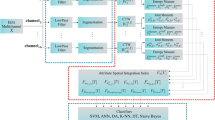
Abstract
Slow biphasic complexes (SBC) have been identified in the EEG of patients suffering for inflammatory brain diseases. Their amplitude, location and frequency of appearance were found to correlate with the severity of encephalitis. Other characteristics of SBCs and of EEG traces of patients could reflect the grade of pathology. Here, EEG rhythms are investigated together with SBCs for a better characterization of encephalitis. EEGs have been acquired from pediatric patients: ten controls and ten encephalitic patients. They were split by neurologists into five classes of different severity of the pathology. The relative power of EEG rhythms was found to change significantly in EEGs labeled with different severity scores. Moreover, a significant variation was found in the last seconds before the appearance of an SBC. This information and quantitative indexes characterizing the SBCs were used to build a binary classification decision tree able to identify the classes of severity. True classification rate of the best model was 76.1% (73.5% with leave-one-out test). Moreover, the classification errors were among classes with similar severity scores (precision higher than 80% was achieved considering three instead of five classes). Our classification method may be a promising supporting tool for clinicians to diagnose, assess and make the follow-up of patients with encephalitis.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Adamczyk M, Genzel L, Dresler M, Steiger A, Friess F (2015) Automatic sleep spindle detection and genetic influence estimation using continuous wavelet transform. Front Hum Neurosci 19(9):624
Amodio P, Marchetti P, Del Piccolo F, de Tourtchaninoff M, Varghese P, Zuliani C, Campo G, Gatta A, Guérit JM (1999) Spectral versus visual EEG analysis in mild hepatic encephalopathy. Clin Neurophysiol 110(8):1334–44
Azuma H, Hori S, Nakanishi M, Fujimoto S, Ichikawa N, Furukawa TA (2003) An intervention to improve the interrater reliability of clinical EEG interpretations. Psychiatry Clin Neurosci 57(5):485–9
Babiloni C, Barry R, Basar E, Blinowska K, Cichocki A, Drinkenburg W, Klimesch W, Knight R, Lopes da Silva F, Nunez P, Oostenveld R, Jeong J, Pascual-Marqui R, Valdes-Sosa P, Hallett M (2020) International Federation of Clinical Neurophysiology (IFCN)–EEG research workgroup: recommendations on frequency and topographic analysis of resting state EEG rhythms. Part 1: applications in clinical research studies. Clin Neurophysiol 131(1):285–307
Barbadoro P, Marigliano A, Ricciardi A, D’Errico MM, Prospero E (2012) Trend of hospital utilization for encephalitis. Epidemiol Infect 140(4):753–64
Beaumanoir A, Magistris M, Nahory A (1985) Sporadic slow biphasic complex: description and clinical correlations. Electroencephalogr Clin Neurophysiol 61(3):S142
Beaumanoir A, Burkhard P, Gauthier G, Le Floch-Rohr J, Ochsner F, Waldvogel F (1988) EEG recordings in 19 cases of AIDS with encephalic involvement. Neurophysiol Clin 18(4):313–22 (in French)
Beaumanoir A, Nahory A (1992) EEG in HIV infection. Neurophysiol Clin 22(5):355–68 (in Review. French)
Beaumanoir A, Grioni D, Kullmann G, Tiberti A, Valseriati D (1997) EEG anomalies in the prodromic phase of Rasmussen’s syndrome. Report of two cases. Neurophysiol Clin 27(1):25–32 (in French)
Bien CG, Granata T, Antozzi C, Cross JH, Dulac O, Kurthen M, Lassmann H, Mantegazza R, Villemure JG, Spreafico R, Elger CE (2005) Pathogenesis, diagnosis and treatment of Rasmussen encephalitis: a European consensus statement. Brain 128(3):454–71
Boashash B, Azem G (2014) A review of time-frequency matched filter design with application to seizure detection in multichannel newborn EEG. Dig Sig Proc 28:28–38
Boucher A, Herrmann JL, Morand P, Buzelé R, Crabol Y, Stahl JP, Mailles A (2017) Epidemiology of infectious encephalitis causes in 2016. Med Mal Infect 47(3):221–35
Burquier V, Koralnik IJ, Vibert D, Burkhard P, Beaumanoir A, Jallon P, Mayer E, Hirschel B (1997) Effect of antiretroviral treatment on early electroencephalographic and otoneurologic manifestations in HIV infection and prognostic importance of verified perturbations. Neurophysiol Clin 27(6):508–519 (in French)
Capovilla G, Paladin F, Dalla Bernardina B (1997) Rasmussen’s syndrome: longitudinal EEG study from the first seizure to epilepsia partialis continua. Epilepsia 38(4):483–8
