Abstract
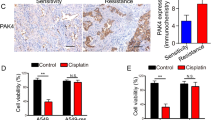
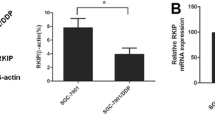
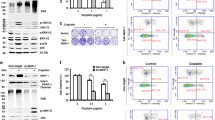
p21-Activated kinase 5 (PAK5) is the last identified member of the PAK family. The PAKs are highly conserved serine/threonine and effector proteins for Cdc42 and Rac and are essential in regulating cell motility and survival. Previous studies have demonstrated that PAK5 played a pivotal role in apoptosis, proliferation, cancer migration, and invasion. However, the biological function of PAK5 in hepatocellular carcinoma, as well as its underlying mechanism, still remains to be fully elucidated. In the present study, we demonstrated that PAK5 markedly inhibited cisplatin-induced apoptosis and promoted cell proliferation in hepatocellular carcinoma cells. Moreover, our results showed that overexpression of PAK5 contributed to cell cycle regulation. In order to elucidate the underlying mechanism of PAK5 on cisplatin-induced apoptosis and cell cycle regulation, we also examined the protein expressions of chk2 and p-chk2. In summary, our study investigated the role of PAK5 in cisplatin-induced cellular processes and provided evidence of its underlying mechanism.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Jaffer ZM, Chernoff J. p21-activated kinases: three more join the Pak. Int J Biochem Cell Biol. 2002;34(7):713–7.
Wen YY, Wang XX, Pei DS, Zheng JN. p21-Activated kinase 5: a pleiotropic kinase. Bioorg Med Chem Lett. 2013;23(24):6636–9. doi:10.1016/j.bmcl.2013.10.051.
Wang X, Gong W, Qing H, Geng Y, Wang X, Zhang Y, et al. P21-activated kinase 5 inhibits camptothecin-induced apoptosis in colorectal carcinoma cells. Tumour Biol. 2010;31(6):575–82. doi:10.1007/s13277-010-0071-3.
Pandey A, Dan I, Kristiansen TZ, Watanabe NM, Voldby J, Kajikawa E, et al. Cloning and characterization of PAK5, a novel member of mammalian p21-activated kinase-II subfamily that is predominantly expressed in brain. Oncogene. 2002;21(24):3939–48. doi:10.1038/sj.onc.1205478.
Dart AE, Wells CM. P21-activated kinase 4—not just one of the PAK. Eur J Cell Biol. 2013;92(4–5):129–38. doi:10.1016/j.ejcb.2013.03.002.
Dan C, Nath N, Liberto M, Minden A. PAK5, a new brain-specific kinase, promotes neurite outgrowth in N1E-115 cells. Mol Cell Biol. 2002;22(2):567–77.
Han ZX, Wang XX, Zhang SN, Wu JX, Qian HY, Wen YY, et al. Downregulation of PAK5 inhibits glioma cell migration and invasion potentially through the PAK5-Egr1-MMP2 signaling pathway. Brain Tumor Pathol. 2013. doi:10.1007/s10014-013-0161-1.
Gong W, An Z, Wang Y, Pan X, Fang W, Jiang B, et al. P21-activated kinase 5 is overexpressed during colorectal cancer progression and regulates colorectal carcinoma cell adhesion and migration. Int J Cancer. 2009;125(3):548–55. doi:10.1002/ijc.24428.
Dummler B, Ohshiro K, Kumar R, Field J. Pak protein kinases and their role in cancer. Cancer Metastasis Rev. 2009;28(1–2):51–63. doi:10.1007/s10555-008-9168-1.
Cotteret S, Jaffer ZM, Beeser A, Chernoff J. p21-Activated kinase 5 (Pak5) localizes to mitochondria and inhibits apoptosis by phosphorylating BAD. Mol Cell Biol. 2003;23(16):5526–39.
Wang XX, Cheng Q, Zhang SN, Qian HY, Wu JX, Tian H, et al. PAK5-Egr1-MMP2 signaling controls the migration and invasion in breast cancer cell. Tumour Biol. 2013;34(5):2721–9. doi:10.1007/s13277-013-0824-x.
Li D, Yao X, Zhang P. The overexpression of P21-activated kinase 5 (PAK5) promotes paclitaxel-chemoresistance of epithelial ovarian cancer. Mol Cell Biochem. 2013;383(1–2):191–9. doi:10.1007/s11010-013-1767-7.
D’Anzeo M, Faloppi L, Scartozzi M, Giampieri R, Bianconi M, Del Prete M, et al. The role of micro-RNAs in hepatocellular carcinoma: from molecular biology to treatment. Molecules. 2014;19(5):6393–406. doi:10.3390/molecules19056393.
Jemal A, Bray F, Center MM, Ferlay J, Ward E, Forman D. Global cancer statistics. CA Cancer J Clin. 2011;61(2):69–90. doi:10.3322/caac.20107.
