Abstract
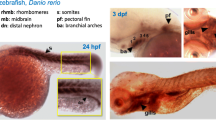
We isolated two atp2a genes, atp2a1 and atp2a2a, from embryonic zebrafish. Amino acid sequences deduced from zebrafish atp2a genes are aligned with orthologue proteins from other species, the results showed that they share high percentage of identities (82%–94%) and acidic pIs (5.03–5.33). Whole mount in situ hybridization experiments showed that atp2a1 and atp2a2a are maternal inherited genes which can be detected at 1-cell stage embryos and express in the entire animal pole from 6 hours post-fertilization (hpf) to 12 hpf. At the later stages (48–96 hpf), expression of atp2a1 was restricted in head and trunk muscles as well as in some neurons. In contrast to the strongly expression of atp2a1 in head muscle, expression of atp2a2a was detected in head muscle in a fainter manner. In addition, transcripts of atp2a2a were observed in the developing heart during early cardiogenesis. The present studies not only help us to comparatively analyze atp2a genes across species, but also provide useful information about expressions during early embryogenesis that will help in further investigations of functional studies of Atp2a in the future.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Altschul SF, Madden TL, Schäffer AA, Zhang J, Zhang Z, Miller W, and Lipman DJ (1997) Gapped BLAST and PSI-BLAST: a new generation of protein database search programs. Nucleic Acids Res. 25: 3389–3402.
Andersson KB, Birkeland JA, Finsen AV, Louch WE, Sjaastad I, Wang Y, Chen J, Molkentin JD, Chien KR, Sejersted OM, and Christensen G (2009) Moderate heart dysfunction in mice with inducible cardiomyocyte-specific excision of the Serca2 gene. J. Mol. Cell Cardiol. 47: 180–187.
Autry JM and Jones LR (1997) Functional co-expression of the canine cardiac Ca2+ pump and phospholamban in Spodoptera frugiperda (Sf21) cells reveals new insights on ATPase regulation. J. Biol. Chem. 272: 15872–15880.
Berridge MJ (2009) Inositol trisphosphate and calcium signalling mechanisms. Biochim. Biophys. Acta. 1793: 933–940.
Berridge MJ, Bootman MD, and Lipp P (1998) Calcium-a life and death signal. Nature 395: 645–648.
Brandl CJ, Green NM, Korczak B, and MacLennan DH (1986) Two Ca2+ ATPase genes: homologies and mechanistic implications of deduced amino acid sequences. Cell 44: 597–607.
Brody IA (1969) Muscle contracture induced by exercise. New Eng. J. Med. 281: 187–192.
Castilho PC, Landeira-Fernandez AM, Morrissette J, and Block BA (2007) Elevated Ca2+ ATPase (SERCA2) activity in tuna hearts: comparative aspects of temperature dependence. Comp. Biochem. Physiol. A Mol. Integr. Physiol. 148: 124–132.
Chen YH, Lee WC, Cheng CH, and Tsai HJ (2000) Muscle regulatory factor gene: zebrafish (Danio rerio) myogenin cDNA. Comp. Biochem. Physiol. B: Biochem. Mol. Biol. 127: 97–103.
Chen YH, Lee WC, Liu CF, and Tsai HJ (2001) Molecular structure, dynamic expression and promoter analysis of zebrafish (Danio rerio) myf-5 gene. Genesis 29: 22–35.
Chen YH, Wang YH, Yu TH, Wu HJ, and Pai CW (2009a) Transgenic zebrafish line with over-expression of Hedgehog on the skin: a useful tool to screen Hedgehog-inhibiting compounds. Transgenic Res. 18: 855–864.
Chen YH, Lin YT, and Lee GH (2009b) Novel and unexpected functions of zebrafish CCAAT box binding transcription factor (NF-Y) B subunit during cartilages development. Bone 44: 777–784.
Dai DF and Rabinovitch PS (2009) Cardiac aging in mice and humans: the role of mitochondrial oxidative stress. Trends Cardiovasc. Med. 19: 213–220.
Ebert AM, Hume GL, Warren KS, Cook NP, Burns CG, Mohideen MA, Siegal G, Yelon D, Fishman MC and Garrity DM (2005) Calcium extrusion is critical for cardiac morphogenesis and rhythm in embryonic zebrafish hearts. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 102: 17705–17710.
Fill M and Copello JA (2002) Ryanodine receptor calcium release channels. Physiol. Rev. 82: 893–922.
Gordon AM, Homsher E, and Regnier M (2000) Regulation of contraction in striated muscle. Physiol. Rev. 80: 853–924.