Chen L, Zhu M, Zhou H, Liang J (2010) Clinical study of West syndrome with PS and late-onset epileptic spasms. Epilepsy Res 89(1):82–8
Cooray GK, Sengupta B, Douglas P, Englund M, Wickstrom R, Friston K (2015) Characterising seizures in anti-NMDA-receptor encephalitis with dynamic causal modelling. Neuroimage 118:508–19
Crevecoeur G, Hallez H, Van Hese P, D’Asseler Y, Dupre L, Van de Walle R (2008) A hybrid algorithm for solving the EEG inverse problem from spatio-temporal EEG data. Med Biol Eng Comput 46(8):767–77
Ding L, Wilke C, Xu B, Xu X, van Drongelen W, Kohrman M, He B (2007) EEG source imaging: correlating source locations and extents with electrocorticography and surgical resections in epilepsy patients. J Clin Neurophysiol 24(2):130–6
Doble M, Narayan SK (2008) Mathematical analysis of EEG of patients with non-fatal nonspecific diffuse encephalitis. Intern J Biol Med Sci 3:4
Drislane FW (2013) Overlap of encephalopathies and epileptic seizures. J Clin Neurophysiol 30(5):468–76
Falchek SJ (2012) Encephalitis in the Pediatric Population. Pediatrics Rev 33:122–33
Furnkranz J (2002) Round robin classification. J Mach Learn Res 2:721–747
Gatti A, Guarneri M, Motto CA, Vigliano P, Beaumanoir A (1997) Slow biphasic complex: electro-clinical considerations. Ital J Neurol Sci 18(4):99
Granata T, Gobbi G, Spreafico R, Vigevano F, Capovilla G, Ragona F, Freri E, Chiapparini L, Bernasconi P, Giordano L, Bertani G, Casazza M, Dalla Bernardina B, Fusco L (2003) Rasmussen’s encephalitis: early characteristics allow diagnosis. Neurology 60(3):422–5
Granata T, Andermann F (2013) Rasmussen encephalitis. Handb Clin Neurol 111:511–9
Grioni D, Contri M, Kullmann G (2009) Are Slow Biphasic Waves (SBW) a possible bioelectrical marker of acute structural cerebral events? Report of four cases with acute symptomatic seizures at the onset. Bull Lega It Epil 138:23–24 (in Italian)
Jacob JE, Nair GK, Iype T, Cherian A (2018) Diagnosis of encephalopathy based on energies of EEG subbands using discrete wavelet transform and support vector machine. Neurol Res Int 2:1613456
Ji Z, Sugi T, Goto S, Wang X, Ikeda A, Nagamine T, Shibasaki H, Nakamura M (2011) An automatic spike detection system based on elimination of false positives using the large-area context in the scalp EEG. IEEE Trans Biomed Eng 58(9):2478–88
Kaminska A, Eisermann M, Plouin P (2019) Child EEG (and maturation). Handb Clin Neurol 160:125–142
Qazi Khurram I, Lam HK, Xiao Bo, Ouyang Gaoxiang, Yin Xunhe (2016) Classification of epilepsy using computational intelligence techniques. CAAI Trans Intell Technol 1(2):137–149
Kneen R, Michael BD, Menson E, Mehta B, Easton A, Hemingway C, Klapper PE, Vincent A, Lim M, Carrol E, Solomon T (2012) National Encephalitis Guidelines Development and Stakeholder Groups. Management of suspected viral encephalitis in children–association of British Neurologists and British Paediatric Allergy, Immunology and Infection Group national guidelines. J Infect 64(5):449–77
Koralnik IJ, Beaumanoir A, Hausler R, Kohler A, Safran AB, Delacoux R, Vibert D, Mayer E, Burkhard P, Nahory A, Magistris MR, Sanches J, Myers P, Paccolat F, Quoex F, Gabriel V, Perrin L, Mermillod B, Gauthier G, Waldvogel FA, Hirschel B (1990) A controlled study of early neurologic abnormalities in men with asymptomatic human immunodeficiency virus infection. N Engl J Med 323(13):864–870. Erratum in: N Engl J Med 323(24):1716, 1990
Longaretti F, Dunkley C, Varadkar S, Vargha-Khadem F, Boyd SG, Cross JH (2012) Evolution of the EEG in children with Rasmussen’s syndrome. Epilepsia 53(9):1539–1545
Lotte F, Congedo M, Lecuyer A, Lamarche F, Arnaldi B (2007) A review of classification algorithms for EEG-based brain-computer interfaces. J Neural Eng 4(2):R1–R13
Lotte F, Bougrain L, Cichocki A, Clerc M, Congedo M, Rakotomamonjy A, Yger F (2018) A review of classification algorithms for EEG-based brain-computer interfaces: a 10 year update. J Neural Eng 15(3):031005
Mesin L, Costa P (2014) Prognostic value of EEG indexes for the Glasgow outcome scale of comatose patients in the acute phase. J Clin Monit Comput 28(4):377–85
Mesin L, Valerio M, Beaumanoir A, Capizzi G (2019) Automatic identification of Slow Biphasic Complexes in EEG: an effective tool to detect Encephalitis. Biomed Phys Eng Express 5:045006
