Abstract
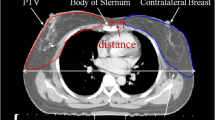
Second cancer induction in the contralateral breast (CB) is an issue of some concern in breast radiotherapy especially for women under the age of 45 years at the time of treatment. The CB dose from 2-field and 3-field techniques in post-mastectomy chest wall irradiations in an anthropomorphic phantom as well as in patients were measured using thermoluminescent dosimeters (TLDs) at the local radiotherapy center. Breast and chest wall radiotherapy treatments were planned conformally (3D-CRT) and delivered using 6-MV photons. The measured CB dose at the surface fell sharply with distance from the field edge. However, the average ratio of the measured to the calculated CB dose using the pencil beam algorithm at the surface was approximately 53%. The mean and median measured internal dose at the posterior border of CB in a phantom was 5.47 ± 0.22 cGy and 5.44 cGy, respectively. The internal CB dose was relatively independent of depth. In the present study the internal CB dose is 2.1–4.1% of the prescribed dose which is comparable to the values reported by other authors.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Majlis Kanser Nasional (National Cancer Council), MAKNA, Kuala Lumpur, http://www.makna.org.my/breastcancer.asp. Cited 10 Oct 2008
Jemal A, Siegel R, Ward E (2007) Cancer statistics. CA Cancer J Clin 57:43–66
Bese NS, Kiel K, El-Gueddari BE, Campbell OB, Awuah B, Vikram B (2006) Radiotherapy for breast cancer in countries with limited resources: program implementation and evidence-based recommendations. Breast J 12:S96–S102
Hall EJ, Giaccia AJ (2006) Radiobiology for the radiologist, 6th edn. Lippincott Williams and Wilkins, Philadelphia
Gao X, Fisher SG, Emami B (2003) Risk of second primary cancer in the contralateral breast in women treated for early-stage breast cancer: a population-based study. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys 56:1038–1045
Obedian E, Fischer DB, Haffty BG (2000) Second malignancies after treatment of early-stage breast cancer: lumpectomy and radiation therapy versus mastectomy. J Clin Oncol 18:2406–2412
Boice JD, Harvey EB, Blettner M, Stovall M, Flannery JT (1992) Cancer in the contralateral breast after radiotherapy for breast cancer. N Engl J Med 326:781–785
Bernstein L, Thompson WD, Risch N, Holford TR (1992) Risk factors predicting the incidence of second primary breast cancer among women diagnosed with a first primary breast cancer. Am J Epidemiol 36:925–936
Hankey BJ, Curtis RE, Naughton MD, Boice JD Jr, Flannery JT (1983) A retrospective cohort analysis of second breast cancer risk for primary breast cancer patients with an assessment of the effect of radiotherapy. J Natl Cancer Inst 70:797–804
Horn PL, Thompson WD, Schwartz SM (1987) Factors associated with the risk of second primary breast cancer: an analysis of data from the Connecticut tumor registry. J Chronic Dis 40:1003–1011
Horn PL, Thompson WD (1988) Risk of contralateral breast cancer-associations with histologic, clinical and therapeutic factors. Cancer 62:412–424
Kollias J, Ellis IO, Elston CW, Blamey RW (1999) Clinical and histologic predictors of contralateral breast cancer. Eur J Surg Oncol 25:584–589
Fraass BA, Roberson PL, Lichter AS (1985) Dose to the contralateral breast due to primary breast irradiation. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys 11:485–497
Muller-Runkel R, Kalokhe UP (1990) Scatter dose from tangential breast irradiation to the uninvolved breast. Radiology 175:873–876
Kelly CA, Wang XY, Chu JCH (1996) Dose to contralateral breast: a comparison of four primary breast irradiation techniques. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys 34:727–732
Kron T (1995) Thermoluminescence dosimetry and its applications in medicine—Part 2: history and applications. Australas Phys Eng Sci Med 18:1–25
