Preclinical evaluation of the proteasome inhibitor bortezomib in cancer therapy Cancer Cell Int 5: 18, 2005
Mitchell BS, The proteasome – an emerging therapeutic target in cancer N Engl J Med 348: 2597–2598, 2003
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Traub, F., Mengel, M., Lück, H.J. et al. Prognostic impact of Skp2 and p27 in human breast cancer. Breast Cancer Res Treat 99, 185–191 (2006). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10549-006-9202-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10549-006-9202-3