Abstract
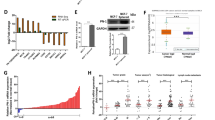
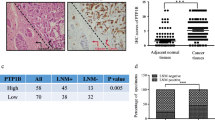
p21-activated kinases (PAKs) are activated by various extracellular stimuli and, in turn, activate other kinases by phosphorylating them at specific serine/threonine residues or through protein–protein interaction. As a recently identified member of the group B PAK family, the role of PAK5 in cancer is poorly understood. In this study, we investigated the effect of PAK5 on the malignant phenotype, such as proliferation, cell cycle, apoptosis, migration, and invasion. Cell growth assay and cell cycle analysis consistently showed that knockdown of PAK5 could significantly inhibit the proliferation of breast cancer cells. Wound healing assay. migration assay, and invasion assay showed that PAK5 promoted cell migration. Furthermore, in order to elucidate the underlying mechanism of PAK5 on cellular growth and migration, we examined the protein expressions of cyclin D1, p21, early growth response protein 1 (Egr1), and matrix metalloproteinase 2 (MMP2). Our work further reveals the PAK5-Egr1-MMP2 signaling pathway to be a critical regulator of cell migration and invasion. These results suggest that PAK5 may be a potential therapeutic target for breast cancer.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Duffy MJ. Biochemical markers in breast cancer: which ones are clinically useful? Clin Biochem. 2001;34:347–52.
DeSantis C, Siegel R, Bandi P, Jemal A. Breast cancer statistics, 2011. CA Cancer J Clin. 2011;61:409–18.
Sells MA, Knaus UG, Bagrodia S, Ambrose DM, Bokoch GM, Chernoff J. Human p21-activated kinase (Pak1) regulates actin organization in mammalian cells. Curr Biol. 1997;7:202–10.
Ridley AJ, Schwartz MA, Burridge K, Firtel RA, Ginsberg MH, Borisy G, et al. Cell migration: integrating signals from front to back. Science. 2003;302:1704–9.
Sells MA, Boyd JT, Chernoff J. P21-activated kinase 1 (PAK1) regulates cell motility in mammalian fibroblasts. J Cell Biol. 1999;145:837–49.
Jaffer ZM, Chernoff J. P21-activated kinases: three more join the Pak. Int J Biochem Cell Biol. 2002;34:713–7.
Dutartre H, Davoust J, Gorvel JP, Chavrier P. Cytokinesis arrest and redistribution of actin-cytoskeleton regulatory components in cells expressing the Rho GTPase CDC42HS. J Cell Sci. 1996;109(Pt 2):367–77.
Li X, Minden A. Targeted disruption of the gene for the PAK5 kinase in mice. Mol Cell Biol. 2003;23:7134–42.
Gong W, An Z, Wang Y, Pan X, Fang W, Jiang B, et al. P21-activated kinase 5 is overexpressed during colorectal cancer progression and regulates colorectal carcinoma cell adhesion and migration. Int J Cancer. 2009;125:548–55.
Cotteret S, Jaffer ZM, Beeser A, Chernoff J. p21-Activated kinase 5 (Pak5) localizes to mitochondria and inhibits apoptosis by phosphorylating BAD. Mol Cell Biol. 2003;23:5526–39.
Hangen E, Blomgren K, Benit P, Kroemer G, Modjtahedi N. Life with or without AIF. Trends Biochem Sci. 2010;35:278–87.
Zhang H, Li Z, Viklund EK, Stromblad S. P21-activated kinase 4 interacts with integrin alpha v beta 5 and regulates alpha v beta 5-mediated cell migration. J Cell Biol. 2002;158:1287–97.
Thiel G, Cibelli G. Regulation of life and death by the zinc finger transcription factor Egr-1. J Cell Physiol. 2002;193:287–92.
Zcharia E, Atzmon R, Nagler A, Shimoni A, Peretz T, Vlodavsky I. Inhibition of matrix metalloproteinase-2 by halofuginone is mediated by the Egr1 transcription factor. Anticancer Drugs. 2012;23:1022–31.
Timm T, Matenia D, Li XY, Griesshaber B, Mandelkow EM. Signaling from MARK to tau: regulation, cytoskeletal crosstalk, and pathological phosphorylation. Neurodegener Dis. 2006;3:207–17.
Callow MG, Clairvoyant F, Zhu S, Schryver B, Whyte DB, Bischoff JR, et al. Requirement for PAK4 in the anchorage-independent growth of human cancer cell lines. J Biol Chem. 2002;277:550–8.
Lee SR, Ramos SM, Ko A, Masiello D, Swanson KD, Lu ML, et al. AR and ER interaction with a p21-activated kinase (PAK6). Mol Endocrinol. 2002;16:85–99.