Poon RT, Fan ST, Lo CM, Ng IO, Liu CL, Lam CM, et al. Improving survival results after resection of hepatocellular carcinoma: a prospective study of 377 patients over 10 years. Ann Surg. 2001;234(1):63–70.
Chen HH, Kuo MT. Role of glutathione in the regulation of Cisplatin resistance in cancer chemotherapy. Met Based Drugs. 2010. doi:10.1155/2010/430939.
Shuck SC, Short EA, Turchi JJ. Eukaryotic nucleotide excision repair: from understanding mechanisms to influencing biology. Cell Res. 2008;18(1):64–72. doi:10.1038/cr.2008.2.
Vitale I, Galluzzi L, Vivet S, Nanty L, Dessen P, Senovilla L, et al. Inhibition of Chk1 kills tetraploid tumor cells through a p53-dependent pathway. PLoS One. 2007;2(12):e1337. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0001337.
Brozovic A, Osmak M. Activation of mitogen-activated protein kinases by cisplatin and their role in cisplatin-resistance. Cancer Lett. 2007;251(1):1–16. doi:10.1016/j.canlet.2006.10.007.
Citri A, Yarden Y. EGF-ERBB signalling: towards the systems level. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 2006;7(7):505–16. doi:10.1038/nrm1962.
Li J, Wang Y, Song Y, Fu Z, Yu W. miR-27a regulates cisplatin resistance and metastasis by targeting RKIP in human lung adenocarcinoma cells. Mol Cancer. 2014;13(1):193. doi:10.1186/1476-4598-13-193.
Unal OU, Yilmaz AU, Yavuzsen T, Akman T, Ellidokuz H. Intra-peritoneal cisplatin combined with intravenous paclitaxel in optimally debulked stage 3 ovarian cancer patients: an Izmir Oncology Group study. Asian Pac J Cancer Prev. 2014;15(15):6165–9.
Liang X, Reed E, Yu JJ. Protein phosphatase 2A interacts with Chk2 and regulates phosphorylation at Thr-68 after cisplatin treatment of human ovarian cancer cells. Int J Mol Med. 2006;17(5):703–8.
Pabla N, Huang S, Mi QS, Daniel R, Dong Z. ATR-Chk2 signaling in p53 activation and DNA damage response during cisplatin-induced apoptosis. J Biol Chem. 2008;283(10):6572–83. doi:10.1074/jbc.M707568200.
Prestayko AW, D’Aoust JC, Issell BF, Crooke ST. Cisplatin (cis-diamminedichloroplatinum II). Cancer Treat Rev. 1979;6(1):17–39.
Galanski M. Recent developments in the field of anticancer platinum complexes. Recent patents on anti-cancer drug discovery. 2006;1(2):285–95.
Cotteret S, Chernoff J. Nucleocytoplasmic shuttling of Pak5 regulates its antiapoptotic properties. Mol Cell Biol. 2006;26(8):3215–30. doi:10.1128/MCB. 26.8.3215-3230.2006.
Fang ZP, Jiang BG, Gu XF, Zhao B, Ge RL, Zhang FB. P21-activated kinase 5 plays essential roles in the proliferation and tumorigenicity of human hepatocellular carcinoma. Acta Pharmacol Sin. 2014;35(1):82–8. doi:10.1038/aps.2013.31.
Gu J, Li K, Li M, Wu X, Zhang L, Ding Q, et al. A role for p21-activated kinase 7 in the development of gastric cancer. FEBS J. 2013;280(1):46–55. doi:10.1111/febs.12048.
Zcharia E, Atzmon R, Nagler A, Shimoni A, Peretz T, Vlodavsky I, et al. Inhibition of matrix metalloproteinase-2 by halofuginone is mediated by the Egr1 transcription factor. Anticancer Drugs. 2012;23(10):1022–31. doi:10.1097/CAD.0b013e328357d186.
Siddik ZH. Cisplatin: mode of cytotoxic action and molecular basis of resistance. Oncogene. 2003;22(47):7265–79. doi:10.1038/sj.onc.1206933.
Damia G, Filiberti L, Vikhanskaya F, Carrassa L, Taya Y, D’Incalci M, et al. Cisplatinum and taxol induce different patterns of p53 phosphorylation. Neoplasia. 2001;3(1):10–6. doi:10.1038/sj/neo/7900122.
Antoni L, Sodha N, Collins I, Garrett MD. CHK2 kinase: cancer susceptibility and cancer therapy - two sides of the same coin? Nat Rev Cancer. 2007;7(12):925–36. doi:10.1038/nrc2251.
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (No. 81372172) and the key project of the Education Department of China (212062) and the Science and Technology Department of Jiangsu Province (BK20130231, BK20141149).
Conflicts of interest
None
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Additional information
Ding-Guo Zhang and Jinling Zhang contributed equally to this work.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zhang, DG., Zhang, J., Mao, LL. et al. p21-Activated kinase 5 affects cisplatin-induced apoptosis and proliferation in hepatocellular carcinoma cells. Tumor Biol. 36, 3685–3691 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13277-014-3007-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13277-014-3007-5