Abstract
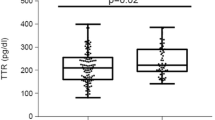
Several adipokines are produced and secreted from adipose tissue, such as retinol binding protein-4, which triggers metabolic syndromes and insulin resistance. Retinol binding protein-4 transfers vitamin A or retinol in the blood. Higher levels of retinol binding protein-4 are interrelated with progress of metabolic disease, comprising obesity, metabolic syndrome, and type 2 diabetes mellitus. The present study investigates the role of retinol-binding protein-4 levels in type 2 diabetic Iraqi patients with metabolic syndrome. Sixty type 2 diabetic patients aged 40–53 years were examined. Of these 30 patients has metabolic syndrome and 30 without metabolic syndrome. The patients sampled were from the National Diabetes Center/ Mustansiriyah University from February 2022 until the end of August 2022. All diabetic patients have been examined and diagnosed from specialist endocrinology. Also, 30 healthy individuals were selected as control group. Anthropometric and clinical characteristics for all participants were assessed. Serum retinol binding protein-4 concentration was considerably elevated in diabetic patients as paralleled to the control (3.00 ± 0.66 ρg/mL with metabolic syndrome and 2.42 ± 0.88 ρg/mL without metabolic syndrome). It is observed that female patients with metabolic syndrome had higher concentrations of retinol binding protein-4 (RBP-4) as compared to the male patients. Serum retinol binding protein-4 is strongly correlated with metabolic syndrome. As such concentration of RBP-4 offers enhanced prognostic value over traditional practices, and may be used for early detection of MetS in public health services.

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abagre TA, Bandoh DA, Addo-Lartey AA. Determinants of metabolic syndrome among patients attending diabetes clinics in two sub-urban hospitals: Bono Region Ghana. BMC Cardiovasc Disord. 2022;22(366):1–13. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12872-022-02805-4.
Ahmed HS. Correlations between serum interleukins-2,-4 levels and some biochemical parameters in Iraqi patients with osteoporosis. Fac Med Baghdad. 2017;59(3):275–9. https://doi.org/10.32007/jfacmedbagdad.593103.
Ahmed HS. Serum adropin and apelin as potential markers predicting acute heart failure-associated renal dysfunction among elderly Iraqi patients. Ann Trop Med Public Health. 2020;23(10):1–15. https://doi.org/10.36295/asro.2020.231024.
Alberti KGMM, Eckel RH, Grundy SM, Zimmet PZ, Cleeman JI, Donato KA, Fruchart J, James WBT, Loria CM, Smith Jr SC, International Diabetes Federation Task Force on Epidemiology and Prevention, Hational Heart, Lung, and Blood Institute, American Heart Association; World Heart Federation, International Atherosclerosis Society, and International Association for the Study of Obesity. Harmonizing the metabolic syndrome: a joint interim statement of the international diabetes federation task force on epidemiology and prevention; national heart, lung, and blood institute; American heart association; world heart federation; and international. Circulation. 2009;120(16):1640–1645. (Epub 2009 Oct 5).
An C, Wang H, Liu X, Li Y, Su Y, Gao X, Jiang W. Serum retinol binding protein 4 is elevated and positively associated with insulin resistance in postmenopausal women. Endocr J. 2009;56(8):987–96. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms21155229.
Banik SD, Pacheco-Pantoja E, Lugo R, Gomez-de-Regil L, Chim Ake R, Mendez Gonzalez RM, Solis ALG. Evaluation of anthropometric indexes and lipid parameters to predict metabolic syndrome among adults in Mexico. Diabetes Metab Syndr Obes. 2021;2021(14):691–701. https://doi.org/10.2147/DMSO.S281894.
Chu SY, Jung JH, Park MJ, Kim SH. Risk assessment of metabolic syndrome in adolescents using the triglyceride/high density lipoprotein cholesterol ratio and the total cholesterol/high-density lipoprotein cholesterol ratio. Ann Pediatr Endocrinol Metab. 2019;24(1):41–8. https://doi.org/10.6065/apem.2019.24.1.41.
