Abstract
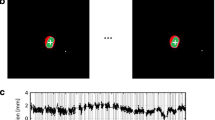
This study quantified the performance of Intra-fraction Motion Review (IMR) during prostate Stereotactic Body Radiotherapy (SBRT) treatments. IMR was evaluated using prostate motion data from patients treated in an SBRT clinical trial (PROMETHEUS, NCT00587990).IMR measured prostate displacements were compared to those of two 3D motion management methods: Kilovoltage Intra-fraction Motion management (KIM) and MV/kV triangulation. A planning study assessing the impact of a defined prostate motion (2–5 mm) on the PTV coverage with and without IMR was performed. A clinically relevant IMR search region for prostate cancer SBRT treatments was determined using a customised anthropomorphic pelvis phantom with implanted gold seeds and a motion platform. IMR showed submillimeter agreement with corresponding 2D projections from both KIM and MV/kV triangulation. However, IMR detected actual displacements consistently in considerably fewer frames than KIM (3D), with the actual numbers depending on the settings. The Default Search Region (DSR) method employing a circular search region proved superior to user-contoured structures in detecting clinically relevant prostate motion. Reducing the DSR search region radius can reduce the impact of the 2D nature of IMR and improve the detectability of actual motion (by 10% per 0.5 mm reduction) but must be balanced against increased beam interruptions from minor, clinically irrelevant motion. The use of IMR for SBRT prostate treatments has the potential to improve target dose coverage (minimum dose to 98% of the PTV, D98%) by > 20% compared to treatment without IMR. Calculated D98% of IMR monitored treatments with motion was within 1.5% of plans without motion.







Similar content being viewed by others

References
Li HS et al (2008) Dosimetric consequences of intrafraction prostate motion. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys 71(3):801–812
Rossi MM et al (2016) Intrafraction motion in stereotactic body radiation therapy for non-small cell lung cancer: intensity modulated radiation therapy versus volumetric modulated arc therapy. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys 95(2):835–843
Keall P (2011) Locating and targeting moving tumors with radiation beams. Front Radiat Ther Oncol 43:118–131
Bertholet J et al (2019) Real-time intrafraction motion monitoring in external beam radiotherapy. Phys Med Biol 64(15):15TR01
O'Neill AG et al (2016) Fiducial marker guided prostate radiotherapy: a review. Br J Radiol 89(1068):20160296
Kaur G et al (2019) Assessment of the accuracy of truebeam intrafraction motion review (IMR) system for prostate treatment guidance. Australas Phys Eng Sci Med 42(2):585–598
Korpics MC et al (2020) Utilizing the TrueBeam Advanced Imaging Package to monitor intrafraction motion with periodic kV imaging and automatic marker detection during VMAT prostate treatments. J Appl Clin Med Phys 21(3):184–191
Cetnar A et al (2021) Prospective dual-surrogate validation study of periodic imaging during treatment for accurately monitoring intrafraction motion of prostate cancer patients. Radiother Oncol 157:40–46
Pryor D et al (2019) Phase 2 multicenter study of gantry-based stereotactic radiotherapy boost for intermediate and high risk prostate cancer (PROMETHEUS). Front Oncol 9:217
Richardson M et al (2018) PROstate Multicentre External beam radioTHErapy Using a Stereotactic boost: the PROMETHEUS study protocol. BMC Cancer 18(1):588
Hunt MA et al (2016) Simultaneous MV–kV imaging for intrafractional motion management during volumetric-modulated arc therapy delivery. J Appl Clin Med Phys 17(2):473–486
Ng JA et al (2012) Kilovoltage intrafraction monitoring for prostate intensity modulated arc therapy: first clinical results. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys 84(5):e655–e661
Kim JH et al (2018) The accuracy and precision of Kilovoltage Intrafraction Monitoring (KIM) six degree-of-freedom prostate motion measurements during patient treatments. Radiother Oncol 126(2):236–243
Keall PJ et al (2016) Real-time 3D image guidance using a standard LINAC: measured motion, accuracy, and precision of the first prospective clinical trial of kilovoltage intrafraction monitoring-guided gating for prostate cancer radiation therapy. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys 94(5):1015–1021
Huang E et al (2002) Intrafraction prostate motion during IMRT for prostate cancer. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys 53(2):261–268
Gao Y et al (2020) Quantifying intra-fractional prostate motion trajectory for establishing a new gating strategy: a preliminary study. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys 108(3):e327
Juneja P et al (2017) Quantification of intrafraction prostate motion and its dosimetric effect on VMAT. Australas Phys Eng Sci Med 40(2):317–324
Acknowledgements
This work was supported and funded by a research Grant from Varian Medical System.
Funding
This study was funded by the Varian Medical systems (Research and Collaboration Approval).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
All authors contributed to the study conception and design. Material preparation, data collection, and analysis were performed by GK, JL, PG, JM, JS. The first draft of the manuscript was written by GK and all authors commented on previous versions of the manuscript. All authors read and approved the final manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Ethical approval
Ethics approval for this PROMETHEUS clinical trial was granted by the South Western Sydney Local Health District Human Research Ethics Committee on the 2/12/2013 Reference Number HREC/13/LPOOL/311.
Informed consent
Written informed consent was obtained from all participants.
Additional information
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Kaur, G., Lehmann, J., Greer, P.B. et al. Clinical validation of the Varian Truebeam intra-fraction motion review (IMR) system for prostate treatment guidance. Phys Eng Sci Med 46, 131–140 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13246-022-01204-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13246-022-01204-5