Abstract
Background
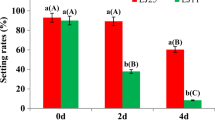
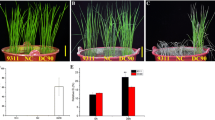
At the seed germination stage, rice is sensitive to cold stress, which adversely affects its growth and development. Guizhou HE rice comprises several different landraces, most of which are cold tolerant.
Objective
To identify differentially expressed genes and molecular mechanism underlying the cold tolerance of Guizhou HE.
Methods
Two Guizhou HE genotypes, AC44 (cold-sensitive) and AC96 (cold-tolerant), which exhibit opposite phenotypes in response to cold treatment at the seed germination stage were used. Comprehensive gene expressions of AC44 and AC96 under 4 °C cold treatment and subsequent recovery conditions were comparatively analyzed by RNA sequencing.
Results
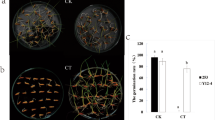
Overall, 11,082 and 7749 differentially expressed genes were detected in AC44 and AC96, respectively. Comparative transcriptome analysis demonstrated that, compared with AC44, AC96 presented fewer upregulated and downregulated genes. Gene Ontology (GO) and Kyoto Encyclopedia of Genes and Genomes (KEGG) pathway analyses demonstrated that AC96 presented more upregulated GO terms, especially terms associated with biological processes. However, AC44 presented more terms related to cellular components, mainly chloroplasts. Moreover, DEGs related to the auxin signaling pathway (including ARF and IAA family members) and transcription factors (including members of the F-box, bZIP, basic helix-loop-helix [bHLH], and MYB-like transcription factor families) were found to be expressed specifically in AC96; thus, these DEGs may be responsible for the cold tolerance of AC96.
Conclusions
These findings present information about the cold tolerance mechanism of Guizhou HE rice at the germination stage, providing valuable resources and candidate genes for breeding cold-tolerant rice genotypes.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
da Maia L, Cadore P, Benitez L, Danielowski R, Braga E, Fagundes P, Magalhães A, de Costa O (2017) Transcriptome profiling of rice seedlings under cold stress. Funct Plant Biol 44(4):419–429. https://doi.org/10.1071/FP16239
Dametto A, Sperotto R, Adamski J, Blasi É, Cargnelutti D, de Oliveira L, Ricachenevsky F, Fregonezi J, Mariath J, da Cruz R, Margis R, Fett J (2015) Cold tolerance in rice germinating seeds revealed by deep RNAseq analysis of contrasting indica genotypes. Plant Sci 238:1–12. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.plantsci.2015.05.009
Fujino K, Sekiguchi H, Sato T, Kiuchi H, Nonoue Y, Takeuchi Y, Ando T, Lin S, Yano M (2004) Mapping of quantitative trait loci controlling low-temperature germinability in rice (Oryza sativa L.). Theor Appl Genet 108(5):794–799. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00122-003-1509-4
Guan S, Xu Q, Ma D, Zhang W, Xu Z, Zhao M, Guo Z (2019) Transcriptomics profiling in response to cold stress in cultivated rice and weedy rice. Gene 685:96–105. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.gene.2018.10.066
Kim D, Park C, Bennett C, Salzberg S (2019) Graph-based genome alignment and genotyping with HISAT2 and HISAT-genotype. Nat Biotechnol 37(8):907–915. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41587-019-0201-4
Li F, Guo S, Zhao Y, Chen D, Chong K, Xu Y (2010) Overexpression of a homopeptide repeat-containing bHLH protein gene (OrbHLH001) from Dongxiang Wild Rice confers freezing and salt tolerance in transgenic Arabidopsis. Plant Cell Rep 9:977–986. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00299-010-0883-z
Liu C, Schläppi M, Mao B, Wang W, Wang A, Chu C (2019) The bZIP73 transcription factor controls rice cold tolerance at the reproductive stage. Plant Biotechnol J 17(9):1834–1849. https://doi.org/10.1111/pbi.13104
Love M, Huber W, Anders S (2014) Moderated estimation of fold change and dispersion for RNA-seq data with DESeq2. Genome Biol 15(12):550. https://doi.org/10.1186/s13059-014-0550-8
Lv Y, Guo Z, Li X, Ye H, Li X, Xiong L (2016) New insights into the genetic basis of natural chilling and cold shock tolerance in rice by genome-wide association analysis. Plant Cell Environ 39(3):556–570. https://doi.org/10.1111/pce.12635
Ma Y, Dai X, Xu Y, Luo W, Zheng X, Zeng D, Pan Y, Lin X, Liu H, Zhang D et al (2015) COLD1 confers chilling tolerance in rice. Cell 160(6):1209–1021. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cell.2015.01.046
Mao X, Cai T, Olyarchuk J, Wei L (2005) Automated genome annotation and pathway identification using the KEGG Orthology (KO) as a controlled vocabulary. Bioinformatics 21(19):3787–3793. https://doi.org/10.1093/bioinformatics/bti430
Pan Y, Liang H, Gao L, Dai G, Chen W, Yang X, Qing D, Gao J, Wu H, Huang J, Zhou W, Huang C, Liang Y, Deng G (2020) Transcriptomic profiling of germinating seeds under cold stress and characterization of the cold-tolerant gene LTG5 in rice. BMC Plant Biol 20(1):371. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12870-020-02569-z
