Abstract
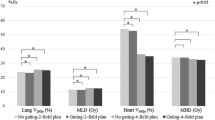
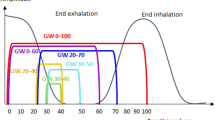
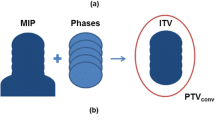
The performance of a visual guidance patient-controlled (VG-PC) respiratory gating system for magnetic-resonance (MR) image-guided radiation therapy (MR-IGRT) was evaluated through a clinical trial of patients with either lung or liver cancer. Patients can voluntarily control their respiration utilizing the VG-PC respiratory gating system. The system enables patients to view near-real-time cine planar MR images projected inside the bore of MR-IGRT systems or an external screen. Twenty patients who had received stereotactic ablative radiotherapy (SABR) for lung or liver cancer were prospectively selected for this study. Before the first treatment, comprehensive instruction on the VG-PC respiratory gating system was provided to the patients. Respiratory-gated MR-IGRT was performed for each patient with it in the first fraction and then without it in the second fraction. For both the fractions, the total treatment time, beam-off time owing to the respiratory gating, and number of beam-off events were analyzed. The average total treatment time, beam-off time, and number of beam-off events with the system were 1507.3 s, 679.5 s, and 185, respectively, and those without the system were 2023.7 s (p < 0.001), 1195.0 s (p < 0.001), and 380 times (p < 0.001), respectively. The VG-PC respiratory gating system improved treatment efficiency through a reduction in the beam-off time, the number of beam-off events, and consequently the total treatment time when performing respiratory-gated MR-IGRT for lung and liver SABR.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Landry G, Corradini S, Belka C (2020) Magnetic resonance-guided radiation therapy: the beginning of a new era. Radiat Oncol 15:163. https://doi.org/10.1186/s13014-020-01599-z
Chin S, Eccles CL, McWilliam A, Chuter R, Walker E, Whitehurst P et al (2020) Magnetic resonance-guided radiation therapy: A review. J Med Imaging Radiat Oncol 64:163–177. https://doi.org/10.1111/1754-9485.12968
van Sornsen JR, Palacios MA, Bruynzeel AME, Slotman BJ, Senan S, Lagerwaard FJ (2018) MR-guided Gated Stereotactic Radiation Therapy Delivery for Lung, Adrenal, and Pancreatic Tumors: A Geometric Analysis. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys 102:858–866. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijrobp.2018.05.048
Keall PJ, Mageras GS, Balter JM, Emery RS, Forster KM, Jiang SB et al (2006) The management of respiratory motion in radiation oncology report of AAPM Task Group 76. Med Phys 33:3874–3900. https://doi.org/10.1118/1.2349696
Mutic S, Dempsey JF (2014) The ViewRay system: magnetic resonance-guided and controlled radiotherapy. Semin Radiat Oncol 24:196–199. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.semradonc.2014.02.008
Roberts DA, Sandin C, Vesanen PT, Lee H, Hanson IM, Nill S et al (2021) Machine QA for the Elekta Unity system: A Report from the Elekta MR-linac consortium. Med Phys 48:e67–e85. https://doi.org/10.1002/mp.14764
Kluter S (2019) Technical design and concept of a 0.35 T MR-Linac. Clin Transl Radiat Oncol 18:98–101. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ctro.2019.04.007
Choi CH, Kim JH, Kim JI, Park JM (2019) Comparison of treatment plan quality among MRI-based IMRT with a linac, MRI-based IMRT with tri-Co-60 sources, and VMAT for spine SABR. PLoS ONE 14. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0220039
Park JM, Wu HG, Kim HJ, Choi CH, Kim JI (2019) Comparison of treatment plans between IMRT with MR-linac and VMAT for lung SABR. Radiat Oncol 14:105. https://doi.org/10.1186/s13014-019-1314-0
Kim JI, Lee H, Wu HG, Chie EK, Kang HC, Park JM (2017) Development of patient-controlled respiratory gating system based on visual guidance for magnetic-resonance image-guided radiation therapy. Med Phys 44:4838–4846. https://doi.org/10.1002/mp.12447
George R, Chung TD, Vedam SS, Ramakrishnan V, Mohan R, Weiss E et al (2006) Audio-visual biofeedback for respiratory-gated radiotherapy: impact of audio instruction and audio-visual biofeedback on respiratory-gated radiotherapy. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys 65:924–933. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijrobp.2006.02.035
He PB, Li Q, Liu XG, Dai ZY, Zhao T, Fu TY et al (2014) Respiratory motion management using audio-visual biofeedback for respiratory-gated radiotherapy of synchrotron-based pulsed heavy-ion beam delivery. Med Phys 41. https://doi.org/10.1118/1.4897391
He PB, Li Q, Zhao T, Liu XG, Dai ZY, Ma YY (2016) Effectiveness of respiratory-gated radiotherapy with audio-visual biofeedback for synchrotron-based scanned heavy-ion beam delivery. Phys Med Biol 61:8541–8552. https://doi.org/10.1088/0031-9155/61/24/8541