Gunaratne HJand Vacquier VD (2006) Cloning of a sea urchin sarco/endoplasmic reticulum Ca2+ ATPase. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 339: 443–449.
Gunteski-Hamblin AM, Greeb J and Shull GE (1988) A novel Ca2+ pump expressed in brain, kidney, and stomach is encoded by an alternative transcript of the slow-twitch muscle sarcoplasmic reticulum Ca-ATPase gene. J. Biol. Chem. 263: 15032–15040.
Hirata H, Saint-Amant L, Waterbury J, Cui W, Zhou W, Li Q, Goldman D, Granato and Kuwada JY (2004) accordion, a zebrafish behavioral mutant, has a muscle relaxation defect due to a mutation in the ATPase Ca2+ pump SERCA1. Development 131: 5457–5468.
Hsu DK, Donohue PJ, Alberts GF and Winkles JA (1993) Fibroblast growth factor-1 induces phosphofructokinase, fatty acid synthase and Ca(2+)-ATPase mRNA expression in NIH 3T3 cells. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 197: 1483–1491.
Karin NJ, Kaprielian Z and Fambrough DM (1989) Expression of avian Ca2+-ATPase in cultured mouse myogenic cells. Mol. Cell. Biol. 9: 1978–1986.
Kimmel C, Ballard WW, Kimmel SR, Ullmann B and Schilling TF (1995) Stages of embryonic development in the zebrafish. Dev. Dyn. 203: 253–310.
Klein SL, Strausberg RL, Wagner L, Pontius J, Clifton SW and Richardson P (2002) Genetic and genomic tools for Xenopus research: The NIH Xenopus initiative. Dev. Dyn. 225: 384–391.
Kontaraki JE, Parthenakis FI, Nyktari EG, Patrianakos AP and Vardas PE (2010) Myocardial gene expression alterations in peripheral blood mononuclear cells of patients with idiopathic dilated cardiomyopathy. Eur. J. Heart Fail. 12: 541–548.
Langenbacher AD, Dong Y, Shu X, Choi J, Nicoll DA, Goldhaber JI, Philipson KD and Chen JN (2005) Mutation in sodium-calcium exchanger 1 (NCX1) causes cardiac fibrillation in zebrafish. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 102: 17699–17704.
Lo J, Lee S, Xu M, Liu F, Ruan H, Eun A, He Y, Ma W, Wang W, Wen Z and Peng J (2003) 15000 unique zebrafish EST clusters and their future use in microarray for profiling gene expression patterns during embryogenesis. Genome Res. 13: 455–466.
Loukianov E, Ji Y, Baker DL, Reed T, Babu J, Loukianova T, Greene A, Shull G and Periasamy M (1998) Sarco(endo)plasmic reticulum Ca2+ ATPase isoforms and their role in muscle physiology and pathology. Ann. NY Acad. Sci. 853: 251–259.
Lytton J and MacLennan DH (1988) Molecular cloning of cDNAs from human kidney coding for two alternatively spliced products of the cardiac Ca2+-ATPase gene. J. Biol. Chem. 263: 15024–15031.
Machuca I, Domenget C and Jurdic P (1999) Identification of avian sarcoplasmic reticulum Ca(2+)-ATPase (SERCA3) as a novel 1,25(OH)(2)D(3) target gene in the monocytic lineage. Exp. Cell Res. 250: 364–375.
MacLennan DH (2000) Ca2+ signaling and muscle disease. Eur. J. Biochem. 267: 5291–5297.
MacLennan DH, Rice WJ and Green NM (1997) The mechanism of Ca2+ transport by sarco(endo)plasmic reticulum Ca2+-ATPase. J. Biol. Chem. 272: 28815–28818.
Magyar A, Bakos E and Váradi A (1995) Structure and tissue-specific expression of the Drosophila melanogaster organellar-type Ca(2+)-ATPase gene. Biochem. J. 310: 757–763.
Maves L, Waskiewicz AJ, Paul B, Cao Y, Tyler A, Moens CB and Tapscott SJ (2007) Pbx homeodomain proteins direct Myod activity to promote fast-muscle differentiation. Development. 134: 3371–3382.
Mikoshiba K (2007) IP3 receptor/Ca2+ channel: from discovery to new signaling concepts. J. Neurochem. 102: 1426–1446.
Odermatt A, Taschner PEM, Khanna VK, Busch HFM, Karpati G, Jablecki CK, Breuning MH and MacLennan DH (1996) Mutations in the gene-encoding SERCA1, the fast-twitch skeletal muscle sarcoplasmic reticulum Ca2+ ATPase, are associated with Brody disease. Nat. Genet. 14: 191–194.