Pan X, Guan L, Lei K, Li J, Zhang X (2022) Transcriptional and physiological data revealed cold tolerance in a photo-thermo sensitive genic male sterile line Yu17S. BMC Plant Biol 22(1):44. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12870-022-03437-8
Pan X, Wu H, Hu M, Wang Z, Jiang X, Guan L, Bai W, Lei K (2021) Global analysis of gene expression profiles in glutinous rice 89–1 (Oryza sativa L.) seedlings exposed to chilling stress. Plant Mol Biol Rep 39(3):1–14. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11105-020-01278-z
Rahman A (2012) Auxin: a regulator of cold stress response. Physiol Plant 147(1):28–35. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1399-3054.2012.01617.x
Saito K, Hayano-Saito Y, Kuroki M, Sato Y (2010) Map-based cloning of the rice cold tolerance gene Ctb1. Plant Sci 179(1-2):97-102. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.plantsci.2010.04.004
Shen C, Li D, He R, Fang Z, Xia Y, Gao J, Shen H, Cao M (2014) Comparative transcriptome analysis of RNA-seq data for cold-tolerant and cold-sensitive rice genotypes under cold stress. J Plant Biol 57(6):337–348. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12374-014-0183-1
Sheteiwy M, An J, Yin M, Jia X, Guan Y, He F, Hu J (2019) Cold plasma treatment and exogenous salicylic acid priming enhances salinity tolerance of Oryza sativa seedlings. Protoplasma 256(1):79–99. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00709-018-1279-0
Shimono H, Ishii A, Kanda E, Suto M, Nagano K (2011) Genotypic variation in rice cold tolerance responses during reproductive growth as a function of water temperature during vegetative growth. Crop Sci 51(1):290–297. https://doi.org/10.2135/cropsci2010.05.0300
Wang Y, Jiao A, Chen H, Ma X, Cui D, Han B, Ruan R, Xue D, Han L (2018) Status and factors influencing on farm conservation of Kam Sweet Rice (Oryza sativa L.) genetic resources in southeast Guizhou Province. China J Ethnobiol Ethnomed 14(1):76. https://doi.org/10.1186/s13002-018-0256-1
Wang Z, Luo Q, Jiang X, Wu X, Xu H, Zhu S (2021) Diversity analysis of the Waxy gene in Oryza sativa L. “Guizhou HE”. ScienceAsia 47(4):434–440. https://doi.org/10.2306/scienceasia1513-1874.2021.055
Xiao N, Gao Y, Qian H, Gao Q, Wu Y, Zhang D, Wang Z, Zhang X, Yu L, Li Y et al (2018) Identification of genes related to cold tolerance and a functional allele that confers cold tolerance. Plant Physiol 177(3):1108–1123. https://doi.org/10.1104/pp.18.00209
Yang S, Hao D, Song Z, Yang G, Wang L, Su Y (2015) RNA-Seq analysis of differentially expressed genes in rice under varied nitrogen supplies. Gene 555(2):305–317. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.gene.2014.11.021
Young M, Wakefield M, Smyth G, Oshlack A (2010) Gene ontology analysis for RNA-seq: accounting for selection bias. Genome Biol 11(2):R14. https://doi.org/10.1186/gb-2010-11-2-r14
Zhang T, Zhao X, Wang W, Pan Y, Huang L, Liu X, Zong Y, Zhu L, Yang D, Fu B (2012) Comparative transcriptome profiling of chilling stress responsiveness in two contrasting rice genotypes. PLoS ONE 7(8):e43274. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0043274
Zhang Q, Chen Q, Wang S, Hong Y, Wang Z (2014) Rice and cold stress: methods for its evaluation and summary of cold tolerance-related quantitative trait loci. Rice 7(1):24. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12284-014-0024-3
Zhang Z, Li J, Pan Y, Li J, Zhou L, Shi H, Zeng Y, Guo H, Yang S, Zheng W et al (2017a) Natural variation in CTB4a enhances rice adaptation to cold habitats. Nat Commun 8:14788. https://doi.org/10.1038/ncomms14788
Zhang T, Huang L, Wang Y, Wang W, Zhao X, Zhang S, Zhang J, Hu F, Fu B, Li Z (2017b) Differential transcriptome profiling of chilling stress response between shoots and rhizomes of Oryza longistaminata using RNA sequencing. PLoS ONE 12(11):e0188625. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0188625
Acknowledgements
We thank Springer (https://secure.authorservices.springernature.com/en/default/submit/select) for editing this manuscript.
Funding
This project was supported by the Guizhou Provincial Science and Technology Project (Qiankehejichu[2020]1Y101), the Guizhou Science and Technology Support Program Project ([2019]2304), the Youth Science and Technology Fund of the Academy of Agricultural Science of Guizhou Province ([2020]21), a Post-Subsidy Project of the NSFC of the Academy of Agricultural Science of Guizhou Province ([2021]15), Post Subsidy Project of Guizhou Province ([2018]5263), and Joint Fund of the NSFC and the Karst Science Research Center of Guizhou Province (Grant No. U1812401).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
YC performed material preparation and collection; ZW, XW, WL and CW analyzed the data; ZW and SZ designed the study; and ZW wrote the manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest to the content of this article.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Wang, Z., Wu, X., Chen, Y. et al. Transcriptomic profiling of the cold stress and recovery responsiveness of two contrasting Guizhou HE rice genotypes. Genes Genom 45, 401–412 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13258-022-01321-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13258-022-01321-1