Abstract
Background
Nasopharyngeal carcinoma (NPC) is the most common head and neck tumor in China. Forkhead box (FOX) proteins have 19 subfamilies, which can maintain cell metabolism, regulate cell cycle and cell growth, etc. FOXK1 is a member of the FOX family, and studies have found that FOXK1 is closely related to tumors.
Objective
This experiment aims to study the effects of FOXK1 interference on proliferation, apoptosis, invasion, epithelial-mesenchymal transition (EMT), and radiosensitivity, by regulating the Janus kinas/signal translator and activator of the transfer 3 (JAK/STAT3) pathway.
Methods
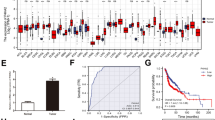
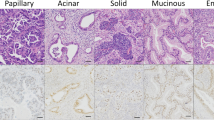
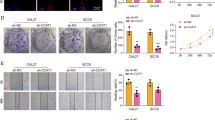
The expression of FOXK1 was detected via immunohistochemistry using clinical nasopharyngeal carcinoma tissues and adjacent tissues. The relationship between FOXK1 expression and tumor stage was subsequently evaluated. The colony formation rate was calculated through the colony formation experiment. Cell apoptosis and cell cycle distribution were detected using flow cytometry, while cell invasion was detected using the Transwell method. The number of cells in the nucleus of each group after 30 min, 4 h, and 24 h of radiotherapy with the 2 Gy dose was counted using immunofluorescence under γ-H2AX focal points of a laser confocal microscope.
Results
FOXK1 is clearly expressed in the patients’ cancer tissues. The expression of FOXK1 was significantly correlated with the patient’s sex. FOXK1 interference or Peficitinib can upregulate the apoptosis rate of 5-8 F and CNE-2 cells; increase the G2 phase of cells; and inhibit the invasion, migration, and EMT of cells. At the same time, FOXK1 interference can downregulate the protein expression of p-JAK1, p-JAK2, and p-STAT3 in cells. Interference from FOXK1 or Peficitinib alone can reduce the rate of cell colony formation under different radiation doses, and enhance the green fluorescence intensity of γ-H2AX in the nucleus after 4 and 24 h of the 2 Gy dose of radiotherapy. These results are optimal when FOXK1 interference and Peficitinib are used together.
Conclusion
FOXK1 interference in NPC cells can regulate EMT through the JAK/STAT3 signal pathway, enhance the radiosensitivity of cells, and thus inhibit tumor cell progression.








Similar content being viewed by others
Data Availability
The data used to support the findings of this study are available from the corresponding author upon request.
References
Al Zaid Siddiquee K, Turkson J (2008) STAT3 as a target for inducing apoptosis in solid and hematological tumors. Cell Res 18(2):254–267. https://doi.org/10.1038/cr.2008.18
Chen D, Wang K, Li X, Jiang M, Ni L, Xu B, Chu Y, Wang W, Wang H, Kang H et al (2017a) FOXK1 plays an oncogenic role in the development of esophageal cancer. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 494(1–2):88–94. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bbrc.2017a.10.080
Chen F, Xiong W, Dou K, Ran Q (2017b) Knockdown of FOXK1 suppresses proliferation, Migration, and Invasion in prostate Cancer cells. Oncol Res 25(8):1261–1267. https://doi.org/10.3727/096504017x14871164924588
Chen YP, Chan ATC, Le QT, Blanchard P, Sun Y, Ma J (2019) Nasopharyngeal carcinoma. Lancet 394(10192):64–80. https://doi.org/10.1016/s0140-6736(19)30956-0
Chua ML, Sun Y, Supiot S (2019) Advances in nasopharyngeal carcinoma-“West meets East. Br J Radiol 92(1102):20199004. https://doi.org/10.1259/bjr.20199004
Emori T, Kasahara M, Sugahara S, Hashimoto M, Ito H, Narumiya S, Higashi Y, Fujii Y (2020) Role of JAK-STAT signaling in the pathogenic behavior of fibroblast-like synoviocytes in rheumatoid arthritis: Effect of the novel JAK inhibitor peficitinib. Eur J Pharmacol 882:173238. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ejphar.2020.173238
Gao Y, Li W, Liu R, Guo Q, Li J, Bao Y, Zheng H, Jiang S, Hua B (2017) Norcantharidin inhibits IL-6-induced epithelial–mesenchymal transition via the JAK2/STAT3/TWIST signaling pathway in hepatocellular carcinoma cells. Oncol Rep 38(2):1224–1232. https://doi.org/10.3892/or.2017.5775