Knoll GF (1979) Radiation detection and measurement. Willey, New York
Johansen S, Olsen DR, Danielsen T, Malinena E (2007) Contralateral breast doses following radiotherapy of the breast and regional lymph nodes: measurements and treatment planning calculations. Radiother Oncol 82:332–336
Kry SF, Titt U, Poenisch F, Followill D, Vassiliev ON, White RA, Mohan R, Salehpour M (2006) A Monte Carlo model for calculating out of field dose from a varian 6-MV beam. Med Phys 33:4405–4413
Charalambous S, Petridou S (1976) The thermoluminescence behaviour of LiF (TLD-100) for doses up to 10 MRad. Nucl Instrum Methods 137:441–444
Fraass BA, Van de Geijn J (1983) Peripheral dose from megavolt beams. Med Phys 10:809–818
McParland BJ (1990) The effect of a dynamic wedge in the medial tangential field upon the contralateral breast dose. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys 19:1515–1520
Weides CD, Mok EC, Chang WC, Findley DO, Shostak CA (1995) Evaluating the dose to the contra lateral breast when using a dynamic wedge versus a regular wedge. Med Dosim 20:287–293
Brooks PS (1995) Dose to contralateral breast—a comparative study. Med Dosim 20:301–307
Chougule A (2007) Radiation dose to contra lateral breast during treatment of breast malignancy by radiotherapy. J Cancer Res Ther 3:8–11
Warlick WB, O’Rear JH, Earley L, Moeller JH, Gaffney DK, Leavitt DD (1997) Dose to the contralateral breast: a comparison of two techniques using the enhanced dynamic wedge versus a standard wedge. Med Dosim 22:185–191
Bhatnagar AK, Brandner E, Sonnik D (2004) Intensity-modulated radiation therapy (IMRT) reduces the dose to the contralateral breast when compared to conventional tangential fields for primary breast irradiation: initial report. Cancer J 10:381–385
Tercilla O, Krasin F, Lawn-Tsao L (1989) Comparison of contralateral breast doses from 1/2 beam block and isocentric treatment techniques for patients treated with primary breast irradiation with Co 60. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys 17:205–210
Hurkmans C, Knöös T, Nilsson P, Svahn-Tapper G, Danielsen H (1995) Limitations of a pencil beam approach to photon dose calculations in the head and neck region. Radiother Oncol 37:74–80
Knoos T, Wieslander E, Cozzi L, Brink C, Fogliata A, Albers D, Nystrom H, Lassen S (2006) Comparison of dose calculation algorithms for treatment planning in external photon beam therapy for clinical situations. Phys Med Biol 51:5785–5807
Cozzi L, Buffa FM, Fogliata A (2001) Dosimetric features of linac head and phantom scattered radiation outside the clinical photon beam: experimental measurements and comparison with treatment planning system calculations. Radiother Oncol 58:193–200
Aspradakis MM, McCallum HM, Wilson N (2006) Dosimetric and treatment planning considerations for radiotherapy of the chest wall. Br J Radiol 79:828–836
Burmeister J, Alvarado N, Way S, Mcdermott P, Bossenberger T, Jaenisch H (2008) Assessment and minimization of contralateral breast dose for conventional and intensity modulated breast radiotherapy. Med Dosim 33:6–13
Xu XG, Bednarz B, Paganetti H (2008) A review of dosimetry studies on external-beam radiation treatment with respect to second cancer induction. Phys Med Biol 53:R193–R241
Acknowledgement
We are indebted to Universiti Sains Malaysia for providing us with a fellowship and a short-term grant. We are grateful to the Radiotherapy Unit of Mt Miriam Cancer Center in Penang, Malaysia for use of the LINAC. We thank the physicists at the Mt Miriam Cancer Center for all their help.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Alzoubi, A.S., Kandaiya, S., Shukri, A. et al. Contralateral breast dose from chest wall and breast irradiation: local experience. Australas Phys Eng Sci Med 33, 137–144 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13246-010-0011-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13246-010-0011-y