Mesin L, Valerio M, Capizzi G (2019) Detection and Assessment of Encephalitis from EEG. IEEE conference on computational intelligence in bioinformatics and computational biology, Certosa di Pontignano (Siena), Tuscany (Italy), 9–11 July
Mohammad SS, Soe SM, Pillai SC, Nosadini M, Barnes EH, Gill D, Dale RC (2016) Etiological associations and outcome predictors of acute electroencephalography in childhood encephalitis. Clin Neurophysiol 127(10):3217–3224
Piquet AL, Cho TA (2016) The clinical approach to encephalitis. Curr Neurol Neurosci Rep 16(5):45
Rosenberg S, Périn B, Michel V, Debs R, Navarro V, Convers P (2015) EEG in adults in the laboratory or at the patient’s bedside. Neurophysiol Clin 45(1):19–37
Rusalova MN (2006) Frequency-amplitude characteristics of the EEG at different levels of consciousness. Neurosci Behav Physiol 36(4):351–8
Scheuer ML, Bagic A, Wilson SB (2017) Spike detection: Inter-reader agreement and a statistical Turing test on a large data set. Clin Neurophysiol 128(1):243–50
Sheth R (2019) Patterns specific to pediatric EEG. J Clin Neurophysiol 36(4):289–293
Stamoulis C, Richardson AG (2010) Application of matched filtering to identify behavioral modulation of brain oscillations. J Comput Neurosci 29(1–2):63–72
Stevenson NJ, Korotchikova I, Temko A, Lightbody G, Marnane WP, Boylan GB (2013) An automated system for grading EEG abnormality in term neonates with hypoxic-ischaemic encephalopathy. Ann Biomed Eng 41(4):775–85
Stroink H, Schimsheimer RJ, de Weerd AW, Geerts AT, Arts WF, Peeters EA, Brouwer OF, Boudewijn Peters A, van Donselaar CA (2006) Interobserver reliability of visual interpretation of electroencephalograms in children with newly diagnosed seizures. Dev Med Child Neurol 48(5):374–377
Sutter R, Kaplan PW (2013) Clinical and electroencephalographic correlates of acute encephalopathy. J Clin Neurophysiol 30(5):443–53
Sutter R, Kaplan PW, Cervenka MC, Thakur KT, Asemota AO, Venkatesan A, Geocadin RG (2015) Electroencephalography for diagnosis and prognosis of acute encephalitis. Clin Neurophysiol 126(8):1524–31
Tanoue K, Oguni H, Nakayama N, Sasaki K, Ito Y, Imai K, Osawa M (2008) Focal epileptic spasms, involving one leg, manifesting during the clinical course of west syndrome (WS). Brain Dev 30(2):155–9
Tauber SC, Eiffert H, Bruck W, Nau R (2017) Septic encephalopathy and septic encephalitis. Expert Rev Anti Infect Ther 15(2):121–32
Thompson C, Kneen R, Riordan A, Kelly D, Pollard AJ (2012) Encephalitis in children. Arch Dis Child 97(2):150–61
Trevor H, Tibshirani R, Friedman J (2001) The elements of statistical learning. Springer Series in Statistics, Springer, New York
Tsamardinos I, Rakhshani A, Lagani V (2014) Performance-estimation properties of cross-validation-based protocols with simultaneous hyperparameter optimization. In: Proceedings of 8th Hellenic conference artificial intelligence: methods and applications, pp 1–14
Tuncer T, Dogan S, Akbal E (2019) A novel local senary pattern based epilepsy diagnosis system using EEG signals. Aust Phys Eng Sci Med 42(4):939–48
Valerio M, Rivera S, Mesin L (2020) Relation between lesions and localization of sources of slow biphasic complexes in encephalitis. Neuroimmunol Neuroinflammation
Venkatesan A (2015) Epidemiology and outcomes of acute encephalitis. Curr Opin Neurol 28(3):277–82
Vora NM, Holman RC, Mehal JM, Steiner CA, Blanton J, Sejvar J (2014) Burden of encephalitis-associated hospitalizations in the United States, 1998–2010. Neurology 82(5):443–51
Weingarten L, Enarson P, Klassen T (2013) Encephalitis. Pediatr Emerg Care 29(2):235–41
Zhao C, Zhao M, Yang Y, Gao J, Rao N, Lin P (2017) The reorganization of human brain networks modulated by driving mental fatigue. IEEE J Biomed Health Inform 21(3):743–55
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Ethical approval
This is a retrospective study conducted on already available data from pediatric patients for which formal consent was obtain from the parents.
Informed consent
As the patients were children, the consent for the examination and data processing was obtained from their parents.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Mesin, L., Valerio, M. & Capizzi, G. Automated diagnosis of encephalitis in pediatric patients using EEG rhythms and slow biphasic complexes. Phys Eng Sci Med 43, 997–1006 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13246-020-00893-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13246-020-00893-0