Yang F, Li X, Sharma M, Zarnegar M, Lim B, Sun Z. Androgen receptor specifically interacts with a novel p21-activated kinase, PAK6. J Biol Chem. 2001;276:15345–53.
Pandey A, Dan I, Kristiansen TZ, Watanabe NM, Voldby J, Kajikawa E, et al. Cloning and characterization of PAK5, a novel member of mammalian p21-activated kinase-II subfamily that is predominantly expressed in brain. Oncogene. 2002;21:3939–48.
Tsang CM, Yip YL, Lo KW, Deng W, To KF, Hau PM, et al. Cyclin D1 overexpression supports stable EBV infection in nasopharyngeal epithelial cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2012;109:E3473–82.
Ferraz C, Lorenz S, Wojtas B, Bornstein SR, Paschke R, Eszlinger M. Inverse correlation of miRNA and cell cycle-associated genes suggests influence of miRNA on benign thyroid nodule tumorigenesis. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2013;98:E8–16.
Zhuo W, Zhang L, Wang Y, Zhu B, Chen Z. Cyclin D1 G870A polymorphism is a risk factor for esophageal cancer among Asians. Cancer Invest. 2012;30:630–6.
Vizkeleti L, Ecsedi S, Rakosy Z, Orosz A, Lazar V, Emri G, et al. The role of CCND1 alterations during the progression of cutaneous malignant melanoma. Tumour Biol. 2012;33:2189–99.
Lee MH, Yang HY. Regulators of G1 cyclin-dependent kinases and cancers. Cancer Metastasis Rev. 2003;22:435–49.
Wang X, Gong W, Qing H, Geng Y, Zhang Y, Peng L, et al. p21-activated kinase 5 inhibits camptothecin-induced apoptosis in colorectal carcinoma cells. Tumour Biol. 2010;31:575–82.
Guo Y, Srinivasula SM, Druilhe A, Fernandes-Alnemri T, Alnemri ES. Caspase-2 induces apoptosis by releasing proapoptotic proteins from mitochondria. J Biol Chem. 2002;277:13430–7.
Srinivasula SM, Ahmad M, Fernandes-Alnemri T, Litwack G, Alnemri ES. Molecular ordering of the Fas-apoptotic pathway: the Fas/APO-1 protease Mch5 is a CrmA-inhibitable protease that activates multiple Ced-3/ICE-like cysteine proteases. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1996;93:14486–91.
Dan C, Nath N, Liberto M, Minden A. PAK5, a new brain-specific kinase, promotes neurite outgrowth in N1E-115 cells. Mol Cell Biol. 2002;22:567–77.
Matenia D, Griesshaber B, Li XY, Thiessen A, Johne C, Jiao J, et al. PAK5 kinase is an inhibitor of MARK/Par-1, which leads to stable microtubules and dynamic actin. Mol Biol Cell. 2005;16:4410–22.
Rosenberg GA. Matrix metalloproteinases in brain injury. J Neurotrauma. 1995;12:833–42.
Ray JM, Stetler-Stevenson WG. The role of matrix metalloproteases and their inhibitors in tumour invasion, metastasis and angiogenesis. Eur Respir J. 1994;7:2062–72.
Stetler-Stevenson WG. Type IV collagenases in tumor invasion and metastasis. Cancer Metastasis Rev. 1990;9:289–303.
Woessner Jr JF, Gunja-Smith Z. Role of metalloproteinases in human osteoarthritis. J Rheumatol Suppl. 1991;27:99–101.
Chambers AF, Matrisian LM. Changing views of the role of matrix metalloproteinases in metastasis. J Natl Cancer Inst. 1997;89:1260–70.
Komatsu K, Nakanishi Y, Nemoto N, Hori T, Sawada T, Kobayashi M. Expression and quantitative analysis of matrix metalloproteinase-2 and −9 in human gliomas. Brain Tumor Pathol. 2004;21:105–12.
Wang M, Wang T, Liu S, Yoshida D, Teramoto A. The expression of matrix metalloproteinase-2 and −9 in human gliomas of different pathological grades. Brain Tumor Pathol. 2003;20:65–72.
Acknowledgments
This project is supported by grants from the key project of the Education Department of China (212062) and the Program for New Century Excellent Talents in University (NCET-08-0700).
Conflicts of interest
None
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Additional information
Xiao-Xia Wang, Qian Cheng, and Shang-Nuan Zhang contributed equally to this paper.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wang, XX., Cheng, Q., Zhang, SN. et al. PAK5-Egr1-MMP2 signaling controls the migration and invasion in breast cancer cell. Tumor Biol. 34, 2721–2729 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13277-013-0824-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13277-013-0824-x