Grant GD, Gamsby J, Martyanov V, Brooks L 3rd, George LK, Mahoney JM, Loros JJ, Dunlap JC, Whitfield ML (2012) Live-cell monitoring of periodic gene expression in synchronous human cells identifies forkhead genes involved in cell cycle control. Mol Biol Cell 23(16):3079–3093. https://doi.org/10.1091/mbc.E11-02-0170
Guo Z, Wang YH, Xu H, Yuan CS, Zhou HH, Huang WH, Wang H, Zhang W (2021) LncRNA linc00312 suppresses radiotherapy resistance by targeting DNA-PKcs and impairing DNA damage repair in nasopharyngeal carcinoma. Cell Death Dis 12(1):69. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41419-020-03302-2
Hu C, Zhuang W, Qiao Y, Liu B, Liu L, Hui K, Jiang X (2019) Effects of combined inhibition of STAT3 and VEGFR2 pathways on the radiosensitivity of non-small-cell lung cancer cells. Onco Targets Ther 12:933–944. https://doi.org/10.2147/ott.S186559
Lee AWM, Ng WT, Chan JYW, Corry J, Mäkitie A, Mendenhall WM, Rinaldo A, Rodrigo JP, Saba NF, Strojan P et al (2019) Management of locally recurrent nasopharyngeal carcinoma. Cancer Treat Rev 79:101890. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ctrv.2019.101890
Li F, Zhao X, Sun R, Ou J, Huang J, Yang N, Xu T, Li J, He X, Li C et al (2020) EGFR-rich extracellular vesicles derived from highly metastatic nasopharyngeal carcinoma cells accelerate tumour metastasis through PI3K/AKT pathway-suppressed ROS. J Extracell Vesicles 10(1):e12003. https://doi.org/10.1002/jev2.12003
Li L, Gong M, Zhao Y, Zhao X, Li Q (2017) FOXK1 facilitates cell proliferation through regulating the expression of p21, and promotes metastasis in ovarian cancer. Oncotarget 8(41):70441–70451. https://doi.org/10.18632/oncotarget.19713
Li X, Xue Y, Liu X, Zheng J, Shen S, Yang C, Chen J, Li Z, Liu L, Ma J et al (2019a) ZRANB2/SNHG20/FOXK1 Axis regulates vasculogenic mimicry formation in glioma. J Exp Clin Cancer Res 38(1):68. https://doi.org/10.1186/s13046-019-1073-7
Li ZQ, Qu M, Wan HX, Wang H, Deng Q, Zhang Y (2019b) FOXK1 promotes malignant progression of breast cancer by activating PI3K/AKT/mTOR signaling pathway. Eur Rev Med Pharmacol Sci 23(22):9978–9987. https://doi.org/10.26355/eurrev_2019b11_19564
Link W (2019) Introduction to FOXO Biology. Methods Mol Biol 1890:1–9. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-1-4939-8900-3_1
Park SY, Lee CJ, Choi JH, Kim JH, Kim JW, Kim JY, Nam JS (2019) The JAK2/STAT3/CCND2 Axis promotes colorectal Cancer stem cell persistence and radioresistance. J Exp Clin Cancer Res 38(1):399. https://doi.org/10.1186/s13046-019-1405-7
Peng Y, Zhang P, Huang X, Yan Q, Wu M, Xie R, Wu Y, Zhang M, Nan Q, Zhao J, Li A et al (2016) Direct regulation of FOXK1 by C-jun promotes proliferation, invasion and metastasis in gastric cancer cells. Cell Death Dis 7(11):e2480. https://doi.org/10.1038/cddis.2016.225
Qing X, Tan GL, Liu HW, Li W, Ai JG, Xiong SS, Yang MQ, Wang TS (2020) LINC00669 insulates the JAK/STAT suppressor SOCS1 to promote nasopharyngeal cancer cell proliferation and invasion. J Exp Clin Cancer Res 39(1):166. https://doi.org/10.1186/s13046-020-01674-z
Shi X, Seldin DC, Garry DJ (2012) Foxk1 recruits the Sds3 complex and represses gene expression in myogenic progenitors. Biochem J 446(3):349–357. https://doi.org/10.1042/bj20120563
Sugase T, Takahashi T, Serada S, Fujimoto M, Hiramatsu K, Ohkawara T, Tanaka K, Miyazaki Y, Makino T, Kurokawa Y et al (2017) SOCS1 gene therapy improves radiosensitivity and enhances Irradiation-Induced DNA damage in esophageal squamous cell carcinoma. Cancer Res 77(24):6975–6986. https://doi.org/10.1158/0008-5472.Can-17-1525
Tang LL, Chen YP, Chen CB, Chen MY, Chen NY, Chen XZ, Du XJ, Fang WF, Feng M, Gao J et al (2021) The chinese society of clinical oncology (CSCO) clinical guidelines for the diagnosis and treatment of nasopharyngeal carcinoma. Cancer Commun (Lond) 41(11):1195–1227. https://doi.org/10.1002/cac2.12218
Tong F, Xiong CJ, Wei CH, Wang Y, Liang ZW, Lu H, Pan HJ, Dong JH, Zheng XF, Wu G et al (2020) Hypo-fractionation radiotherapy normalizes tumor vasculature in non-small cell lung cancer xenografts through the p-STAT3/HIF-1 alpha signaling pathway. Ther Adv Med Oncol 12:1758835920965853. https://doi.org/10.1177/1758835920965853
van der Heijden M, Essers PBM, Verhagen CVM, Willems SM, Sanders J, de Roest RH, Vossen DM, Leemans CR, Verheij M, Brakenhoff RH et al (2020) Epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition is a prognostic marker for patient outcome in advanced stage HNSCC patients treated with chemoradiotherapy. Radiother Oncol 147:186–194. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.radonc.2020.05.013