Lamb JM, Ginn JS, O’Connell DP, Agazaryan N, Cao MS, Thomas DH et al (2017) Dosimetric validation of a magnetic resonance image gated radiotherapy system using a motion phantom and radiochromic film. J Appl Clin Med Phys 18:163–169. https://doi.org/10.1002/acm2.12088
Linthout N, Bral S, Van de Vondel I, Verellen D, Tournel K, Gevaert T et al (2009) Treatment delivery time optimization of respiratory gated radiation therapy by application of audio-visual feedback. Radiother Oncol 91:330–335. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.radonc.2009.03.019
Nelson C, Starkschall G, Balter P, Fitzpatrick MJ, Antolak JA, Tolani N et al (2005) Respiration-correlated treatment delivery using feedback-guided breath hold: a technical study. Med Phys 32:175–181. https://doi.org/10.1118/1.1836332
Timmerman RD, Hu C, Michalski JM, Bradley JC, Galvin J, Johnstone DW et al (2018) Long-term Results of Stereotactic Body Radiation Therapy in Medically Inoperable Stage I Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer. JAMA Oncol 4:1287–1288. https://doi.org/10.1001/jamaoncol.2018.1258
Bezjak A, Paulus R, Gaspar LE, Timmerman RD, Straube WL, Ryan WF et al (2019) Safety and Efficacy of a Five-Fraction Stereotactic Body Radiotherapy Schedule for Centrally Located Non-Small-Cell Lung Cancer: NRG Oncology/RTOG 0813 Trial. J Clin Oncol 37:1316–1325. https://doi.org/10.1200/JCO.18.00622
Nagata Y, Hiraoka M, Shibata T, Onishi H, Kokubo M, Karasawa K et al (2015) Prospective Trial of Stereotactic Body Radiation Therapy for Both Operable and Inoperable T1N0M0 Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer: Japan Clinical Oncology Group Study JCOG0403. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys 93:989–996. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijrobp.2015.07.2278
Wahl DR, Stenmark MH, Tao Y, Pollom EL, Caoili EM, Lawrence TS et al (2016) Outcomes After Stereotactic Body Radiotherapy or Radiofrequency Ablation for Hepatocellular Carcinoma. J Clin Oncol 34:452–459. https://doi.org/10.1200/JCO.2015.61.4925
Feng M, Suresh K, Schipper MJ, Bazzi L, Ben-Josef E, Matuszak MM et al (2018) Individualized Adaptive Stereotactic Body Radiotherapy for Liver Tumors in Patients at High Risk for Liver Damage: A Phase 2 Clinical Trial. JAMA Oncol 4:40–47. https://doi.org/10.1001/jamaoncol.2017.2303
Rim CH, Kim HJ, Seong J (2019) Clinical feasibility and efficacy of stereotactic body radiotherapy for hepatocellular carcinoma: A systematic review and meta-analysis of observational studies. Radiother Oncol 131:135–144. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.radonc.2018.12.005
Finazzi T, Palacios MA, Haasbeek CJA, Admiraal MA, Spoelstra FOB, Bruynzeel AME et al (2020) Stereotactic MR-guided adaptive radiation therapy for peripheral lung tumors. Radiother Oncol 144:46–52. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.radonc.2019.10.013
Funding
This work was supported by the Radiation Technology R&D program through the National Research Foundation of Korea funded by the Ministry of Science and ICT (2019M2A2B4095126 and 2019M2A2B4096540).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Hyung Jin Choun and Jong Min Park conceived the study concept, analyzed the data, drafted the manuscript, and participated in all aspects of the study. Jung-in Kim, Chang Heon Choi, Seongmoon Jung, and Hyeongmin Jin gathered and processed the data. Hong Gyun Wu and Eui Kyu Chie performed the clinical trial and evaluated the VG-PC respiratory gating system performance. Hyung Jin Choun, Jong Min Park, Jung-in Kim, and Chang Heon Choi performed discussions to improve the significance of this study. Jong Min Park oversaw and verified the completion of the study. All the authors read and approved the final manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors have no relevant financial or non-financial interests to disclose.
Ethics approval
All procedures performed in studies involving human participants were in accordance with the ethical standards of the institutional and/or national research committee and with the 1964 Helsinki Declaration and its later amendments or comparable ethical standards. The study was approved by the Institutional Review Board of Seoul National University Hospital (IRB No. 1908-133-1057).
Informed consent
Informed consent was obtained from all individual participants included in the study.
Consent to participate
Informed consent was obtained from all individual participants included in the study.
Consent to publish
Not applicable.
Additional information
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Choun, H., Kim, Ji., Choi, C. et al. Performance evaluation of a visual guidance patient-controlled respiratory gating system for respiratory-gated magnetic-resonance image-guided radiation therapy. Phys Eng Sci Med 45, 809–816 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13246-022-01144-0
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13246-022-01144-0