Cin NNA, Yardımci H, Koc N, Uçakturk SA, Ok MA. Triglycerides/high-density lipoprotein cholesterol is a predictor similar to the triglyceride-glucose index for the diagnosis of metabolic syndrome using international diabetes federation criteria of insulin resistance in obese adolescents: a cross-sectional study. J Pediatr Endocrinol Metab. 2020;33(6):777–84. https://doi.org/10.1515/jpem-2019-0310.
Do R, Willer CJ, Schmidt EM, Sengupta S, Gao C, Peloso GM. Common variants associated with plasma triglycerides and risk for coronary artery disease. Nat Genet. 2013;45(11):1345–52. https://doi.org/10.1038/ng.2795. (Epub 2013 Oct 6).
Dobiasova M, Frohlich J. The plasma parameter log (TG/HDLC) as an atherogenic index: correlation with lipoprotein particle size and esterification rate in apoB-lipoprotein-depleted plasma (FERHDL). Clin Biochem. 2001;34(7):583–8. https://doi.org/10.1016/s0009-9120(01)00263-6.
Dobiasova M. AIP-atherogenic index of plasma as a significant predictor of cardiovascular risk: From research to practice. Vnitr Lek. 2006;52(1):64–71.
Eckel RH, Grundy SM, Zimmet PZ. The metabolic syndrome. Lancet. 2005;365(9468):1415–28. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0140-6736(05)66378-7.
Essiarab F, Taki H, Lebrazi H, Sabri M, Saile R. Usefulness of lipid ratios and atherogenic index of plasma in obese Moroccan women with or without metabolic syndrome. Ethn Dis. 2014;24(2):207–12.
Gadde KM, Martin CK, Berthoud H-R, Heymsfield SB. Obesity, pathophysiology and management. J Am Coll Cardiol. 2018;71(1):69–84. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jacc.2017.11.011.
Ghyselinck NB, Duester G. Retinoic acid signaling pathways. Development. 2019;146(13):dev.67502. https://doi.org/10.1242/dev.167502.
Ginsberg HN. New perspectives on atherogenesis: Role of abnormal triglyceride-rich lipoprotein metabolism. Circulation. 2002;106(16):2137–42. https://doi.org/10.1161/01.CIR.0000035280.64322.31.
Goossens GH, Jocken JWE, Blaak EE. Sexual dimorphism in cardiometabolic health: the role of adipose tissue, muscle and liver. Nat Rev Endocrinol. 2021;17(1):47–66. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41574-020-00431-8.
Hamza MA, AL-Tamer YY, AL-Habib OA. Modification of irisin level in overweight/obese women during pregnancy and its association with some metabolic risk factors. Baghdad Sci J. 2020;17(3):1124–32.
Hermans MP, Sacks FM, Ahn SA, Rousseau MF. Non-HDL-cholesterol as valid surrogate to apolipoprotein B100 measurement in diabetes: discriminant ratio and unbiased equivalence. Cardiovasc Diabetol. 2011;10(20):1–7. https://doi.org/10.1186/1475-2840-10-20.
Karamfilova V, Gateva A, Alexiev A, Zheleva N, Velikova T, Ivanova-Boyanova R, Ivanova R, Cherkezov N, Kamenov Z, Mateva L. The association between retinol-binding protein 4 and prediabetes in obese patients with nonalcoholic fatty liver disease. Arch Physiol Biochem. 2022;128(1):217–22. https://doi.org/10.1080/13813455.2019.1673429.
Kilicarslan M, de Weijer BA, Simonyte Sjodin K, Aryal P, Ter Horst KW, Cakir H, Brzozowska A, Szybalska A, Puzianowska-Kuznicka M, Grodzicki T, Więcek A, Olszanecka-Glinianowicz M, Chudek J. RBP4 increases lipolysis in human adipocytes and is associated with increased lipolysis and hepatic insulin resistance in obese women. FASEB J. 2020;34(5):6099–110. https://doi.org/10.1096/fj.201901979RR.