Olson BD, Sgourdou P and Downes GB (2010) Analysis of a zebrafish behavioral mutant reveals a dominant mutation in atp2a1/SERCA1. Genesis 48: 354–361.
Pai CW and Chen YH (2010) Transgenic expression of prothymosin alpha on zebrafish epidermal cells promotes proliferation and attenuates the UVB-induced apoptosis. Transgenic Res. 19: 655–665.
Pan Y, Zvaritch E, Tupling AR, Rice WJ, de Leon S, Rudnicki M, McKerlie C, Banwell BL and MacLennan DH (2003) Targeted disruption of the ATP2A1 gene encoding the sarco(endo)plasmic reticulum Ca2+ATPase isoform 1 (SERCA1) impairs diaphragm function and is lethal in neonatal mice. J. Biol. Chem. 278: 13367–13375.
Peng HC, Wang YH, Wen CC, Wang WH, Cheng CC and Chen YH (2010) Nephrotoxicity assessments of acetaminophen during zebrafish embryogenesis. Comp. Biochem. Physiol. C: Toxicol. Pharmacol. 151: 480–486.
Periasamy M, Reed TD, Liu LH, Ji Y, Loukianov E, Paul RJ, Nieman ML, Riddle T, Duffy JJ, Doetschman T, Lorenz JN and Shull GE (1999) Impaired cardiac performance in heterozygous mice with a null mutation in the sarco(endo)plasmic reticulum Ca2+-ATPase isoform 2 (SERCA2) gene. J. Biol. Chem. 274: 2556–2562.
Sakuntabhai A, Ruiz-Perez V, Carter S, Jacobsen N, Burge S, Monk S, Smith M, Munro CS, O’Donovan M et al. (1999) Mutations in ATP2A2, encoding a Ca2+ pump, cause Darier disease. Nat. Genet. 21: 271–277.
Schleef M, Simon-Chazottes D, Lengeling A, Klocke R, Jockusch H, Yarden Y and Guenet J (1996) The gene encoding sarcoplasmic reticulum calcium ATPase-1 (Atp2a1) maps to distal mouse chromosome 7. Mamm. Genome 7: 788.
Stokke MK, Hougen K, Sjaastad I, Louch WE, Briston SJ, Enger UH, Andersson KB, Christensen G, Eisner DA, Sejersted OM et al. (2010) Reduced SERCA2 abundance decreases the propensity for Ca2+ wave development in ventricular myocytes. Cardiovasc. Res. 86: 63–71.
Summerfield N, Peters ME, Hercock CA, Mobasheri A and Young IS (2010) Immunohistochemical evidence for expression of fast-twitch type sarco(endo)plasmic reticulum Ca2+ ATPase (SERCA1) in German shepherd dogs with dilated cardiomyopathy myocardium. J. Vet. Cardiol. 12: 17–23.
Varga-Szabo D, Braun A and Nieswandt B (2009) Calcium signaling in platelets. J. Thromb. Haemost. 7: 1057–1066.
Wang YH, Cheng CC, Lee WJ, Chiou ML, Pai CW, Wen CC, Chen WL, Chen YH (2009a) A novel phenotype-based approach for systematically screening antiproliferation metallodrugs. Chem-Biol. Interact. 182: 84–91.
Wang YH, Wen CC, Yang ZS, Cheng CC, Tsai JN, Ku CC, Wu HJ and Chen YH (2009b) Development of a whole-organism model to screen new compounds for sun protection. Mar. Biotechnol. 11: 419–429.
Westerfield M (1995) The zebrafish book. Third edition. University of Oregon Press.
Wu KD, Lytton J 1993 Molecular cloning and quantification of sarcoplasmic reticulum Ca(2+)-ATPase isoforms in rat muscles. Am. J. Physiol. 264: C333–C341.
Zádor E, Vangheluwe P and Wuytack F (2007) The expression of the neonatal sarcoplasmic reticulum Ca2+ pump (SERCA1b) hints to a role in muscle growth and development. Cell Calcium. 41: 379–388.
Zhang Y, Fujii J, Phillips MS, Chen HS, Karpati G, Yee WC, Schrank B, Cornblath DR, Boylan KB and MacLennan DH (1995) Characterization of cDNA and genomic DNA encoding SERCA1, the Ca(2+)-ATPase of human fast-twitch skeletal muscle sarcoplasmic reticulum, and its elimination as a candidate gene for Brody disease. Genomics. 30: 415–424.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Lai, YY., Pai, CW., Tsai, I.T. et al. Molecular structure and developmental expression of zebrafish atp2a genes. Genes Genom 33, 541–548 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13258-011-0013-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13258-011-0013-5