Wang J, Liu G, Liu M, Xiang L, Xiao Y, Zhu H, Wu X, Peng Y, Zhang W, Jiang P et al (2018) The FOXK1-CCDC43 Axis promotes the Invasion and Metastasis of Colorectal Cancer cells. Cell Physiol Biochem 51(6):2547–2563. https://doi.org/10.1159/000495924
Wang Y, Qiu W, Liu N, Sun L, Liu Z, Wang S, Wang P, Liu S, Lv J (2020) Forkhead box K1 regulates the malignant behavior of gastric cancer by inhibiting autophagy. Ann Transl Med 8(4):107. https://doi.org/10.21037/atm.2019.12.123
Wang Y, Qiu W, Liu N, Sun L, Liu Z, Wang S, Wang P, Liu S, Lv J (2014) FOXO transcription factors: their clinical significance and regulation. Biomed Res Int 2014: 925350. https://doi.org/10.1155/2014/925350
Wu M, Wang J, Tang W, Zhan X, Li Y, Peng Y, Huang X, Bai Y, Zhao J, Li A et al (2016a) FOXK1 interaction with FHL2 promotes proliferation, invasion and metastasis in colorectal cancer. Oncogenesis 5(11):e271. https://doi.org/10.1038/oncsis.2016a.68
Wu MH, Chen XY, Cai KR (2009) Effects of a JAK inhibitor, AG490, on proliferation and apoptosis of human nasopharyngeal carcinoma cell line CNE-2Z. Ai Zheng 28(1):24–28
Wu Y, Peng Y, Wu M, Zhang W, Zhang M, Xie R, Zhang P, Bai Y, Zhao J, Li A et al (2016b) Oncogene FOXK1 enhances invasion of colorectal carcinoma by inducing epithelial-mesenchymal transition. Oncotarget 7(32):51150–51162. https://doi.org/10.18632/oncotarget.9457
Xie R, Wang J, Liu X, Wu L, Zhang H, Tang W, Li Y, Xiang L, Peng Y, Huang X et al (2017) RUFY3 interaction with FOXK1 promotes invasion and metastasis in colorectal cancer. Sci Rep 7(1):3709. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-017-04011-1
Xu H, Huang S, Zhu X, Zhang W, Zhang X (2018) FOXK1 promotes glioblastoma proliferation and metastasis through activation of snail transcription. Exp Ther Med 15(3):3108–3116. https://doi.org/10.3892/etm.2018.5732
Zhang H, Luo H, Jiang Z, Yue J, Hou Q, Xie R, Wu S (2016) Fractionated irradiation-induced EMT-like phenotype conferred radioresistance in esophageal squamous cell carcinoma. J Radiat Res 57(4):370–380. https://doi.org/10.1093/jrr/rrw030
Zhang X, Jiang L, Liu H (2021) Forkhead Box protein O1: functional diversity and post-translational modification, a New Therapeutic Target? Drug Des Devel Ther 15:1851–1860. https://doi.org/10.2147/dddt.S305016
Zhao H, Chang A, Ling J, Zhou W, Ye H, Zhuo X (2020) Construction and analysis of miRNA-mRNA regulatory networks in the radioresistance of nasopharyngeal carcinoma. 3 Biotech 10(12):511. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13205-020-02504-x
Zheng X, Zhu Y, Wang X, Hou Y, Fang Y (2021) Silencing of ITGB6 inhibits the progression of cervical carcinoma via regulating JAK/STAT3 signaling pathway. Ann Transl Med 9(9):803. https://doi.org/10.21037/atm-21-1669
Zhou YC, Pang XZ, Zhu HL, He Y, Shen Y, Ma DY (2022) [The IL-6/STAT3 signaling pathway mediated by radiotherapy regulates the expression of PD-L1 in esophageal cancer cells]. Zhonghua Zhong Liu Za Zhi 44(5):389–394. https://doi.org/10.3760/cma.j.cn112152-20200320-00236
Zhu X, Wei L, Bai Y, Wu S, Han S (2017) FoxC1 promotes epithelial-mesenchymal transition through PBX1 dependent transactivation of ZEB2 in esophageal cancer. Am J Cancer Res 7(8):1642–1653
Funding
This project was supported by National Natural Science Foundation of China (81903137).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of Interest
Liqun Duan, Jinlong Huang, Yong Zhang, Guoliang Pi, Xiaofang Ying, Fanyu Zeng, DeshengHu and Jia Ma declare that they have no conflict of interest.
There are no conflicts of interest to declare.
Additional information
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Liqun Duan and Jinlong Huang contributed equally to this study.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Duan, L., Huang, J., Zhang, Y. et al. FOXK1 regulates epithelial-mesenchymal transition and radiation sensitivity in nasopharyngeal carcinoma via the JAK/STAT3 signaling pathway. Genes Genom 45, 749–761 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13258-023-01380-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13258-023-01380-y