Krawczyk M, Ruminska M, Witkowska-Sedek E, Majcher A, Pyrzak B. Usefulness of the triglycerides to high-density lipoprotein cholesterol ratio (TG/HDL-C) in prediction of metabolic syndrome in polish obese children and adolescents. Acta Biochim Pol. 2018;65(4):605–11. https://doi.org/10.18388/abp.2018_2649.
Li N, Fu J, Koonen DP, Kuivenhoven JA, Snieder H, Hofker MH. Are hypertriglyceridemia and low HDL causal factors in the development of insulin resistance? Atherosclerosis. 2014;233(1):130–8. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.atherosclerosis.2013.12.013.
Lima VC, Lyra CO, Pinheiro LGB, de Azevedo PRM, Arrais RF, Pedrosa LFC. Association between dyslipidemia and anthropometric indicators in adolescents. Nutr Hosp. 2011;26(2):304–10. https://doi.org/10.1590/S0212-16112011000200010.
Majerczyk M, Kocełak P, Choręza P, Arabzada H, Owczarek AJ, Bozentowicz-Wikarek M, Brzozowska A, Szybalska A, Puzianowska-Kuźnicka M, Grodzicki T, Więcek A, Olszanecka-Glinianowicz M, Chudek J. Components of metabolic syndrome in relation to plasma levels of retinol binding protein 4 (RBP4) in a cohort of people aged 65 years and older. J Endocrinol Investig. 2018;41(10):1211–9. https://doi.org/10.1007/s40618-018-0856-6.
Mateo-Gallego R, Lamiquiz-Moneo I, Perez-Calahorra S, Marco-Benedi V, Bea AM, Baila-Rueda L, Laclaustra M, Penalvo JL, Civeira F, Cenarro A. Different protein composition of low-calorie diet differently impacts adipokine profile irrespective of weight loss in overweight and obese women. Nutr Metab Cardiovasc Dis. 2019;28(2):133–42. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.numecd.2017.10.024.
Mogre V, Salifu ZS, Abedandi R. Prevalence, components and associated demographic and lifestyle factors of the metabolic syndrome in type 2 diabetes mellitus. J Diabetes Metab Disord. 2014;13(1):80. https://doi.org/10.1186/2251-6581-13-80.
Moraes-Vieira PM, Yore MM, Sontheimer-Phelps A, Castoldi A, Norseen J, Aryal P, Sjodin KS, Kahn BB. Retinol binding protein 4 primes the NLRP3 inflammasome by signaling through Toll-like receptors 2 and 4. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 2020;117(49):31309–18. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.2013877117.
Nankam NPA, Bluher M. Retinol-binding protein 4 in obesity and metabolic dysfunctions. Mol Cell Endocrinol. 2021;531(111312):1–14. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.mce.2021.111312.
Nie G, Hou S, Zhang M, Peng W. High TG/HDL ratio suggests a higher risk of metabolic syndrome among an elderly Chinese population: a cross-sectional study. BMJ Open. 2021;11(3):e041519. https://doi.org/10.1136/bmjopen-2020-041519.
Noh MFM, Gunasegavan RDN, Mustar S. Vitamin A in health and disease. Vitamin A. 2019. https://doi.org/10.5772/intechopen.84460.
Radetti G, Fanolla A, Grugni G, Lupi F, Sartorio A. Indexes of adiposity and body composition in the prediction of metabolic syndrome in obese children and adolescents: Which is the best? Nutr Metab Cardiovasc Dis. 2019;29(11):1189–96. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.numecd.2019.06.011.
Rajaei E, Jalali MT, Shahrabi S, Asnafi AA, Pezeshki SMS. HLAs in autoimmune diseases: dependable diagnostic biomarkers? Curr Rheumatol Rev. 2019;15(4):269–76. https://doi.org/10.2174/1573397115666190115143226.
Raoof EM, Ahmed HS. Circulating adipsin as biomarker and its implication in type 2 diabetes mellitus. IJDDT. 2022;12(2):588–93.
Reaven GM. Banting lecture. Role of insulin resistance in human disease. Nutrition. 1988;37(12):1595–607.
Sadiq GH, Hussein RH, Maulood IM. Ghrelin and leptin and their relations with insulin resistance in diabetes mellitus type 2 patients. Baghdad Sci J. 2022;19(1):33–42.
Salman ED, Ahmed HS. Bone mineral density and vitamin D status among postmenopausal Iraqi women. Plant Arch. 2020;20(2):4613–20.
Sheth J, Shah A, Sheth F, Trivedi S, Nabar N, Shah N, Thakor P, Vaidya R. The association of dyslipidemia and obesity with glycated hemoglobin. Clin Diabetes Endocrinol. 2015;1(1):1–7. https://doi.org/10.1186/s40842-015-0004-6.
Steinhoff JS, Lass A, Schupp M. Biological functions of RBP4 and its relevance for human diseases. Front Physiol. 2021;12(659977):1–15. https://doi.org/10.3389/fphys.2021.659977.
Taheri S, Zaghloul H, Chagoury O, Elhadad S, Ahmed SH, El Khatib N, Amona RA, El Nahas K, Suleiman N, Alnaama A, Al-Hamaq A, Charlson M, Wells MT, Al-Abdulla S, Abou-Samra A. Effect of intensive lifestyle intervention on bodyweight and glycaemia in early type 2 diabetes (DIADEMI): an open-label, parallel-group, randomised controlled trial. Lancet Diabetes Endocrinol. 2020;8(6):477–89. https://doi.org/10.1016/S2213-8587(20)30117-0.
Tahir NT, Ahmed HS, Mohsen FY. Vitamin D and risk of osteoarthritis among Iraqi patients with and without metabolic syndrome. Plant Arch. 2020;20(1):2731–6.
Turki KM, Ahmed HS, Saifullah PH. Leptin and insulin resistance in type 2 diabetic Iraqi patients. IJAERS. 2012;1(3):232–4.
Vanavanan S, Srisawasdi P, Rochanawutanon M, Kumproa N, Kruthkul K, Kroll MH. Performance of body mass index and body fat percentage in predicting cardiometabolic risk factors in Thai adults. Diabetes Metab Syndr Obes. 2018;11:241–53. https://doi.org/10.2147/DMSO.S167294.
Wang Y, Sun L, Lin X, Yuan JM, Koh WP, Pan A. Retinol binding protein 4 and risk of type 2 diabetes in Singapore Chinese men and women: a nested case-control study. Nutr Metab (Lond). 2019;16(3):1–11. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12986-018-0329-0.
WHO. Classification of Diabetes Mellitus. World Health Organization; 2019:1–40. https://apps.who.int/iris/rest/bitstreams/1233344/retrieve.
Zhou W, Ye SD, Chen C, Wang W. Involvement of RBP4 in diabetic atherosclerosis and the role of vitamin D intervention. J Diabetes Res. 2018;2018(7329861):1–9. https://doi.org/10.1155/2018/7329861.
Acknowledgements
Authors express sincere gratitude to the National Diabetes Center/ Mustansiriyah University, Baghdad, Iraq for facilities, and the patients who gave their consent to participate in this study.
Funding
There was no funding.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
NTT performed the experimental study, HSA and HSA conceived and supervised the study, all authors have revised the manuscript and accepted the last version.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
Authors declare that there is no conflict of academic or commercial interest.
Ethical approval
Necessary approval was obtained by the institute according to Helsinki declaration.
Informed consent
All authors read the manuscript and approved for publication. The patients involved have consented to participate in the study.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Corresponding Editor: Ansuman Chattopadhyay; Reviewers: Pallab Shaw, Manas Ranjan Ray.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Tahir, N.T., Ahmed, H.S. & Ahmed, H.S. Studies on the role of retinol binding protien-4 in type 2 diabetic Iraqi patients with metabolic syndrome. Nucleus (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13237-023-00430-w
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13237-023-00430-w